文章编号:1004-0609(2009)09-1636-06
复合稀土钼材料次级发射性能
刘 伟,王金淑,高 非,任志远,周美玲
(北京工业大学 材料科学与工程学院 教育部功能材料重点实验室,北京 100124)
摘 要:利用溶胶-凝胶法制备稀土氧化物掺杂钼粉,随后利用放电等离子体烧结法将该粉末制备成稀土钼金属陶瓷材料,利用SEM、DTA、电子发射性能测试等方法对样品次级电子发射性能进行研究。结果表明:稀土氧化物均匀掺杂和组织的细化有利于材料发射性能提高,但不能降低其激活温度;经过高温氢气处理,样品的真空激活温度大幅降低,发射系数提高;稀土氧化物易吸收水分和气体的特性导致后续真空激活过程中阴极表层钼氧化,而高温氢气处理消除了样品中多余的水分和气体,保持了样品中金属与氧化物的相间分布状态,这是样品在活化前后发射性能发生变化的主要原因。
关键词:稀土;钼;次级发射;烧结
中图分类号:TF 124 文献标识码:A
Secondary electron emission property of
composite REO-Mo materials
LIU Wei, WANG Jin-shu, GAO Fei, REN Zhi-yuan, ZHOU Mei-ling
(The Key Laboratory of Advanced Function Materials, Ministry of Education,
School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China)
Abstract: The sol-gel doping method was utilized to dope the rare earth oxide powder into molybdenum. Such powders were sintered by spark plasma sintering and traditional sintering combined with compaction method for fabricating REO-Mo cermet cathodes. SEM, DTA and electron emission property measurements were used to investigate the secondary electron emission properties of the materials. The results show that the emission performance of the materials can be enhanced by symmetrical distribution of rare earth oxides and the refinement of structure. However, such treatments can’t reduce the activation temperature in vacuum. Compared with the un-treated samples, the obvious drop of activation temperature and increase of secondary electron yield occur in samples annealed at high temperature in hydrogen. The activation temperature decreases obviously, and the secondary electron emission yield is enhanced apparently. Such easy adsorption of moisture and gas in the REO lead to oxidation phenomena of molybdenum in the subsequent activation in vacuum. The hydrogen annealing technology eliminates the excess moisture and gas and retain the distribution of REO in molybdenum. This is the main reason of variation of secondary electron emission for un-treated samples and pre-activating samples.
Key words: rare earth; molybdenum; secondary electron emission; sintering
磁控管是应用最为广泛的一种微波电真空器件,其结构简单、单位质量输出功率高,在高功率、高频率电磁波应用领域具有很大发展潜力,兆瓦级、毫米波乃至亚毫米波磁控管的研制一直是世界各国的研究重点[1-5]。次级电子发射阴极材料是磁控管的关键部件,大功率、高频率磁控管性能有赖于阴极材料在电子轰击时能保持较大的次级发射系数(δ)。
目前,在磁控管使用的阴极主要有氧化物阴极、合金阴极、扩散型阴极和金属陶瓷型阴极。其中,氧化物阴极是一类含Ba、Sr和Ca的复合氧化物涂层及海绵体类型阴极材料,其次级发射系数能达到3以上,但其最大的问题在于它的阻热效应。为降低涂层的电阻率,HODGSON等[6]将Ni添加到氧化物中,HAYASHIDA等[7]采用共沉淀方式在氧化物中加入ZrO2和Eu2O3。两者都使阴极发射性能得到提升,但氧化物阴极较低的工作温度仍决定其无法在大功率磁控管中应用。合金阴极是由一种性质比较稳定且易加工的金属来充当基体,另外一种性质比较活泼的金属作为表面层,由这一层活性物质提供次级电子发射。能够在磁控管中使用的合金阴极主要有La-Re、Ir-La、Pt-Ba和Pd-Ba等,具有性能稳定、易输出高电流密度等优点[8-10]。但合金阴极工作温度较高,且成本昂贵,不利于大规模推广使用。扩散阴极主要是指钡钨阴极及其各种变种阴极,它具有优异的热电子和二次电子发射能力,在磁控管中获得了广泛应用。但研究显 示[11],钡钨阴极的二次电子发射来自于阴极表面BaO,随着磁控管功率和频率的进一步提高,更为强烈的电子回轰使阴极表层BaO消耗过快,导致阴极次级发射系数下降,因此,钡钨阴极不适合在大功率和高频率磁控管中应用。ThO2金属陶瓷型阴极材料是一种发射性能优异的次级阴极材料,该阴极工作温度范围较宽,目前仍应用在某些型号的大功率磁控管中,但是由于Th的放射性危害,人们逐步限制其使用。由此可见,为满足大功率(兆瓦级)和高频率(毫米波、亚毫米波)磁控管发展的需求,研制一种新型的次级发射阴极材料具有重要意义。
王金淑等[12]研究发现,稀土氧化物可替代ThO2作为发射活性物质,但基于单元稀土氧化物的金属陶瓷阴极材料发射性能低于ThO2阴极,在此基础上,又研发了复合稀土钼金属陶瓷阴极材料,一系列研究结果显示二元稀土钼阴极发射性能高于单元稀土钼材料,组织细化使得材料发射性能进一步提高[13-16]。由于次级发射系数是次级阴极的关键参数,提高阴极材料的次级发射系数有利于改善磁控管的信噪比。YANG等[15]添加Re元素并利用SPS烧结获得亚微米结构的阴极材料,但阴极的发射系数仍保持在3左右。由此看出,阴极激活温度过高的问题尚未解决,给实际应用带来很大困难。为此,本文作者针对以上问题,首次采用一种处理工艺,研究其对样品次级发射性能的影响规律,并利用SEM、TG-DTA和发射性能测试手段研究其对性能影响的内在机制。
1 实验
选定样品成分为La2O3-Y2O3-Mo,其中稀土氧化物总含量为30%,余量为钼。采用液液掺杂方法实现稀土和钼的混合,在氢气气氛下,采用500、900 ℃两步还原获得稀土氧化物掺杂钼粉,每步保温时间为2 h。将获得的稀土氧化物掺杂钼粉随后在Sumimoto公司的SPS-3.20 MK-V 型等离子体烧结系统上进行烧结,烧结压力为30 MPa,烧结温度为1 450 ℃,保温时间为4 min。将稀土-钼烧结体进行机加工获得测试样品圆片(d 9 mm×1.5 mm),将其与钼筒进行激光焊接。随后在氢气气氛下进行加热处理,保温时间为30 min。随后在钼筒下部安装裸钨丝热子,以便对样品进行加热处理,然后将样品安装在测试架上待测。
在高真空系统中利用直流电子枪法测试样品的次级发射性能,利用二次电子发射系数(δ)与入射电子能量(Ep)的关系曲线表征样品的发射性能。测试过程中真空保持在1×10-6 Pa,一次电子束束斑面积约为1 mm2。采用光学高温计测量样品的温度(亮度温度),样品首先在800 ℃以下进行去气,随后从900 ℃逐步加热到1 400 ℃,每次升温间隔为100 ℃,每个温度保温时间为20 min。一次电子束流为40 μA,测试二次电子发射性能时样品温度保持在600 ℃。在扫描电子显微镜(JEOL 6500F)上对样品表面进行形貌观察,利用TG-DTA分析样品的热力学行为。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 处理前样品的次级发射性能
次级发射系数是次级阴极的关键参数,提高次级发射系数有利于改善磁控管频谱特性,但前期研究中REO-Mo材料一直停留在2~3的水平[12-16],如何进一步提高该类阴极的δmax是本实验的研究重点。前期研究[14]中指出稀土与钼的均匀掺杂有利于发射性能提 高,为此采用溶胶-凝胶掺杂结合放电等离子体烧结制备阴极材料,并与前期研究中同制备条件下液固掺杂样品性能进行比较。图1所示为在不同温度激活后样品的次级发射性能曲线。由图1可知,样品的二次电子发射系数(δ)随着激活温度的提高而增大,最大二次电子发射系数(δmax)为2.94。该数值比前期研究[14]中液固掺杂样品的发射系数提高约10%,但δmax对应的激活温度仍达到1 400 ℃。以上数据对比显示出液液掺杂提高样品发射性能的能力有限,且在磁控管中难以实现上述较高的激活温度。对真空激活后稀土-钼阴极材料表面进行观察,结果如图2所示。由图2可知,样品表面存在大面积白色区域和大量孔洞,图2(b)中的能谱结果证实白色区域含Y、La和O元素,没有Mo的信号,说明该区域主要是稀土氧化物,阴极表面被稀土氧化物层覆盖。LI等[14]研究发现SPS烧结样品测试后,样品表层同样出现了稀土氧化物富集层,且该层厚度达到5 μm。众所周知,稀土氧化物是导电较差的物质,如果表层富集稀土氧化物,则在次级发射过程中会出现“荷电”效应,从而导致次级发射性能下降,这说明表层大量的稀土氧化物是次级发射性能较差的原因。

图1 氢气热处理后样品在真空不同温度激活后的δ—Ep曲线
Fig.1 δ—EP curves of samples annealed in hydrogen after activation in vacuum at different temperatures

图2 未经过氢气热处理样品在真空激活后的表面SEM 像(a)和EDAX谱(b)
Fig.2 SEM image(a) and EDAX pattern(b) of annealed samples after activation in vacuum
2.2 处理后样品的次级发射性能
YANG等[15]在REO-Mo阴极寿命管壁发现了MoO3的沉积物,分析认为高真空下存在的氧肯定来自于材料中。为去除多余氧,将样品装管测试前于氢气气氛下进行退火处理,退火温度为1 300 ℃,保温时间1 h。随后测试退火后样品的二次电子发射性能,结果如图3所示。由图3可知,经过氢气退火处理后,样品的δ大幅提高,激活温度显著下降。其中,1 200 ℃激活后样品的δmax由激活前的2.34提高至4.34,1 000 ℃激活后样品的δmax已超过活化前样品的δmax(2.87),多次重复上述实验得到相同的实验结果。由以上结果可知,该工艺大幅度改善了样品的性能,特别是降低了样品的真空激活温度,使得该种材料在磁控管中实现优化激活成为可能。而经过活化处理的稀土-钼样品表面仍保持着金属钼和稀土氧化物相间分布,如图4所示。这说明活化处理使阴极表层的金属钼得以保持。未活化处理的阴极在装管过程中,已经过高真空处理,其表层仍然有钼的“丢失”,前期研究[15]中发现激活后真空管的管壁上皆有Mo(氧化物) 的沉积,表明真空管在高温激活过程中有O2的存在,使阴极表层的金属钼氧化物升华。氧的来源只能从稀土钼阴极材料中带入,分析认为主要有以下两方面原因:1) 前驱粉末是比表面较大的亚微米级粉末,易吸附气体,在SPS烧结的真空条件下,无H2介质,不可能还原样品中的O2,因此,SPS烧结样品相对于传统H2烧结样品中的氧含量偏高,高温激活时将导致阴极表层钼氧化物的升华或分解;2) 样品中含有大量稀土氧化物,而稀土氧化物容易吸收空气中的水分和二氧化碳发生化学组成和化学性质的变化。在真空高温处理时,稀土氧化物会释放出水分和气体使金属钼氧化升华。
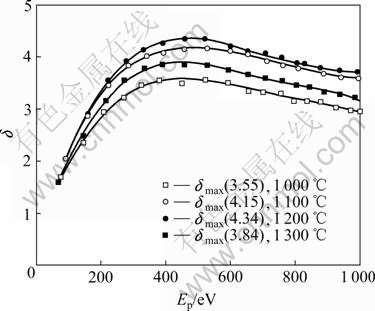
图3 氢气热处理后样品在真空中不同温度激活后的δ—EP曲线
Fig.3 δ—EP curves of samples annealed in hydrogen after activation in vacuum at different temperatures

图4 氢气热处理样品在真空激活后的表面SEM像
Fig.4 Surface SEM image of annealed samples after activation in vacuum
2.3 处理温度对样品次级发射性能的影响
将样品于氢气气氛下1 450 ℃保温1 h,随后测试其次级发射性能,结果如图5所示。由图5可知,900 ℃激活后,δmax达到8.66,随着激活温度的提高,δmax经历了先减小后增大的过程。在较宽的温度范围内,样品的δ都保持在2以上。与图3对比可以看出,活化温度只提高了150 ℃,而样品在900 ℃就可以实现较好的次级发射。从图5还可以看出,当激活温度升高,δ经历了先增大后降低的过程,关于这一现象的解释将另文讨论。这种特性十分有利于阴极在器件中的激活及后续处理工艺。由此可知,这种氢气热处理工艺不同于传统的热处理工艺,它大幅降低了激活温度并改善发射系数,为此将此工艺命名为“活化”工艺。

图5 1 450 ℃氢气热处理后样品经不同温度激活后的δ—EP曲线
Fig.5 δ—EP curves of samples annealed at 1 450 ℃ in hydrogen after activation in vacuum at different temperatures
上述实验结果表明,氢气高温处理使试样的次级发射性能获得很大提升。对同活化工艺处理的同成分液固掺杂样品进行了次级发射性能测试,结果如图6所示。由图6可知,次级发射性能也得到大幅度提高,甚至接近溶胶-凝胶掺杂样品的发射性能。特别需要注意的是该样品在活化后立即装架,未激活时就已经具有一定的次级发射性能,这说明活化工艺确实大幅度改善了材料性能。该结果对稀土-钼材料的实用化具有重要意义,虽然溶胶-凝胶掺杂方式可以实现中小规模生产,但与液固掺杂工艺制粉相比,其制粉过程相对复杂。通过活化工艺处理后,液固掺杂样品的发射性能也得到了改善,使稀土-钼材料在实用管型中达到最佳激活态成为可能,为稀土难熔钼阴极材料的实用奠定了重要基础。

图6 液固掺杂样品在1 450 ℃氢气热处理后的δ—EP曲线
Fig.6 δ—EP curves of liquid-solid doping samples annealed at 1 450 ℃ in hydrogen after activation in vacuum at different temperatures
2.4 活化工艺原理研究
对活化后未激活样品表面进行观察,结果如图7所示。由图7(a)可知,未处理样品表面较为模糊,分析认为这是由于样品导电性能较差所致,而从图7(b)中可以清晰地观察到氧化物区域底部的金属钼组织结构。分析认为,氧化物底部的金属中激发出的电子能够穿过氧化物层逸出,然后被SEM的探测器接收。由此推断出,从底部金属穿过氧化物向发射层进行的电子补充也将得到改善。另一方面,由于电子在氧化物层的输运特性得到改善,更多的内次级电子也能够向表面运动,这两方面的作用对二次电子发射现象产生有益的影响。

图7 未激活样品在退火处理前(a)和处理后(b)的表面微观形貌
Fig.7 Surface SEM images before(a) and after(b) annealing for samples without activation
在以上的分析中发现,样品中残留气体在激活过程中导致金属-氧化物结构遭到破坏,为了进一步分析残留气体的来源,对在干燥皿中保存的4种稀土氧化物进行DTA-TG分析,结果如图8所示。由图8可以看出,4种稀土氧化物在400 ℃以下都存在吸热峰,同时伴随着质量损失,这是稀土氧化物放出其吸附H2O的过程。与Y2O3、Gd2O3和CeO2不同的是,La2O3在900 ℃附近存在一个很强的吸热峰,同时伴随着较大的质量损失,从文献[17]得知,La2O3化学性质不稳定,易吸收H2O反应形成La(OH)3,而La(OH)3在900 ℃时会分解,重新生成H2O和La2O3。很明显,La2O3在900 ℃时的质量损失是La(OH)3分解造成的。以上结果说明稀土氧化物(特别是La2O3)有很强的吸收水分和气体的性质,很可能在后续真空高温激活过程中使金属钼氧化,因此,稀土-钼样品在测试和使用前须进行氢气高温处理。综上所述,真空高温激活时阴极材料中释放较多的氧使阴极表层的钼氧化,氧化物(MoO3)升华的气体分子对逸出样品表面的电子起阻挡作用,影响次级发射性能的提高。MoO3升华后在阴极表面留下较厚的一层稀土氧化物,使金属基底向氧化物层的电子补充受阻。因此,稀土钼金属陶瓷阴极材料应保存于真空中,且无论使用哪种烧结方法,在阴极测试或应用前必须进行氢气高温活化处理。

图8 不同稀土氧化物的DTA-TG曲线
Fig.8 DTA-TG curves of different rare earth oxides
3 结论
1) 经过氢气退火处理后,样品的二次电子发射系数成倍提高,激活温度大幅下降。其中,1 200 ℃激活后样品的δmax由激活前的2.34提高至4.34。
2) 经过活化处理的样品真空激活后稀土氧化物与钼呈相间分布状态,而未活化处理的样品表面金属钼消失,这是样品在活化前后发射性能发生巨大变化的原因。
3) 稀土氧化物特别是La2O3易吸水,后续真空激活过程中使阴极表层钼氧化,而活化处理的稀土-钼样品表面仍保持金属钼和稀土氧化物相间分布状态,这是阴极发射性能提高的原因。
REFERENCES
[1] BLANCHETTE G, GUSS B, DOHERTY M. Development of a long life Ka-band inverted coaxial magnetron for use in an airborne military radar system[C]//2006 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference Held Jointly with 2006 IEEE International Vacuum Electron Sources. Monterey, CA: IEEE, 2006: 2-4.
[2] VAVRIV D M, VOLKOV V A. Millimeter-wave magnetron transmitters for high-resolution radars[C]//7th Workshop on High Energy Density and High Power RF. Kalamata: The Institution of Engineering Technology, 2006: 320-325.
[3] YERYOMKA V D, KOPOT M A, KULAGIN O P. Surface-wave magnetrons: Electromagnetic radiation oscillators in THz range[C]//16th International Crimean Conference- Microwave and Telecommunication Technology. Sevastopol: The Institution of Engineering Technology, 2006: 1-4.
[4] YERYOMKA V D, KOPOT M A, KULAGIN O P, NAUMENKO V D. Spatial-harmonic magnetrons-THz electromagnetic radiation oscillators[C]//2008 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology. Nanjing: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Computer Society, 2008: 1967-1969.
[5] CHURYUMOV G I, FROLOVA T I, BASRAWI K M. The two-stage magnetron for radar applications[C]//Proceedings International Radar Symposium. Krakow: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2007: 671-673.
[6] HODGSON S, BAKER A P, GOODHAND C J, Van der HEIDE P, LEE T, RAY A K, AL-AJILI A. Processing and performance of a novel cathode material[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1999, 146: 79-83.
[7] HAYASHIDA Y, OZAWA T. Simulation for the dope effect mechanism in CRT oxide cathodes, IDW 2000[C]//Proceedings of the Seventh International Display Workshops. Kobe, Japan: IEE, 2000: 517-520.
[8] KULASHEV O K, KURANOVA E D, MAKAROV A P. Metal alloy cathode aging mechanisms[J]. Bulletin of the Academy of Science of the USSR, Physical Series, 1988, 52: 142-144.
[9] DJUBUA B Ch, POLIVNIKOVA O V. Stratum-like structured metal alloy cathode[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2003, 215: 242-248.
[10] KULTASHEV O, DJUBUA B. Miniature metal alloy thermionic cathodes[J]. Physica Scripta, 1997, T71: 127-129.
[11] THOMAS R E, MORRILL C D. Secondary emission properties of impregnated tungsten cathodes[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1983, 16: 292-311.
[12] 王金淑, 刘 娟, 周美玲. 掺杂稀土氧化物的钼阴极二次电子发射性能的研究[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2002, 28(3): 374-378.
WANG Jin-shu, LIU Juan, ZHOU Mei-ling. Study on secondary emission properties of molybdenum cathode doped with rare earth[J]. Journal of Beijing Polytechnic University, 2002, 28(3): 374-378.
[13] WANG Jin-shu, LI Hong-yi, LIU Juan, WANG Yi-man, ZHOU Mei-ling, GAO Yu-juan, TAO Si-wu, ZHANG Jiu-xing. A study of secondary electron emission properties of the molybdenum cathode doped with RE2O3[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2003, 215: 273-279.
[14] WANG Jin-shu, LI Hong-yi, YANG Sa, CUI Ying, ZHOU Mei-ling. A study of emission property and microstructure of rare earth oxide-molybdenum cermet cathode materials made by spark plasma sintering[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2004, 379: 247-251.
[15] YANG Sa, WANG Jin-shu, ZHOU Mei-ling, GAO Yu-juan, LI Hong-yi. Durability experiment on anti-electron-bombardment of RE2O3-Mo secondary emission materials[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2004, 14(2): 274-277.
[16] 王金淑, 刘 娟, 周美玲, 李洪义, 张久兴, 左铁镛. La2O3-Y2O3-Mo次级电子发射材料研究[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2003(1): 23-26.
WANG Jin-shu, LIU Juan, ZHOU Mei-ling, LI Hong-yi, ZHANG Jiu-xing, ZUO Tie-yong. Secondary emission properties of molybdenum cathode doped with La2O3-Y2O3-Mo [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2003(1): 23-26.
[17] 王思清, 魏光明, 李淑霞. 稀土元素La对钼还原及制坯的影响[J]. 中国钼业, 1997(21): 99-101.
WANG Si-qing, WEI Guang-ming, LI Shu-xia. Effect of La2O3 on reduction of molybdenum oxide and blanks making of molybdenum powder[J]. China Molybdenum Industry, 1997(21): 99-101.
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2006ZZ03Z524;2008AA031001);国家自然科学基金项目(50801001)
收稿日期:2008-09-08;修订日期:2009-01-30
通信作者:刘 伟,讲师,博士;电话:010-67391101;E-mail: liuw@bjut.edu.cn
(编辑 李向群)