Cu(Ⅱ)在谷氨酸根配合物体系中的电沉积行为
杨天足,雷存茂,刘伟,窦爱春,张杜超,刘伟锋
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:采用循环伏安法研究谷氨酸根配合物体系中谷氨酸根离子的稳定性和铜在阴极的电沉积过程,利用线性扫描伏安法求体系的表观活化能、表观传递系数和交换电流密度;计时电流法判断铜在电极上的成核方式。实验结果表明:在扫描电位-1.5~3 V内,谷氨酸钠溶液中仅有水的电解反应,谷氨酸根离子无氧化还原反应;铜在阴极沉积时为不可逆过程;循环伏安曲线的感抗环说明铜在阴极沉积时经历了电结晶过程;由线性扫描伏安法求得表观活化能为34.065 kJ/mol,表观传递系数为0.360,电流交换密度为0.105 A/m2;铜在不锈钢电极上的成核方式为连续成核。
关键词:Cu(Ⅱ);谷氨酸配合物体系;电化学;电沉积
中图分类号:TQ150.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)02-0305-07
Copper(Ⅱ) electrodeposition behavior in system of glutamine
YANG Tian-zu, LEI Cun-mao, LIU Wei, DOU Ai-chun, ZHANG Du-chao, LIU Wei-feng
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Copper electrodeposition behavior was studied in the system of glutamine (Gln). The stability of Gln in the system of Cu-Gln and copper electrodeposition on cathode were investigated by Cyclic Voltammogram(CV). Apparent activation energy, apparent transfer coefficient and exchange current density were obtained by linear sweep voltammogram(LSV). Nucleation mechanism of Cu deposition was determined by current-time-transient (CTT). The experimental results show that there is no other redox reaction but hydrolysis in the voltage arranging from -1.5 V to 3 V vs SCE, CV shows that copper experiences the process of nucleation and copper electrodeposition is completely inreversible. The apparent activation energy is calculated to be 34.065 kJ/mol, apparent transfer coefficient is 0.360 and exchange current density is 0.105 A/m2. CTT measurement of Cu deposition exhibits potential-independent kinetics that is well described by progressive nucleation model.
Key words: Cu(Ⅱ); glutamic acid complex; electrochemical; electrodeposition
目前铜的矿产资源愈趋贫乏,有关低品位铜矿处理的研究越来越深入[1-2]。对于低品位氧化矿的处理,一般采用硫酸浸出—萃取—电积或氨浸—萃取—电 积[3]工艺,但两者都存在后续处理难,浸出过程中硫酸消耗[4]或氨的挥发损失量大等问题。采用氯化铵取代部分氨水[5]可降低氨的污染程度,但在随后的电积工序中,氨根离子易在阳极生成氮气,导致氨的消耗量增加。针对以上问题,本文作者根据有机配体对金属的配位作用,研究金属氧化矿的浸出工艺[6-7];通过谷氨酸根离子与铜的配位作用浸出氧化铜矿,采用电积工序回收含铜溶液中的铜;谷氨酸根离子则返回浸出过程循环利用。该体系在温和弱碱性条件下进行,具有对设备材质要求低、试剂不挥发、环境友好等优点。自然界普遍存在谷氨酸盐,它既是蛋白质或肽的结构氨基酸之一,又是游离氨基酸。Miranda等[8-9]谷氨酸铜配合物的结构性质进行了研究。铜在不同体系中的电沉积过程已有很多研究,常用的电沉积体系有碱性氰化物[10]、硫酸盐[11]、焦磷酸盐[12]、柠檬酸盐[13],还有离子液体吡啶盐类[14]、咪唑盐类[15]和季铵盐[16]。Grujicic等[17]运用循环伏安法和计时电流法研究了氨体系中铜在玻碳电极上的还原和成核机理,但是铜在谷氨酸配合物体系中电沉积研究尚未见报道,为此,本文作者对其进行研究。
1 实验
本实验所用仪器为CHI660C电化学工作站;采用传统的三电极体系及三电极电化学池,以不锈钢片(面积为0.729 4 cm2)和铂片(面积为2.419 8 cm2)为工作电极。不锈钢片(面积为3.596 9 cm2)为辅助电极,饱和甘汞电极为参比电极,电位皆为对饱和甘汞电极电位。除不同温度条件下阴极线性扫描伏安实验外,所有实验都在常温下进行。实验使用的KCl为分析纯;碱式碳酸铜为分析纯,含铜(质量分数)为52%~56%;市售谷氨酸钠含量≥99%。实验时,电极和溶液都保持静置状态。工作电极用1至5号金相砂纸依次打磨,用乙醇除油,并用二次蒸馏水清洗。采用循环伏安法研究谷氨酸根离子在体系中的稳定电位范围以及铜在阴极的电沉积过程;采用线性扫描伏安法求表观活化能、表观传递系数和交换电流密度等动力学参数;采用计时电流法判断铜在电极上的成核方式。
1.1 谷氨酸钠溶液的制取
称取定量的谷氨酸钠溶于蒸馏水中,使用10 mol/L的NaOH溶液调节pH至10并定容。得到浓度为1.575 mol/L,pH为10的谷氨酸钠溶液。
1.2 谷氨酸铜配合物溶液的制取
称取定量的谷氨酸钠溶于蒸馏水中,使用10 mol/L的NaOH溶液调pH至10左右,加入一定量的碱式碳酸铜搅拌溶解,调节pH至10并定容,得到铜浓度为0.315 mol/L,谷氨酸根浓度为1.575 mol/L,pH为10的谷氨酸铜溶液。
2 实验结果和讨论
2.1 谷氨酸根离子稳定性研究
图1所示为谷氨酸钠溶液循环伏安曲线。工作电极为铂片,扫描速率为50 mV/s。在-0.9 ~0.8 V电位范围内,电流几乎为0 A,体系中无氧化还原反应。电位负向扫描经过-0.9 V后电流开始迅速增大,同时可以观察到工作电极上有气体放出。在-1.5 V反向扫描,在正向扫描至0.8 V左右,氧化电流迅速增大,工作电极开始产生气体,在1.5 V后达到极限电流。
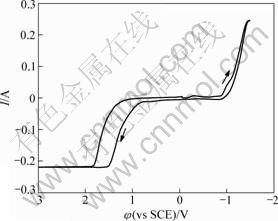
图1 铂电极上谷氨酸钠溶液的循环伏安曲线
Fig.1 Cyclic voltammogram of sodium glutamate on Pt in glutamic acid solution
图2所示为谷氨酸铜溶液的循环伏安曲线(Cyclic voltammogram,以下简称CV)图,工作电极为铂片,扫描速率为50 mV/s。从起始电位开始往负电位向扫描,电流逐渐增大,电位在-1 V左右时出现1个小的电流峰,为铜的沉积峰,电位继续负向扫描,电流迅速增大,观察电极有大量气泡冒出。在-1.5 V后回扫,到-0.40 V时出现氧化电流,铜开始溶解。在0.8 V电流最小,继续正向扫描,电流又开始增大,此时工作电极上有气体产生,在1.40 V后达到极限电流。
碱性溶液中析氢过程为:
2H2O+2e=2OH-+H2 (1)
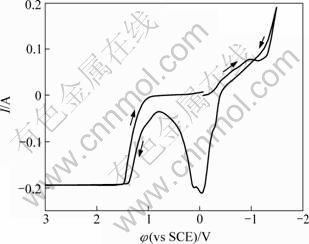
图2 铂电极上谷氨酸铜配合溶液循环伏安曲线
Fig.2 Cyclic voltammogram of Cu-Gln on Pt
析氢平衡电位为:
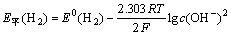 (2)
(2)
将E0(H2)=-0.828 V,pH为10,代入式(2)求得 E平(H2)=-0.591 V。从图2可知在电位-1.0~-1.4 V时,氢在铂电极上的过电位服从η=a+blg i,碱性溶液中a=0.48,b=0.12[18],求得当电流密度J=251 A/m2氢的析出电位(vs.SHE)为-0.879 V,实验测量值为-0.982 V,测量值较计算值偏负。
在碱性溶液中析氧过程为:
4OH-=2H2O+O2+4e (3)
体系中O2的平衡电位为:
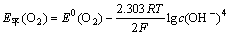 (4)
(4)
将E0(O2)=0.401 V,pH=10,代入式(4),求得E平(O2)=0.637 V。
从图2可知:在电位1.0~1.4 V时,氧在铂电极上的过电位服从塔菲尔公式。在电流密度为200 A/m2时,氧在铂片上的过电位为0.92 V[18],求得氧的析出电位为1.557 V,实验测量值为1.484 V,计算值较实验测量值偏正。
导致测量值与理论计算值发生偏离的主要原因是铂片表面不平整,实际析氢析氧面积与计算面积不同。其次是体系与塔菲尔公式参数不完全相同,从而有微小的偏差。
对比单纯谷氨酸钠与含铜的谷氨酸体系循环伏安曲线可以看出:在扫描电位区间-1.5~3 V内,谷氨酸钠溶液中仅有水的电解反应,谷氨酸根离子无氧化还原反应,具有很宽的稳定电位范围。因此,谷氨酸铜溶液在-0.9~0.8 V电位范围内的氧化峰对应铜的氧化反应,而-0.4 V左右的还原峰对应于铜的还原反应。
2.2 谷氨酸铜阴极沉积CV图
图3所示为不同扫描速率的铜阴极沉积过程的循环伏安曲线。工作电极为不锈钢,扫描速率分别为2,4,8 mV/s。在-0.34~-1.0 V电位范围内进行CV扫描时,谷氨酸根离子为非电活性物质。电位从开路电位-0.34 V往负方向扫描,电极有充电电流和反应电流通过,在-0.8 V左右开始发生显著的铜沉积,随后到达峰值电流密度J,体系发生浓差极化,受电活性物质的扩散控制。在电位为-1.0时反向扫描,循环伏安图出现了交叉闭合环,表明铜的电沉积过程可能经历了晶核形成过程。电位为-0.4 V开始有铜的溶出。图3中所示曲线1是扫描速率为8 mV/s,曲线2为4 mV/s,曲线3为2 mV/s的铜沉积循环伏安曲线。曲线1~3的峰电位和峰电流分别为-0.952 V和68.3 A·m-2,-0.901 V和52.4 A·m-2以及-0.857 V和42.5 A·m-2,可知峰电位Ep和峰电流密度随着扫描速率的增大而都相应地增大,说明铜在谷氨酸铜体系中沉积过程为不可逆过程。
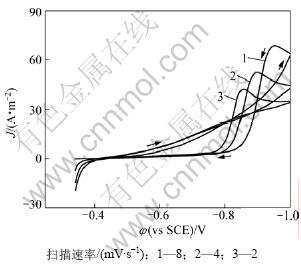
图3 不锈钢电极上谷氨酸铜溶液循环伏安曲线图
Fig.3 Cyclic voltammograms of Cu-Gln on stainless steel
2.3 铜的阴极沉积动力学参数
2.3.1 电极反应表观活化能
通过电极反应活化能的测定,对于判断反应机理也是一种常用的手段[19]。图4所示为20,30,40,50和60 ℃谷氨酸铜溶液的阴极极化曲线,扫描速率均为8 mV/s。取过电位为-0.335 V时,不同温度下的电流密度J,绘制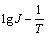 关系图。图5所示为根据不同温度的极化曲线得到的
关系图。图5所示为根据不同温度的极化曲线得到的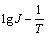 关系图,经线性拟合,得到下列方程式:
关系图,经线性拟合,得到下列方程式:
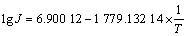 (5)
(5)
表观活化能表达式为:
 (6)
(6)
式中:B为常数;A为表观活化能。求得表观活化能为34.065 kJ/mol。
当电极反应受扩散控制时,反应速度的温度系数较低,由此得出电极反应活化能为12~16 kJ/mol;若控制步骤是电化学放电过程,则反应速度的温度系数较大,活化能一般为40 kJ/mol[19]。本实验所求得的表观活化能较大,推测电极过程的控制步骤为电化学放电过程。
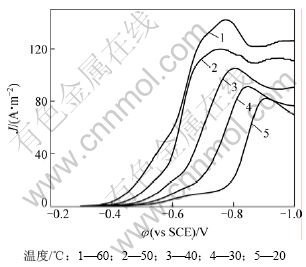
图4 谷氨酸铜溶液不同温度下线性扫描伏安曲线图
Fig.4 Linear sweep voltammogram of Cu-Gln at different temperatures
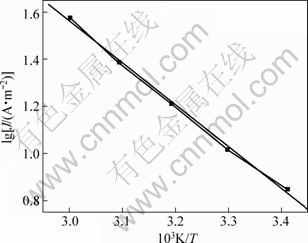
图5 lg J与温度倒数的Arrhenius关系图
Fig.5 Arrhenius plot showing relationship between lg J and temperature
2.3.2 Tafel关系式
图6所示为不锈钢电极上铜电沉积的阴极极化曲线,扫描速率为8 mV/s。过电位与电流密度存在如下关系:
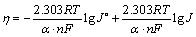 (7)
(7)
式中:α?n为表观传递系数;F为法拉第常数;T为热力学温度,K;J0为交换电流密度。将所测得的阴极极化曲线转化为η-lg J曲线,经线性拟合,即可求出α?n及J0。
图7和图8所示为Gln和Cu物质的量比为5时0.07~0.24 V及0.43~0.54 V范围内进行线性拟合,得的η-lgJ曲线及其拟合直线。将所得数据在过电位到Tafel直线方程式:
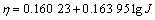 ,
,
过电位为0.07~0.24 V时 (8)
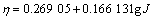 ,
,
过电位为0.43~0.54 V时 (9)
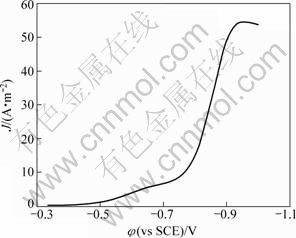
图6 谷氨酸铜溶液线性扫描伏安曲线图
Fig.6 Linear sweep voltammogram of Cu-Glu
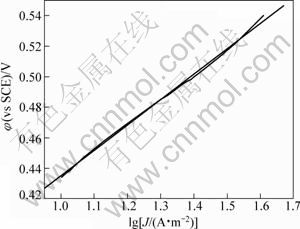
图7 lg J与φ(0.43~0.54 V)线性拟合关系
Fig.7 Linear fit showing relationship between lg J and φ(0.43~0.54 V)
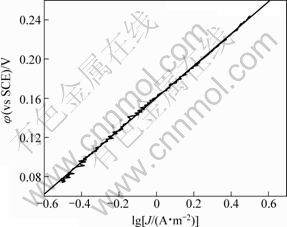
图8 lg J与φ(0.07~0.24 V)线性拟合关系
Fig.8 Linear fit showing relationship between lg J and φ(0.07~0.24 V)
分别求得表观传递系数为0.360,J0=0.105 A/m2 (过电位为0.07~0.24 V)和表观传递系数为0.356,J0=0.024 A/m2 (过电位为0.43~0.54 V)。图7和图8显示η-J呈线性半对数关系,与Cu(硫酸体系)、Pb和Hg等金属的交换电流密度(10~1 000 A/m2)相比 较[19-20],本实验所求得的J0较小,表明电极体系易极化,可逆程度小。
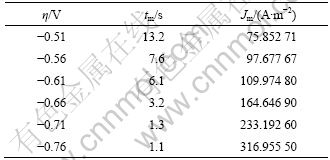
电结晶是电沉积的初级阶段,包括基底表面活性点上形成晶核及其生长2个过程。电结晶所得沉积层的结构和性质在很大程度上决定了沉积镀层的形貌、结构和性质[21]。图9所示为铜沉积的计时电流曲线,由曲线特性可知铜电结晶成核过程曲线的特征:电结晶初期由于晶核的形成和新相的生成,电流迅速上升,当达到最大值后开始衰减,此时铜电结晶经历了生长中心交叠并向外生长伸向溶液,同时伴随生长中心的消失和新生长中心的再生。当生长中心为半球状而微晶的生长速度受溶液中电活性离子的扩散控制[22]时,电结晶三维成核过程的瞬时成核和连续成核机理的无因次方程见表1(其中:z为沉积离子的摩尔电荷;D和c为该离子的扩散系数和浓度;N0为晶核密度;A为成核速度常数;k和k′为反应速率常数)。不同过电位下的tm和Jm见表2。
取图中数据作无因次曲线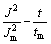 得到图10,从图10可以看出:铜电结晶初期的实验曲线与连续成核的理论曲线非常相近,表明铜的电结晶初期按连续成核方式进行。
得到图10,从图10可以看出:铜电结晶初期的实验曲线与连续成核的理论曲线非常相近,表明铜的电结晶初期按连续成核方式进行。
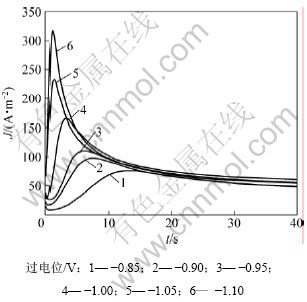
图9 铜电沉积电流密度-时间暂态曲线
Fig.9 Current density-time transient curves for Cu electrodeposition
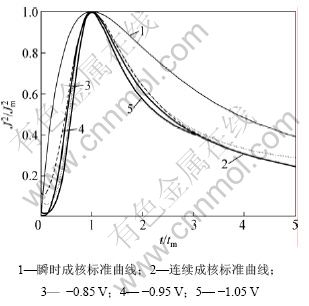
图10 铜电沉积电流密度-时间无因次暂态曲线
Fig.10 Non-dimensional plots of J2/J2m-t/tm for Cu electrodeposition
表1 成核机理方程式
Table 1 Nucleation mechanism equations

表2 铜电沉积电流-时间暂态法结果
Table 2 Current-time transient results of Cu electrodeposition
3 结论
(1) 在-0.9~0.8 V电位范围内,体系中无氧化还原反应。电位低于-0.9 V时,体系析出氢气;电位高于0.8 V时,体系析出氧气;在1.5 V后析出氧气到达极限电流。在扫描电位-1.5 V~3 V内,谷氨酸钠溶液中仅有水的电解反应,谷氨酸根离子无氧化还原反应,谷氨酸根离子具有很宽的稳定电位范围。铜在谷氨酸铜体系中的沉积过程为不可逆过程,交叉闭合环表明铜的电沉积过程经历了晶核形成过程。
(2) 根据不同温度下所测得的极化曲线,得到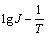 关系图,经线性拟合求得表观活化能为34.065 kJ/mol。可以认为电极过程的控制步骤为电化学放电过程。将所测得的阴极极化曲线转化为
关系图,经线性拟合求得表观活化能为34.065 kJ/mol。可以认为电极过程的控制步骤为电化学放电过程。将所测得的阴极极化曲线转化为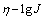 曲线,经线性拟合,求得在过电位为0.07~0.24 V时,表观传递系数为0.360,J0=0.105 A/m2及过电位为0.43~0.54 V时,表观传递系数为0.356,J0= 0.024 A/m2。η-J呈半对数关系,所求得的J0较小,表明电极易极化,可逆程度小。
曲线,经线性拟合,求得在过电位为0.07~0.24 V时,表观传递系数为0.360,J0=0.105 A/m2及过电位为0.43~0.54 V时,表观传递系数为0.356,J0= 0.024 A/m2。η-J呈半对数关系,所求得的J0较小,表明电极易极化,可逆程度小。
(3) 铜在谷氨酸铜配合物体系中沉积的成核方式为连续成核。
参考文献:
[1] Nasernejad B. Bioleaching of molybdenum from low-grade copper ore[J]. Process Biochemistry, 1999, 35(5): 437-440.
[2] 徐慧. 低品位铜矿资源湿法浸出直接提取技术发展述评[J]. 有色金属: 矿山部分, 2007, 59(4): 11-18.
XU Hui. Commentary on development of direct extraction technology used for leaching of low-grade copper resources[J]. Nonferrous Metals: Mining, 2007, 59(4): 11-18.
[3] 程琼, 张文彬. 汤丹高钙镁氧化铜矿氨浸技术的进展[J]. 云南冶金, 2005, 34(6): 17-20.
CHENG Qiong, ZHANG Wen-bing. Technical progress in ammonia leaching of Tangdan oxidized copper ore containing alkaline gangues[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2005, 34(6): 17-20.
[4] 招国栋, 伍衡山, 刘清, 等. 浅论低品位铜矿的浸出技术及其发展趋势[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2004(2): 65-69.
ZHAO Guo-dong, WU Heng-shan, LIU Qing, et al. Leaching technique and its development trend of low-grade copper ores[J]. West-China exploration engineering, 2004(2): 65-69.
[5] 唐谟堂, 杨声海. Zn(Ⅱ)-NH3-NH4Cl-H2O体系电积锌工艺及阳极反应机理[J]. 中南工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 1999, 30(2): 153-156.
TANG Mo-tang, YANG Shen-hai. Electrowinning zinc in the system of Zn(Ⅱ)-NH3-NH4Cl-H2O and mechanism of anodic reaction[J]. J Cent South Univ Technol: Natural Science, 1999, 30(2): 153-156.
[6] 杨天足, 任晋, 刘伟锋,等. Zn(Ⅱ)-Glu2--CO32--H2O体系热力学平衡分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(6): 1155-1161.
YANG Tian-zu, REN Jin, LIU Wei-feng, et al. Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis in the system of Zn(Ⅱ)-Glu2--CO32--H2O[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(6): 1155-1161.
[7] 杨天足, 刘珍珍, 任晋, 等. Cu(Ⅱ)-Glu2--CO32--H2O体系热力学平衡分析过程[J]. 工程学报, 2009, 9(4): 745-749.
YANG Tian-zu, LIU Zhen-zhen, REN Jin, et al. Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis on Cu(Ⅱ)-Glu2--CO32--H2O system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(4): 745-749.
[8] Miranda J L, Coelho J D. Deamination process in the formation of a copper(II) complex with glutamic acid and a new ligand derived from guanidinoacetic acid: Synthesis,characterization, and molecular modeling studies[J]. Polyhedron, 2008, 27(11): 2386-2394.
[9] Mizutani M, Maejime N. An infinite chiral single-helical structure formed in Cu(II)-L-/D-glutamic acid system[J]. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 1998, 283(1): 105-110.
[10] Mayanna S M, Maruthi B N. A noncyanide alkaline bath for industrial copper plating[J]. Metal Finishing, 1996, 94(3): 42-45.
[11] Schneider O, Mati? S, Argirusis C. Application of the electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance technique to copper sonoelectrochemistry: Part 1. Sulfate based electrolytes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(17): 5485-5495.
[12] Johannsen K, Page D, Roy S. A systematic investigation of current efficiency during brass deposition from a pyrophosphate electrolyte using RDE, RCE, and QCM[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2000, 45(22/23): 3691-3702.
[13] Eskhult J, Herranen M, Nyholm L. On the origin of the spontaneous potential oscillations observed during galvanostatic deposition of layers of Cu and Cu2O in alkaline citrate solutions[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2006, 594(1): 35-49.
[14] Murase K, Nitta K, Hirato T, et al. Electrochemical behaviour of copper in Trimethyl-n-HexylammoniumBis[(tri-fluoromethyl) sulfonyl]Amide, an ammonium imide-type room temperature molten salt[J]. J Appl Electrochem, 2001, 31(10): 1089-1094.
[15] Chen P Y, Sun I W. Electrochemical study of copper in a basic 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate room tempera- ture molten salt[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 45(3): 441- 450.
[16] Abedin Z S, Saad A Y, Farag H K, et al. Electrodeposition of selenium, indium and copper in an air-and water-stable ionic liquid at variable temperatures[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(8): 2746-2754.
[17] Grujicic D, Pesic B. Reaction and nucleation mechanisms of copper electrodeposition from ammoniacal solutions on vitreous carbon[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 50(22): 4426-4443.
[18] 朱元保, 沈子琛, 张传福, 等. 电化学数据手册[M]. 湖南科学技术出版社, 1985: 354-355.
ZHU Yuan-bao, SHEN Zi-chen, ZHANG Chuan-fu, et al. Handbook of electrochemical data[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1985: 354-355.
[19] 蒋汉瀛. 冶金电化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1983: 124-142.
JIANG Han-yin. Metallurgical electrochemistry[M]. Beijing: Metallugical Industry Press, 1983: 124-142.
[20] 方景礼. 电镀配合物理论与应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007: 331.
FANG Jing-li. Theory and application of coordination compounds in electroplating[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007: 331.
[21] 李强, 辜敏, 鲜晓红. 铜电结晶的研究进展[J]. 化学进展, 2008, 20(4): 483-490.
LI Qiang, GU Min, XIAN Xiao-hong. Progress of copper electrocrystallization[J]. Progress in chemistry, 2008, 20(4): 483-490.
[22] Fabricius G, Kontturi K, Sundholm G. Influence of thiourea on the nucleation of copper from acid sulphate solutions[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1994, 39(16): 2353-2357.
(编辑 张曾荣)
收稿日期:2009-12-07;修回日期:2011-03-01
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划项目(2007CB613604)
通信作者:杨天足(1958-),男,广西贺州人,教授,博士生导师,从事贵、重金属冶炼和提纯以及相关化工产品的开发;电话:0731-88836791;E-mail:tianzuyang@163.com