文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)07-1300-06
热处理对铝合金牺牲阳极电化学性能的影响
朱元良1, 赵艳娜2, 齐公台1, 刘 斌1
(1. 华中科技大学 化学系, 武汉 430074;
2. 南阳理工学院 生物与化学工程系, 南阳 473066)
摘 要: 针对不同均匀化处理方式会引起合金微观组织和电化学性能变化现象, 采用电子探针(EPMA)、 动电位极化及恒电流极化等方法研究不同热处理(水淬、 空冷、 炉冷)方式对Al-Zn-In合金的微观组织和合金在3%NaCl溶液中的开路电位、 工作电位、 腐蚀形貌和电流效率等电化学性能的影响。 结果表明: 510℃, 10h的均匀化处理使晶界偏析减少, 抑制析氢自腐蚀和晶粒脱落, 提高电流效率, 但对阳极开路电位、 工作电位及溶解行为的影响并不明显, 且水淬处理试样的电流效率最高。
关键词: 热处理; 铝合金; 牺牲阳极; 电流效率
中图分类号: TG174.41 文献标识码: A
Effect of heat treatment on electrochemical performance of aluminium alloy sacrificial anode
ZHU Yuan-liang1, ZHAO Yan-na2, QI Gong-tai1, LIU Bin1
(1. Department of Chemistry, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,
Wuhan 430074, China;
2. Department of Biological and Chemical Engineering, Nanyang Institute of Technology,
Nanyang 473066, China)
Abstract: The effect of different heat treatments (quenching in water, cooling in air, cooling in furnace) on the microstructure and electrochemical performance of Al-Zn-In alloys in 3%NaCl solution were investigated by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), potentiodynamic and galvanostatic polarizations. The results show that the homogenization at 510℃ for 10h reduces the grain boundary segregation, restrains the hydrogen evolution and grain falling and improves the current efficiency. But the influences of homogenization on the open circuit potential, operating potential and dissolving behaviour are unobvious. The anode current efficiency of water-quenched samples is biggest.
Key words: heat treatment; aluminium alloys; sacrificial anode; current efficiency
纯Al中添加一种或多种合金元素, 如Zn、 In、 Cd、 Si、 Sn、 Mg、 Ti可制得Al-Zn-In系合金牺牲阳极, 该系列阳极的平均工作电位为-1.10V(vs SCE), 电流效率可达85%以上, 表面溶解均匀, 产物易脱落, 因而广泛应用于海水介质中的船舶、 海洋工程设施、 海水冷却水系统和储罐沉积水部位等工业领域的阴极保护[1]。 对铸造阳极进行热处理, 可以减少偏析和增加α(Al)固溶体中合金元素的含量, 从而有利于提高阳极的综合性能[2-6]。 但也有实验结果表明, 热处理对阳极电化学性能影响不大[7], 甚至使阳极性能恶化[8]。 本文作者通过比较不同均匀化处理方式引起合金微观组织和电化学性能的变化, 研究了热处理对Al-5%Zn-0.03%In合金在3%NaCl(质量分数)溶液中的开路电位、 工作电位、 腐蚀形貌和电流效率等电化学性能的影响。
1 实验
1.1 合金阳极制备
将Al锭(99.99%)在石墨坩锅中加热至760℃, 待熔化后加入裹有纯Zn(99.99%)、 纯In(99.999%)的Al包, 添加C2Cl6除气, 用石墨棒搅拌均匀后捞渣, 在铸铁模具中浇注成铸棒, 自然冷却得到理论含量为Al-5%Zn-0.03%In的合金铸态试样。 将铸态试样在马弗炉中在(510±5)℃保温10h后分别水淬、 空气冷却和随炉冷却, 得到冷却速度不同的3种热处理试样。 所有试样都机械加工为d16mm×28mm的圆柱电极, 一端钻有螺孔以连接铜导线, 用绝缘胶密封两端, 留出的工作面积为14cm2, 表面打磨至1.6μm。
1.2 微观分析
合金试样在金相砂纸和“绒布+W0.5金刚石墨膏+蒸馏水”上打磨抛光后, 用Keller试剂(2mL HF+3mL HCl+5mL HNO3+190mL H2O)浸蚀1min, 然后在JEOL公司生产的JXA-8800型电子探针分析仪(EPMA)上进行形貌观察及成分测定, 加速电压为20kV。
1.3 电化学测试
采用传统的三电极体系在IM6电化学工作站测量合金阳极的开路电位和动电位极化曲线, 扫描速率为1mV/s。 电流效率通过恒电流极化法测定, 参比电极为带有饱和KCl盐桥的饱和甘汞电极(SCE), 辅助阴极为840cm2的圆筒状不锈钢, 极化电流1mA/cm2, 时间240h, 阳极表面的析氢量采用排水法收集。 实验介质为质量分数为3%的NaCl溶液, pH值约为6.2, 温度为室温((22±3)℃), 所用试剂均为分析纯。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 热处理对阳极微观组织的影响
合金阳极不同均匀化处理前后的微观组织如图1所示。 其中图1(c)和(d)所示分别为铸态和水淬试样中析出相的分布情况。 由图1可看出, 热处理前后组织变化明显, 铸态组织(图1(a))晶粒粗大, 晶枝发达, 为典型的放射状树枝晶; 热处理试样(图1(b)、 (e)和(f))则晶界明显, 晶枝消失, 偏析减少, 为均匀的等轴晶组织。 经不同冷却方式处理后, 合金晶粒大小顺序为炉冷>空冷>水淬。 偏析相和杂质相的分布形式在热处理前后发生明显变化, 铸态试样中析出物(图1(c))沿晶界和晶枝边缘分布, 析出物尺寸较大。 EPMA分析结果表明, 其成分主要为Al(Zn, Fe, Si), 其中元素Zn质量分数高达9.78%, 高出理论含量5%较多; 热处理试样析出物(图1(d))以小球或链状形式分布, 大部分出现在晶界, 也有在晶内弥散分布, 析出物成分上更纯, 多为初晶硅和杂质铁。 于510℃保温10h后, 不同冷却速度虽然对合金组织的影响似乎不明显, 但对析出相的类型和尺寸有显著影响, 冷却速度较慢时会析出Al2Zn和AlIn等新相[8]。 热处理试样的基体成分比铸态试样的更接近理论含量, 但测试过程中都没有检测到In, 这可能因为In含量太少, 又易在熔炼过程中燃烧损失, 超出了仪器的检测限。 热处理前后试样都由温度传感器引入微量的杂质Fe、 Si, 也都存在极少的疏松铸造缺陷, 但长时间高温均匀化处理使偏析得到了明显抑制, 促进了合金元素最大限度地溶于α(Al)固溶体。
2.2 热处理对阳极电位及极化曲线的影响
将合金试样浸入质量分数为3%NaCl溶液中, 监测开路电位随时间的变化曲线, 结果如图2所示。 由图2可看出, 30min后, 电位都达到稳定, 随时间延长变化不大。 在外加电流极化时, 4种阳极试样的工作电位较稳定((-0.929±0.003)V), 但随着表面溶解而有所波动。 图3所示为合金在3%NaCl溶液中的极化曲线。 由图3可看出, 4条动电位极化曲线在开路电位附近接近重合, 没有太大的差异。
牺牲阳极材料要有足够负电位, 保证使被保护金属设备发生阴极极化, 但是电位又不宜太负, 以免在阴极区发生析氢反应, 损伤被保护体表面有机涂层及石灰覆盖层, 或引起被保护金属的氢脆。 实践中规定, 钢在海水中(不含氧)的保护电位为-0.88V[9], 因此电位越负, 牺牲阳极可保护的范围就越广, 但均匀化处理前后4种合金的开电位都趋于稳定(为-0.965V), 且极化时的工作电位也趋于一致, 这说明热处理对阳极的开路电位和工作电位的影响不大, 起始时电位的差异主要是由于表面粗糙度和打磨后在空气中暴露时间不同而引起的。 Salinas等[10]在研究Al-5%Zn铸态合金时, 根据冷却速度不同可分为表面细晶粒区、 中间柱状晶区和内部等轴晶区, 但3种不同组织结构的试样
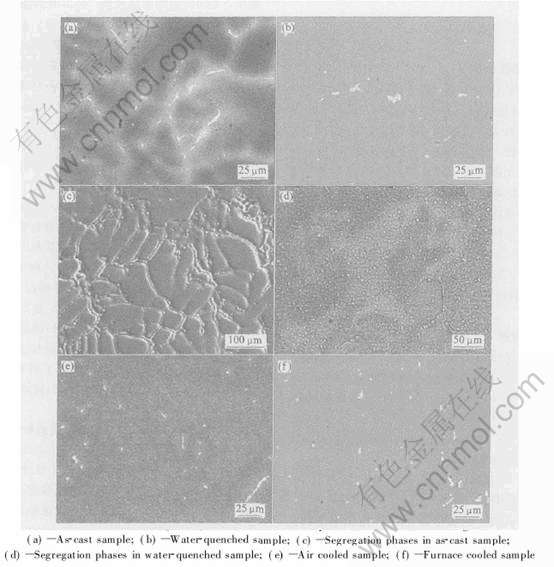
图1 Al-Zn-In合金Keller试剂浸蚀后的EPMA形貌
Fig.1 EPMA morphologies of Al-Zn-In alloys etched in Kellers reagent
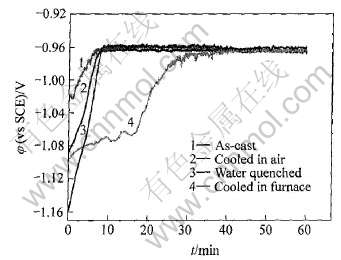
图2 Al-Zn-In合金在3%NaCl溶液中开路电位随
时间的变化曲线
Fig.2 Change curves of open circuit potential with time of Al-Zn-In alloys in 3% NaCl solution

图3 合金在在3%NaCl溶液中的极化曲线
Fig.3 Polarization curves of Al-Zn-In alloys in 3% NaCl solution
在0.5mol/L NaCl溶液中的工作电位都是-0.965V[10], 这与实验结果一致。 4条极化曲线的重合反映了4种合金试样的极化行为一致, 阴极发生析氢反应, 阳极发生合金的溶解, 即均匀化处理对阳极的溶解行为没有太大的影响。 影响合金电位和极化行为的因素主要是合金表面氧化膜在3%NaCl中的性质。 根据表面自由能理论[4, 11], 合金表面Al2O3膜厚度越小, 表面自由能越低, 金属与表面氧化物膜的结合力也就越弱, 即电位越负。 表面自由能按公式F=4.99846×10-11×E×a计算, 其中F为表面自由能, E为杨氏模量, a为原子间距。 经过均匀化处理后, 虽然能使合金元素固溶度增大, 偏析减少, 即杨氏模量减小, 但同时也使原子间距增大, 因此表面自由能有可能变化不大, 均匀化对阳极的开路电位、 工作电位和极化行为的影响不大。
2.3 热处理对阳极电流效率的影响
热处理前后4种试样的电流效率如表1所列, 电流效率由如下公式计算而得:

均匀化处理后电流效率得到大幅度提高, 按效率大小依次为水淬>炉冷>空冷铸态。 图4所示为恒电流极化过程中阳极表面析出氢气随时间的变化曲线。 由图4可看出, 析氢速率随反应时间延长都有所增大, 但铸态的析氢速度(即曲线斜率)远大于热处理后的3个试样, 即铸态空冷≈水淬>炉冷, 这和电流效率有一定的对应关系, 即析氢速度越大, 电流效率越低。
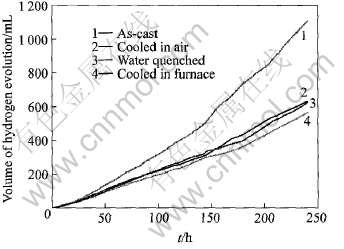
图4 合金在恒电流极化时的析氢速率随时间的变化曲线
Fig.4 Change curves of hydrogen evolution rate with time of Al-Zn-In alloys during galvanostatic polarization at 1mA/cm2
4种试样的析氢速率随时间延长都有所增大, 这可能是由于合金表面溶解引起表面粗糙度增大, 比表面积增大, 导致有效反应界面增加的缘故。 阳极表面析氢是合金自腐蚀的结果, 也有认为是溶解的低价态中间产物(Al+)化学反应引起[12], 无论是哪一种解释, 都指出这种析氢过程消耗了用于阴极保护回路电流的电子。 结合图1(c)可以看出, 铸态组织晶界偏析严重, 偏析区的晶界能比基体的高, 杂质元素富集, 缺陷密集, 处于不稳定状态, 阳极极化时晶界偏析区的腐蚀电流密度高于晶粒基体, 优先发生腐蚀[13], 优先腐蚀区和未腐蚀部位可构成微观腐蚀电池, 即优先腐蚀区作为电池的阳极不断溶解, 未腐蚀部位作为电池的阴极发生阴极析氢还原反应, 因此铸态试样的平均析氢速率较大, 引起的电流损失也越大。 均匀化处理有效地抑制偏析, 使合金溶解过程中表面能构成腐蚀微电池的数目减少, 因此析氢较慢, 阳极电流效率较高。
2.4 热处理对阳极溶解形态的影响
图5所示为4种试样宏观腐蚀形貌。 由图5可看出, 铸态试样(图5(a))溶解均匀, 产物发白, 表面粗糙, 金属颗粒疏松, 并有较深的蚀坑; 水淬试样(图5(b))溶解均匀, 表面细密, 无产物粘附; 空冷(图5(c))和炉冷(图5(d))试样表面形貌相似, 溶解均匀, 产物灰黑色, 表面粗糙, 金属颗粒有脱落。
外加阳极电流极化时, 根据铝合金阳极的质量损失(假设以Al3+溶解)计算出理论电量QT, 总电量满足QT=QC+QH+QG, 其中QC为流过回路的实际电量, QH为析氢腐蚀引起损失的电量, QG为表面由于微观或宏观的局部腐蚀引起金属微粒脱落而损失的电量。 QG可根据该式计算得出, 结果如表1所列。 铸态试样QG损失最严重, 水淬试样的损失最小, 和电流效率也有一定的对应关系。 铸态组织中的偏析部位优先溶解, 破坏晶界, 影响晶粒间的结合力, 易引起未腐蚀金属颗粒的脱落, 部分金属微粒脱落后仍能溶解析出氢气表现为析氢自腐蚀, 但部分颗粒则不溶解引起电流效率的损失。 如合金中可能存在的第二相α-AlFeSi、 FeSiAl5及β-Al3Fe等[7, 14], 这些金属间化合物在阳极溶解过程中脱落, 且在溶液中稳定存在, 同样引起电流损失。 由此可看出, 水淬均匀化处理使晶粒间的结合力最牢靠, 晶粒脱落最少。
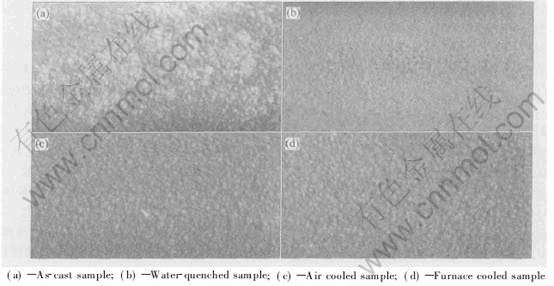
图5 合金的腐蚀形貌
Fig.5 Corrosion morphologies of Al-Zn-In alloys after galvanostatic polarization for 10d
表1 铝合金牺牲阳极的电化学性能
Table 1 Electrochemical performance of aluminium alloy sacrificial anodes
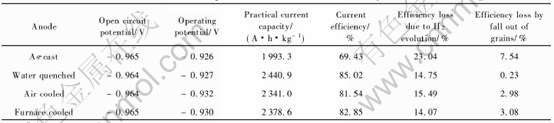
综合热处理前后的微观组织和各项电化学性能的测试结果, 510℃高温均匀化处理能有效地减轻铝合金的偏析, 改善组织的均匀程度, 增大合金元素的固溶度, 这种均质化过程对抑制阳极自腐蚀及晶粒脱落有明显的效果, 大大提高了阳极的电流效率, 但对阳极的开路电位、 工作电位和活化溶解过程的影响不大; 由晶粒脱落引起的电量损失比析氢引起的电量损失要小得多, 即析氢自腐蚀是电流效率损失的主要原因。 不同均匀化处理方式中以水淬试样的综合电化学性能最好。
3 结论
1) Al-5%Zn-0.03%In合金在510℃保温10h可以有效地抑制合金的偏析, 改善组织的均匀程度, 增大合金元素Zn、 In在α(Al)固溶体中的溶解度, 水淬、 空冷和炉冷3种均匀化处理方式对析出相的类型和尺寸有影响。
2) 热处理对铝合金阳极的开路电位、 工作电位和极化行为没有太大影响, 但对析氢自腐蚀和晶粒脱落有明显的抑制作用, 从而大大提高阳极的电流效率。 不同均匀化处理方式中以水淬处理的综合电化学性能最好。
REFERENCES
[1]GB/T 4948—2002. 铝-锌-铟系合金牺牲阳极[S].
GB/T 4948—2002. Sacrificial anode of Al-Zn-In series alloy[S].
[2]Reboul M C, Gimenez P H, Ramaeu J J. Proposed activation mechanism for Al anodes[J]. Corrosion, 1984, 40(7): 366-371.
[3]Breslin C B, Carroll W M. Activation of aluminum by activator elements[J]. Corrosion Science, 1993, 35(1): 197-203.
[4]Gurrappa I. The surface free energy and anode efficiency of aluminium alloys[J]. Corrosion Prevention and Control, 1993, 40(10): 111-114.
[5]廖海星, 齐公台, 喻克雄. 固溶处理对含RE铝牺牲阳极组织与性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2004, 25(3): 54-56.
LIAO Hai-xing, QI Gong-tai, YU Ke-xiong. Effect of water quenching on microstructure and electrochemical performance of aluminum anode containing RE[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2004, 25(3): 54-56.
[6]Bessone J B, Flamini D O, Saidman S B. Comprehensive model for the activation mechanism of Al-Zn alloys produced by indium[J]. Corrosion Science, 2005, 47(1): 95-105.
[7]齐公台, 郭稚弧, 魏伯康, 等. 固溶处理对Al-Zn-In-Sn-Mg阳极组织与电化学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理学报, 2000, 21(4): 68-72.
QI Gong-tai, GUO Zhi-hu, WEI Bo-kang, et al. Effect of water-quenching on microstructure and electrochemistry performance of Al-Zn-In-Sn-Mg anode[J]. Transactions of Metal Heat Treatment, 2000, 21(4): 68-72.
[8]Ashok S R, Venkataramani A, Parthiban G T, et al. Performance of aluminium anodes under heat treatment[J]. Corrosion Prevention and Control, 2002, 49(2): 60-63.
[9]Pautasso J P, Guyader H L, Debout V. Low voltage cathodic protection for high strength steels (part 1): Definition of a new aluminium galvanic anode material[A]. Corrosion[C]. Huston: NACE, 1998, 725.
[10]Salinas D R, Garcia S G, Bessone J B. Influence of alloying elements and microstructure on aluminum sacrificial anode performance: Case of Al-Zn[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29(9): 1063-1071.
[11]Kulkarni A G, Gurrappa I. Effect of magnesium addition on surface free energy and anode capacity of indium activated aluminium alloys[J]. British Corrosion Journal, 1993, 28(1): 67-70.
[12]许刚, 曹楚南, 林海潮, 等. 纯铝在NaCl溶液中活化溶解时电化学行为研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 1998, 10(6): 321-326.
XU Gang, CAO Chu-nan, LIN Hai-chao, et al. Electrochemical study of actived dissolution for aluminum in neutral NaCl solution[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 1998, 10(6): 321-326.
[13]毛卫民, 陈垒, 萨丽曼, 等. 晶界对低压电解电容器铝箔腐蚀结构的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(1): 1-5.
MAO Wei-min, CHEN Lei, SA Li-man, et al. Influence of grain boundaries on corrosion structure of low voltage aluminum foil[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(1): 1-5.
[14]Buchheit R G. A compilation of corrosion potentials reported for intermetallic phases in aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1995, 142(11): 3994-3996.
(编辑李艳红)
收稿日期: 2005-12-23; 修订日期: 2006-03-23
通讯作者: 朱元良; 电话: 027-87543432; 传真: 027-87543632; E-mail: zhuyl117@yahoo.com.cn