
DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2020.12.023
冻融作用下不同饱和度红砂岩损伤力学特性
宋勇军,车永新,陈佳星,任建喜,毕冉,陈少杰
(西安科技大学 建筑与土木工程学院,陕西 西安,710054)
摘要:为研究不同饱和度条件下冻融循环作用对岩石损伤规律及力学特性的影响,以饱和度分别为30%,50%,70%,90%和100%的红砂岩为对象,进行冻融循环、电镜扫描(SEM)及单轴压缩试验,分别得到不同冻融循环次数后岩样孔隙率、SEM图像及应力-应变曲线,建立不同饱和度冻融受荷岩石宏观统计损伤演化方程,从细微观角度系统分析饱和度影响下冻融受荷岩石的劣化机制。研究结果表明:随着冻融循环次数增加,孔隙率呈现先快后慢的增长趋势,且当饱和度大于70%后,孔隙率迅速增大。低饱和度下岩样矿物颗粒黏结紧密,颗粒边界不明显,孔隙较少;随着饱和度增大,胶结物的溶蚀作用逐渐加速,颗粒间胶结减弱,溶蚀孔洞增多;岩样冻融循环后裂隙平均长度和孔隙平均面积均随饱和度增大逐渐增长。岩样整体呈剪切破坏,剪切破坏面随饱和度增大逐渐增多并贯穿整个岩样。峰值强度和弹性模量随饱和度增大呈“上凸式”指数减小,当饱和度达到70%后,降幅迅速增大;随冻融循环次数增加,峰值强度和弹性模量呈“下凹式”指数降低,冻融循环10次后,降幅趋于减小。饱和度为70%、冻融循环为10次是该红砂岩损伤劣化的界限值。相比冻融循环作用的损伤劣化影响,饱和度对岩石性质的改变更显著。
关键词:饱和度;冻融循环;扫描电子显微镜;力学特性;损伤演化
中图分类号:TU452 文献标志码:A 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
文章编号:1672-7207(2020)12-3493-10
Damage mechanical properties of red sandstone with different saturation during freeze-thaw
SONG Yongjun, CHE Yongxin, CHEN Jiaxing, REN Jianxi, BI Ran, CHEN Shaojie
(School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Xi'an University of Science and Technology, Xi'an 710054, China)
Abstract: To investigate the effects of freeze-thaw cycles on rock damage and mechanical properties in different saturated states, red sandstone with different saturations (30%, 50%, 70%, 90% and 100%) were selected for freeze-thaw cycle, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and uniaxial compression tests. The porosity variation, SEM image and stress-strain curve of rock samples were obtained after the action of freeze-thaw cycles. The macroscopic statistical damage evolution equations of frozen-thawed rocks with different saturated states were established. The degradation mechanisms of frozen-thawed and loading rocks were systematically analyzed under the influence of saturation from microscopic perspective. The results show that, as the number of freeze-thaw cycles increases, the porosity increases quickly firstly and then slowly. When the saturation is greater than 70%, the porosity increases rapidly. In low saturated states, the mineral particles of rock sample are tightly bonded, the grain boundary is not obvious, and the pores are few. As the saturation increases, the dissolution of the cement is gradually accelerated, the cementation of particles is weakened, and the dissolution holes increase. After the freeze-thaw cycle of the rock sample, the average length of cracks and the average area of pores gradually increase with the increase of saturation. The rock sample shows shear failure, and the shear failure surface increases gradually with the increase of saturation and penetrates the whole rock sample. The strength and elastic modulus of rock samples decrease with the increase of saturation as the "upward convex" index. When the saturation reaches 70%, the decreasing amplitude increases rapidly. The strength and elastic modulus of rock samples decrease with the number of increases of freeze-thaw cycles as the "under concave" index. After 10 freeze-thaw cycles, the decreasing amplitude tends to decrease. The saturation value is 70%, and the freeze-thaw cycle is performed 10 times as the limit value of the damage deterioration of the rock sample. Compared with the damage and degradation effects of freeze-thaw cycles, the saturated states changes more significantly for rock properties.
Key words: saturation; freeze-thaw cycle; scanning electron microscope (SEM); mechanical properties; damage evolution
随着“一带一路”国家战略的提出,西部寒区矿山和隧道等岩土工程建设逐渐增多,冻融环境下岩体的力学特性和工程稳定性问题受到广泛关注。实际工程往往受到冻融循环和荷载等多种因素的共同作用,但由于自然界中地质、地理、气候及水文等条件的多样性,造成岩体饱和状态差异明显,饱和度对冻融环境下岩体损伤力学特性具有较大影响[1],因此,研究不同饱和度岩石冻融损伤差异性对岩体工程具有重要意义。
冻融循环引起岩体发生水冰相变,导致内部孔隙逐渐变大、裂隙发育和贯通,造成岩体损伤程度增大,最终导致力学性质衰减。针对不同饱和状态下岩石的力学特性研究,WONG等[2]通过文献调研,得到了不同种类岩力学特性随含水率变化规律;HAWKINS等[3]对35组砂岩进行试验,发现含水率与强度之间存在负指数关系,且对含水率敏感程度主要由石英和黏土矿物的比例控制;MCGREEY等[4]认为岩体初始含水率决定其冻胀损伤程度,其水分率会随冻融循环次数、冻结历时和季节变化而波动;KODAMA等[5]研究了含水率对高寒地区岩石强度和岩石破裂过程的影响;周翠英等[6]对华南地区不同类型的典型软岩开展不同饱水状态下的力学试验,探讨了软岩软化的力学规律;方杰等[7]探讨了含水率对泥质粉砂岩强度、破坏形式的损伤演化及声发射特征的变化规律;王鹏等[8]开展冻融循环作用下不同含水状态红砂岩力学试验,发现红砂岩力学指标随含水率和冻融循环次数增大程度存在差异;訾凡等[9]通过核磁共振T2谱分析了不同饱和度岩石冻结后的含水状态,并探讨了饱和度对岩石冻结状态下力学强度的影响机制。岩体是否会产生冻融损伤破坏与其饱和度有极大关系,只有超过临界饱和度的岩体才会产生有效的冻融损伤[10]。刘泉声等[11]在岩体冻融损伤研究中指出,初始饱和度对岩体冻胀力有着重要影响;ALOMARI等[12]认为临界饱和度是灰岩冻融破坏的主要控制因素;CHEN等[13-14]讨论了冻融循环作用下饱和度对岩石力学特性的损伤影响,发现当饱和度达到临界值70%之后,岩石的损伤劣化才开始显著出现。在冻融受荷岩石的损伤本构研究方面,张慧梅等[15-16]得出不同冻融循环次数下岩石的损伤扩展规律,并建立冻融与荷载耦合作用下的岩石损伤本构模型;袁小清等[17]建立了一维应力状态下冻融节理岩体的损伤本构模型;李新平等[18]建立冻融受荷裂隙岩石的损伤劣化模型,讨论了寒区裂隙岩体的冻融损伤及受荷损伤劣化机制。
上述研究对认识冻融环境下含水率对岩石力学特性指标的影响奠定了良好基础,但大多数损伤研究仅针对冻融受荷后的宏观力学反应,对不同含水状态岩石冻融损伤机理及冻融后的微细观损伤差异研究尚不充分。为此,本文选取多孔隙红砂岩作为研究对象,对5种不同初始饱和度砂岩(30%,50%,70%,90%和100%)进行不同冻融循环次数后的宏观和细观试验,分析在冻融环境下不同饱和度岩石的损伤差异和力学特性,并据此建立考虑饱和度影响的冻融岩石损伤演化方程。
1 岩样制备及试验方案
1.1 岩样制备
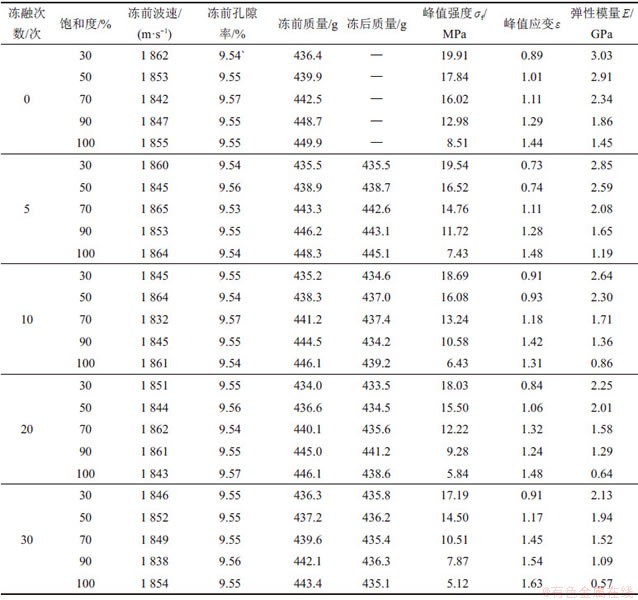
试验岩样取自陕西彬长矿区的红砂岩,经X线衍射分析(XRD),其主要矿物质量分数如下:石英为35%、斜长石为14%、方解石为8%、钾长石为3%,黏土矿物及其他矿物为40%。按照《国际岩石力学学会》试验规程将岩样加工成直径×高度为50 mm×100 mm的标准圆柱体,选取完整性较好岩样放入105 ℃的烘箱中烘烤24 h,待岩样冷却后测得其干密度和纵波波速。并按纵波波速(1 832~1 865 m/s)和干密度(2.30~2.32 g/cm3)相近原则,选出2组,第1组进行单轴压缩试验,第2组作为平行组进行扫描电镜试验,每组25个,共计50个岩样。岩样初始基本物理参数均值如下:纵波波速为1 863 m/s,干密度为2.31 g/cm3,孔隙率为9.56%,饱和含水率为5.29%,饱水密度为2.45 g/cm3。
1.2 试验方案
1) 不同饱和度岩样制备。用真空饱和机对所有岩样强制饱和24 h,得到饱和岩样质量;岩样强制饱和后自然风干,每隔一定时间(30 min)称质量,并按照式(1)得出不同饱和度岩样对应质量;得到试验要求的饱和度岩样后将其用保鲜膜密封,再将其用保鲜袋装好后放入水中水封。岩样完全被水浸没,保证冻融循环试验前岩样饱和度恒定。
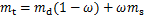 (1)
(1)
式中: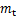 为不同饱和度岩样对应质量;
为不同饱和度岩样对应质量;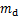 为岩样干燥质量;
为岩样干燥质量;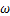 为岩样饱和度;
为岩样饱和度;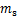 为岩样饱和质量。
为岩样饱和质量。
2) 冻融循环试验。冻融循环试验前将不同饱和度岩样放于水封装置中静置7 d,保持岩样中水分均匀分布。为保持饱和度稳定,冻融循环试验均在水封装置中进行。岩样在-20 ℃下冻结12 h,在20 ℃下融化12 h,每24 h为1个冻融循环周期,分别进行0,5,10,20和30次冻融循环。
3) 力学试验。在岩石力学试验机上对第1组岩样进行不同冻融循环次数和饱和度条件下的单轴压缩试验,加载方式按位移控制,速率为0.002 mm/s,得到不同条件下的应力-应变曲线以及峰值强度,峰值应变和弹性模量等力学参数。试验加载装置利用TAW-1000岩石力学试验机,该试验机可进行常规单轴、三轴压缩和蠕变试验,其轴向力最大可加载至1 000 kN,围压最大可加载至100 MPa。
4) 电镜扫描试验。根据第1组岩样相同冻融次数及饱和度条件下压缩破坏后的剪切面及断口特征,选取第2组上、中和下3个不同典型部位制取切片进行电镜扫描。扫描前对切片进行干燥和镀金处理。
2 试验结果
2.1 孔隙率变化
采用抽真空饱和的方法,得到岩样冻融循环后完全饱水状态的质量,通过干燥和饱和状态质量变化从而计算出孔隙率。图1所示为不同饱和度红砂岩孔隙率随冻融循环次数变化曲线。由图1可见:不同饱和度岩样孔隙率随冻融循环次数增加逐渐增大。在饱和度为30%时,岩样接近自然状态,受冻融损伤程度较弱,孔隙率未见明显变化;饱和度为50%时,岩样冻融损伤效应较为明显,但由于岩样饱和度较低,仍不能产生危害岩体稳定性的冻胀力,因而,孔隙率随冻融循环次数增加变化较小;当饱和度大于70%时,由于岩样中水分持续增多,岩样孔隙和裂隙冰的体积膨胀引起新裂隙的萌生、发育和扩展,孔隙率迅速增大。另外,随着冻融循环次数增加,孔隙率呈现先快后慢的增长趋势,说明岩样在达到一定饱和度后,前期冻融循环对岩样内部结构的影响较大。
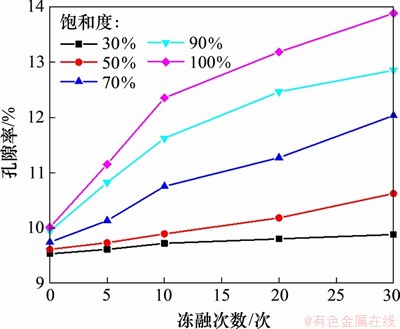
图1 不同饱和度砂岩孔隙率随冻融次数变化
Fig. 1 Variation of porosity of sandstone with different saturation and freeze-thaw times
2.2 微观特征
为进一步直观研究饱和度对红砂岩冻融循环后微观结构影响特征,分别采用100,200,500和1 000倍放大倍数,共得到100余幅照片。将获取的SEM图像用PCAS软件进行二值化处理[19]。经对比,100倍放大倍数的照片反映微观信息较为丰富和全面,限于篇幅仅给出冻融循环30次不同饱和度岩样电镜扫描图。
图2所示为不同饱和度岩样冻融循环30次后电镜扫描、二值化处理图像及单轴压缩下岩样破坏形态。二值化图像中黑色部分代表扫描切片的孔隙和裂隙。从二值化图像可以清楚看到,在不同饱水状态下,岩样冻融循环一定次数后孔隙数量、孔隙面积、裂隙长度和宽度均存在明显差异。因颗粒胶结较强,即使岩样经历30次冻融循环后,低饱和度下岩样矿物颗粒仍黏结紧密,颗粒边界不明显,孔隙较少;随着饱和度增大,岩样中胶结物与矿物颗粒的黏结状态逐渐改变,胶结物的溶蚀作用逐渐加速,导致颗粒间胶结物严重流失,颗粒间胶结减弱,溶蚀孔洞变多,颗粒边界明显,沿颗粒边界甚至穿越颗粒的贯穿裂缝[8]。岩石的最终宏观断裂与其内部微结构和微缺陷紧密相关。
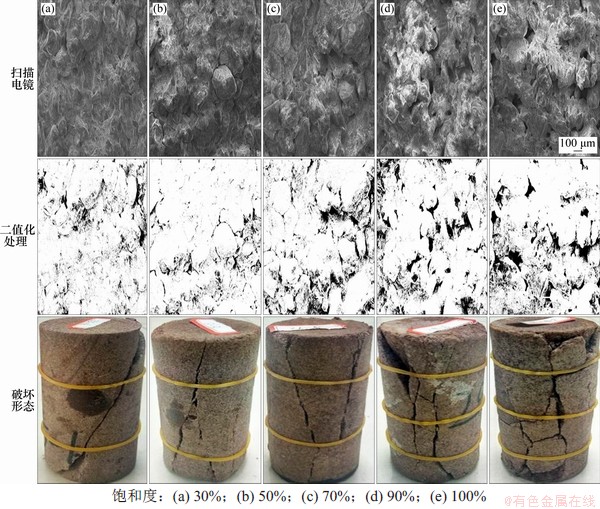
图2 不同饱和度砂岩电镜扫描、二值化处理及破坏形态图
Fig. 2 Scanning electron microscope, binarization and failure morphology of sandstone with different saturation
从压缩破坏形态可以看出,饱和度小于70%时,岩样整体呈剪切破坏,剪切破坏面随饱和度增大逐渐增多并贯穿整个岩样;当饱和度大于70%时,岩样张拉破坏逐渐显现,出现多裂缝开裂且岩样破坏后的完整性较差。从表1可见,冻融循环后岩样的质量随饱和度增大逐渐减小,且饱和度越大,质量衰减幅值越明显。
采用PCAS软件提取电镜扫描信息[19],得到孔隙长度、宽度和面积等几何参数。图3所示为提取得到的孔隙平均面积和裂隙平均长度随饱和度变化曲线。由图3可见:岩样冻融循环后裂隙平均长度和孔隙平均面积均随饱和度增大逐渐增大,说明饱水状态的不同显著影响和改变了红砂岩的微观形貌。
2.3 力学特性
不同饱和度红砂岩经历不同冻融循环后的单轴压缩试验结果如表1和图4所示。由图4可见:压缩曲线大致经历了压密阶段(OA)、弹性阶段(AB)、塑性发展阶段(BC)、破坏阶段[20]。在相同冻融次数下,随着饱和度的增大,应力-应变关系曲线逐渐向右下方移动,具体表现为:压密阶段变长,曲线OA段趋于右移,线弹性阶段变短且斜率减小,峰值应变增大,峰值强度降低。说明随着饱和度增大,岩样内部颗粒胶结性减弱且冻胀变形对岩体结构影响逐渐增大,在融化过程中这种变形不能恢复,岩样内部的缩胀、损伤开裂交替变化的程度逐渐加剧,造成岩样孔隙发育越明显[14],从而降低岩样弹性,提高塑性。由此表明,饱和度对岩样的力学特性有着重要的影响,岩样冻融损伤破坏随饱和度增大逐渐加剧,不同冻融条件下存在相似变化。但相比冻融作用对红砂岩力学特性的改变,饱和度的影响更为显著。
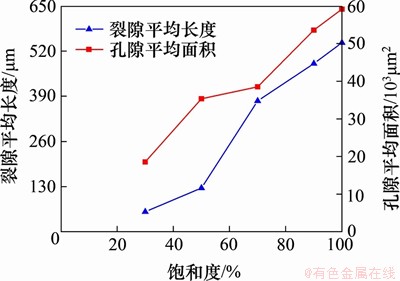
图3 孔隙平均面积、裂隙平均长度随饱和度变化曲线
Fig. 3 Curve of average pore area and average crack length with saturation
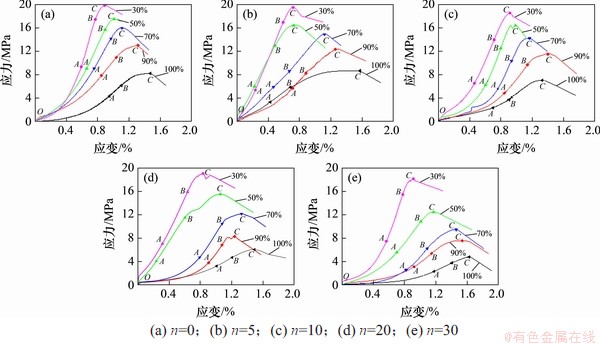
图4 不同饱和度砂岩冻融后单轴应力-应变曲线
Fig. 4 Uniaxial stress-strain curves after freeze-thaw of different saturated sandstone
表1 冻融砂岩单轴压缩试验结果
Table 1 Results of uniaxial compression test of freeze-thaw sandstone
2.3.1 饱和度对砂岩力学特性影响
为进一步分析饱和度对红砂岩力学特性的影响差异,根据表1试验数据对冻融循环岩样的峰值强度和弹性模量与饱和度进行拟合,拟合曲线如图5所示,限于篇幅仅列出了饱和度为70%时的拟合函数:
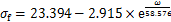 (2)
(2)
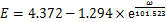 (3)
(3)
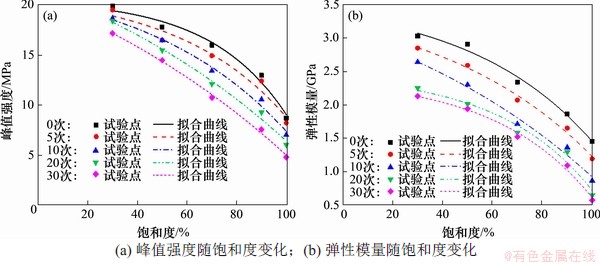
图5 峰值强度和弹性模量随饱和度变化曲线
Fig. 5 Curves of peak intensity and elastic modulus with saturation
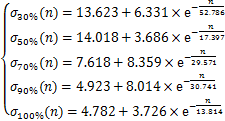 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
式中: 为峰值强度;
为峰值强度; 为弹性模量。从表1和图5可以看到:峰值强度和弹性模量均随饱和度增大呈“上凸式”指数衰减。当饱和度由30%增加到70%时,曲线下降平缓,峰值强度降幅较小,经0,5,10,20和30次循环,峰值强度仅分别降低了19.54%,24.46%,29.16%,32.22%和38.86%;而饱和度大于70%后,曲线由平滑转为直线段,峰值强度迅速下降,经0,5,10,20和30次冻融次后分别降低46.88%,49.66%,51.44%,52.21%和51.29%,弹性模量降低幅度随饱和度增加也表现出相同变化规律。表明当饱和度从30%增加到70%时,饱和度对岩样力学性能影响较小;当饱和度大于70%以后,岩样冻融损伤过程中力学性能的劣化速率随饱和度的持续增大而逐渐加快。这是由于在低饱和度下,水分子的溶蚀、润滑及软化作用较弱,随着饱和度升高到70%左右,岩样内部胶结性减弱,导致矿物颗粒之间联结性变差,孔隙率增大[8]。由以上分析可以得出,70%可作为红砂岩冻融损伤的临界饱和度。
为弹性模量。从表1和图5可以看到:峰值强度和弹性模量均随饱和度增大呈“上凸式”指数衰减。当饱和度由30%增加到70%时,曲线下降平缓,峰值强度降幅较小,经0,5,10,20和30次循环,峰值强度仅分别降低了19.54%,24.46%,29.16%,32.22%和38.86%;而饱和度大于70%后,曲线由平滑转为直线段,峰值强度迅速下降,经0,5,10,20和30次冻融次后分别降低46.88%,49.66%,51.44%,52.21%和51.29%,弹性模量降低幅度随饱和度增加也表现出相同变化规律。表明当饱和度从30%增加到70%时,饱和度对岩样力学性能影响较小;当饱和度大于70%以后,岩样冻融损伤过程中力学性能的劣化速率随饱和度的持续增大而逐渐加快。这是由于在低饱和度下,水分子的溶蚀、润滑及软化作用较弱,随着饱和度升高到70%左右,岩样内部胶结性减弱,导致矿物颗粒之间联结性变差,孔隙率增大[8]。由以上分析可以得出,70%可作为红砂岩冻融损伤的临界饱和度。
2.3.2 冻融作用对砂岩力学特性影响
为分析冻融循环作用对红砂岩力学特性的影响差异,根据表1对冻融循环岩样的峰值强度和弹性模量与冻融循环次数进行拟合,拟合曲线如图6所示,式(4)给出了不同饱和度岩样峰值强度与冻融循环次数拟合函数,式(5)为不同饱和度岩样弹性模量随冻融次数拟合函数。
由图6可见:随着冻融循环次数增多,峰值强度和弹性模量均呈“下凹式”指数衰减。以图6(a)中100%饱和度为例,[0,5],(5,10],(10,20]和(20,30]次冻融循环后岩样峰值强度降幅分别为13.0%,9.68%,10.56%和10.61%;由图6(b)中70%饱和度为例,[0,5],(5,10],(10,20]和(20,30]次冻融循环后岩样弹性模量分别降低了28.76%,3.99%,1.43%和3.67%,其他饱和度情况下也存在相同规律。
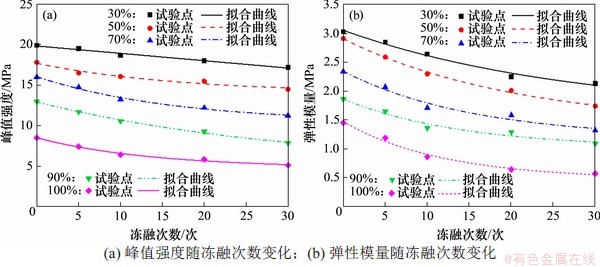
图6 峰值强度和弹性模量随冻融次数变化曲线
Fig. 6 Curves of peak intensity and elastic modulus with the number of freeze-thaw cycles
当冻融循环次数达到10次时,岩样冻融循环过程中力学性能的劣化速率随冻融次数增大逐渐减缓,说明冻融作用对岩样损伤劣化影响主要体现在冻融循环前期。因此,10次可作为红砂岩冻融损伤的临界冻融次数。对比饱和度和冻融循环对砂岩力学特性的影响,冻融循环前,当饱和度由30%增加到100%时,峰值强度降低了58.7%,弹性模量降低了62.8%;即使在完全饱水状态下,冻融循环30次后峰值强度和弹性模量分别仅降低了41.43%和54.42%。因此,相较于冻融循环对砂岩力学特性的损伤劣化,饱和度的影响程度则更为显著。
3 岩石冻融受荷损伤演化
3.1 建立损伤本构模型
分析红砂岩冻融循环后力学特性可知,随着冻融循环次数增加,不同饱和度岩样力学特性存在明显差异。由于宏观唯象损伤力学认为岩石宏观物理力学性能的响应能够代表材料内部的劣化程度,基于此选取能够充分反映不同饱和度砂岩冻融后弹性模量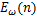 来定义损伤变量
来定义损伤变量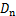 ,因此,可将红砂岩冻融损伤变量
,因此,可将红砂岩冻融损伤变量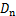 表示为
表示为
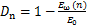 (6)
(6)
式中: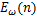 为不同饱和度岩样经历n次冻融循环后的弹性模量;
为不同饱和度岩样经历n次冻融循环后的弹性模量;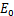 为饱和度为30%时未冻岩样的弹性模量。
为饱和度为30%时未冻岩样的弹性模量。
岩石材料内部构造极不均匀,各微元所具有的度均不相同,考虑到岩石损伤是一个连续过程,结合张慧梅等[15]运用岩石应变强度理论和Weibull分布的损伤模型的方法,研究冻融循环作用下不同饱和度砂岩损伤演化规律。双参数Weibull分布下概率密度函数为
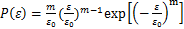 (7)
(7)
式中: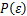 为微元强度分布函数;
为微元强度分布函数;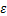 为微元强度随机分布变量,指岩石材料的应变;
为微元强度随机分布变量,指岩石材料的应变; 和
和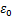 为分布参数。定义损伤变量
为分布参数。定义损伤变量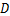 为岩样中已经破坏的微元数目与总微元数目之比,则
为岩样中已经破坏的微元数目与总微元数目之比,则
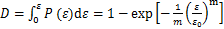 (8)
(8)
饱和度、冻融循环和荷载3种因素作用引起岩样损伤劣化,基于张全胜等[24]在Lemaitre应变等价原理的基础上提出推广后的应变等价原理,将不同饱和度岩样冻融后的损伤状态作为第1种损伤状态,荷载作用下引起的损伤作为第2种损伤状态,得到不同饱和度岩样在两种损伤状态下的一维本构关系分别为:
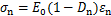 (9)
(9)
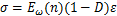 (10)
(10)
将式(6)代入式(9)和(10)可以得到冻融作用下不同饱和度岩样的应-应变关系为
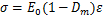 (11)
(11)
其中:
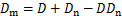 (12)
(12)
由式(12)可知:
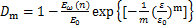 (13)
(13)
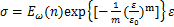 (14)
(14)
式中: 为冻融受荷岩样总损伤量;
为冻融受荷岩样总损伤量; 为应力。
为应力。
3.2 损伤演化验证
结合表1试验结果,将式(5)分别代入式(13),得到不同饱和度红砂岩冻融受荷损伤演化曲线如图7所示。由图7可见:在加载初始阶段,岩样的冻融初始损伤量随饱和度增加而加剧,这是因为在冻结过程中冰的体积膨胀造成孔隙变大和新裂隙的萌生、发育和扩展,冻胀力随饱和度增加不断变大,导致孔隙率随饱和度增加而增大;之后,随着变形的逐渐累积,增大速率趋近于平缓,最终岩样总损伤量趋近于1。该类型曲线能够准确地反映冻融循环作用下不同饱和度红砂岩损伤劣化。
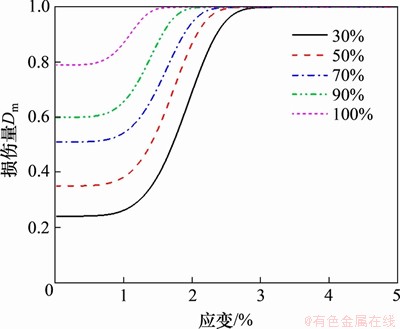
图7 冻融循环20次不同饱和度砂岩受荷损伤演化曲线
Fig. 7 Damage evolution curve of sandstone with different saturation after 20 freeze-thaw cycles
4 结论
1) 孔隙率随饱和度和冻融次数增加呈增大趋势。当冻融循环次数达到30次,随着岩样接近完全饱水状态,岩样内部孔隙面积逐渐增大、裂隙逐渐贯通。
2) 不同饱和度岩样冻融循环作用后应力-应变变化存在显著差异。随着饱和度增大,压密和塑性变形阶段突出,弹性阶段持续时间减小;峰值强度和弹性模量随饱和度增大呈“下凸式”指数降低,而随冻融循环次数增加呈“下凹式”指数减小;饱和度为70%、冻融为10次是岩样损伤劣化的界限值;相较于冻融作用对砂岩力学特性的影响,饱和度的影响更加显著。
3) 依据应变强度理论和Weibull分布,建立考虑饱和度因素影响的损伤演化方程;在冻融过程中,冻胀力随饱和度增加不断变大,造成岩样孔隙率逐渐增大,表现为加载初期损伤量逐渐增大;在加载过程中,岩样随变形逐渐累积,增大速率趋近于平缓,最终总损伤量趋近于1。
参考文献:
[1] 王俐. 不同初始含水率红砂岩冻融损伤的试验研究及其机理分析[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院研究生院(武汉岩土力学研究所), 2006: 10-11.
WANG Li. Experiment studies and mechanism analysis on different initial water-saturated red sandstones under condition of frost and thaw[D]. Wuhan: Graduate University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(Wuhan Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics), 2006: 10-11
[2] WONG L N Y, MARUVANCHERY V, LIU Gang. Water effects on rock strength and stiffness degradation[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2016, 11(4): 713-737.
[3] HAWKINS A B, MCCONNELL B J. Sensitivity of sandstone strength and deformability to changes in moisture content[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 1992, 25(2): 115-130.
[4] MCGREEVY J P, WHALLEY W B. Rock moisture content and frost weathering under natural and experimental conditions: a comparative discussion[J]. Arctic Antarctic and Alpine Research, 1985, 17, 337-346.
[5] KODAMA J, GOTO T, FUJII Y, et al. The effects of water content, temperature and loading rate on strength and failure process of frozen rocks[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2013, 62: 1-13.
[6] 周翠英, 邓毅梅, 谭祥韶, 等. 饱水软岩力学性质软化的试验研究与应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(1): 33-38.
ZHOU Cuiying, DENG Yimei, TAN Xiangshao, et al. Experimental research on the softening of mechanical properties of saturated soft rocks and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(1): 33-38.
[7] 方杰, 姚强岭, 王伟男, 等. 含水率对泥质粉砂岩强度损伤及声发射特征影响的研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(S2): 412-419.
FANG Jie, YAO Qiangling, WANG Weinan, et al. Experimental study on damage characteristics of siltstone under water action[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(S2): 412-419.
[8] 王鹏, 许金余, 方新宇, 等. 红砂岩吸水软化及冻融循环力学特性劣化[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(6): 2065-2072.
WANG Peng, XU Jinyu, FANG Xinyu, et al. Water softening and freeze-thaw cycling induced decay of red-sandstone[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(6): 2065-2072.
[9] 訾凡, 杨更社, 贾海梁. 饱和度对泥质粉砂岩冻结力学性质的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 2018, 40(4): 748-755.
ZI Fan, YANG Gengshe, JIA Hailiang. Influence of saturation degree on the mechanical properties of frozen argillaceous siltstone[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2018, 40(4): 748-755.
[10] PRICK A. Critical degree of saturation as a threshold moisture level in frost weathering of limestones[J]. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 1997, 8(1): 91-99.
[11] 刘泉声, 黄诗冰, 康永水, 等. 裂隙岩体冻融损伤研究进展与思考[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(3): 452-471.
LIU Quansheng, HUANG Shibing, KANG Yongshui, et al. Advance and review on freezing-thawing damage of fractured rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(3): 452-471.
[12] AIOMARI A, BECK K, BRUNETAUD X, et al. Critical degree of saturation: A control factor of freeze-thaw damage of porous limestones at Castle of Chambord, France[J]. Engineering. Geology, 2015, 185: 71-80.
[13] CHEN T C, YEUNG M R, MORI N. Effect of water saturation on deterioration of welded tuff due to freeze-thaw action[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2004, 38 (2/3): 127-136.
[14] 刘海康, 张思渊, 张鑫鑫. 不同初始含水率下砂岩冻融劣化特性试验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(26): 322-327.
LIU Haikang, ZHANG Siyuan, ZHANG Xinxin. Experimental study of freeze-thaw deterioration specialty of sandstone in different initial moisture content[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(26): 322-327.
[15] 张慧梅, 杨更社. 冻融与荷载耦合作用下岩石损伤模型的研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(3): 471-476.
ZHANG Huimei, YANG Gengshe. Research on damage model of rock under coupling action of freeze-thaw and load[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(3): 471-476.
[16] 吴安杰, 邓建华, 顾乡, 等. 冻融循环作用下泥质白云岩力学特性及损伤演化规律研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2014, 35(11): 3065-3072.
WU Anjie, DENG Jianhua, GU Xiang, et al. Research on mechanical properties and damage evolution law of argillaceous dolomite under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(11): 3065-3072.
[17] 袁小清, 刘红岩, 刘京平. 冻融荷载耦合作用下节理岩体损伤本构模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(8): 1602-1611.
YUAN Xiaoqing, LIU Hongyan, LIU Jingping. A damaging model of jointed rock under coupled action of freezing and thawing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(8): 1602-1611.
[18] 李新平, 路亚妮, 王仰君. 冻融荷载耦合作用下单裂隙岩体损伤模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(11): 2307-2315.
LI Xinping, LU Yani, WENG Yangjun. Research on damage model of single jointed rock masses under coupling action of freeze-thaw and loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(11): 2307-2315.
[19] 唐朝生, 施斌, 刘春, 等. 影响黏性土表面干缩裂缝结构 形态的因素及定量分析[J]. 水利学报, 2007, 38(10): 1186-1193.
TANG Chaosheng, SHI Bin, LIU Chun, et al. Factors affecting the surface cracking in clay due to drying shrinkage[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 38(10): 1186-1193.
[20] 张慧梅, 杨更社. 冻融岩石损伤劣化及力学特性试验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(10): 1756-1762.
ZHANG Huimei, YANG Gengshe. Experimental study of damage deterioration and mechanical properties for freezing-thawing rock[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2013, 38(10): 1756-1762.
[21] KHANLARI G, SAHAMIEH R Z, ABDILOR Y. The effect of freeze-thaw cycles on physical and mechanical properties of upper red formation sandstones, central part of Iran[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2015, 8(8): 5991-6001.
[22] PARK J, HYUN C U, PARK H D. Changes in microstructure and physical properties of rocks caused by artificial freeze-thaw action[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2015, 74(2): 555-565.
[23] TAN Xianjun, CHEN Weizhong, YANG Jianping, et al. Laboratory investigations on the mechanical properties degradation of granite under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2011, 68(3): 130-138.
[24] 张全胜, 杨更社, 任建喜. 岩石损伤变量及本构方程的新探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2003, 22(1): 30-34.
ZHANG Quansheng, YANG Gengshe, REN Jianxi. New study of damage variable and constitutive equation of rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(1): 30-34.
[25] 杨更社, 申艳军, 贾海梁, 等. 冻融环境下岩体损伤力学特性多尺度研究及进展[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(3): 545-563.
YANG Gengshe, SHEN Yanjun, JIA Hailiang, et al. Research progress and tendency in characteristics of multi-scale damage mechanics of rock under freezing-thawing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(3): 545-563.
(编辑 秦明阳)
收稿日期: 2020 -04 -20; 修回日期: 2020 -06 -23
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(11972283,11872299,11802230);陕西省自然科学基金资助项目(2017JM1039) (Projects(11972283, 11872299, 11802230) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2017JM1039) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province)
通信作者:宋勇军,副教授,从事岩石力学与地下工程研究;E-mail:songyj79@163.com