LiTFSi/KTf熔盐电解质中锂在铝电极上的电化学行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2012年第6期
论文作者:屠晓华 褚有群 马淳安
文章页码:1495 - 1500
关键词:熔盐;铝电极;循环伏安;库仑效率;成核过程
Key words:molten salt; aluminum electrode; cyclic voltammetry; coulombic efficiency; nucleation process
摘 要:采用循环伏安、计时电位和计时电流等电化学测试技术考察LiTFSI/KTf熔盐电解质中锂在铝电极上的电化学行为。结果表明:在该熔盐中,锂在铝电极上的电化学还原过程伴随着锂铝合金的成核过程,锂在铝电极上的嵌入过程平缓、稳定。恒电流充放电循环实验发现,首次循环的库仑效率很低,这主要归结于Li-Al合金对锂元素的持留能力。通过XRD和SEM表征了充放电前后铝电极的物相组成和表面形貌。计时电流实验发现,锂原子嵌入铝电极中形成a-Li-Al合金的过程受锂在铝基体内的扩散步骤控制,且该扩散系数为1.8×10-10 cm2/s。
Abstract: The electrochemical behavior of lithium incorporated in aluminum electrode in LiTFSI/KTf (lithium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide/CF3SO3K) molten salt electrolyte was studied by a variety of electrochemical techniques including cyclic voltammetry, chronopotentiometry and chronoamperometry. The reduction reaction is found involving a nucleation process on the aluminum electrode. The results of chronopotentiometry indicate that the process of lithium incorporation in aluminum is smooth and uniform. The galvanostatic cycle experiments show that the coulombic efficiency is very low in the first cycle, which is mainly due to the “retention capacity” of Li-Al alloys. This characteristic is testified by the results of XRD and SEM. The results of chronoamperometry indicate that the incorporation of lithium into aluminum for the formation of a-phase Li-Al alloy is limited by its diffusion rate, with a measured diffusion coefficient of 1.8×10-10 cm2/s.

![]()

Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 1495-1500
TU Xiao-hua1, 2, 3, CHU You-qun2, MA Chun-an2
1. College of Biological and Chemical Engineering, Jiaxing University, Jiaxing 314001, China;
2. State Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Green Chemistry-Synthesis Technology,
College of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310032, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Clean Chemical Process of Jiaxing, Jiaxing 314001, China
Received 17 June 2011; accepted 29 September 2011
Abstract: The electrochemical behavior of lithium incorporated in aluminum electrode in LiTFSI/KTf (lithium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide/CF3SO3K) molten salt electrolyte was studied by a variety of electrochemical techniques including cyclic voltammetry, chronopotentiometry and chronoamperometry. The reduction reaction is found involving a nucleation process on the aluminum electrode. The results of chronopotentiometry indicate that the process of lithium incorporation in aluminum is smooth and uniform. The galvanostatic cycle experiments show that the coulombic efficiency is very low in the first cycle, which is mainly due to the “retention capacity” of Li-Al alloys. This characteristic is testified by the results of XRD and SEM. The results of chronoamperometry indicate that the incorporation of lithium into aluminum for the formation of a-phase Li-Al alloy is limited by its diffusion rate, with a measured diffusion coefficient of 1.8×10-10 cm2/s.
Key words: molten salt; aluminum electrode; cyclic voltammetry; coulombic efficiency; nucleation process
1 Introduction
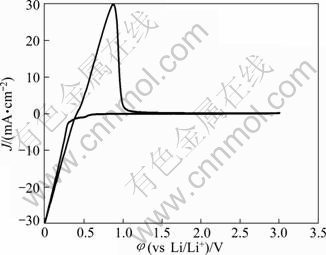
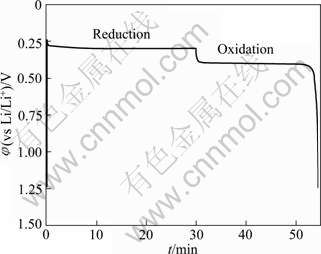
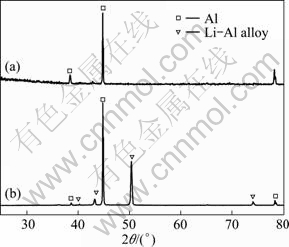
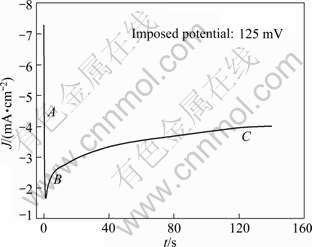
Molten salts which consist of cations and anions are normally free of any solvents as electrolytes. They differ from the classic solutions of electrolyte due to the special systems which lead to the excellent characteristics such as low vapor pressure, nonflammability, high ionic conductivity and large electrochemical window [1-3]. Molten salts could be simply classified into three groups by the operating temperature range, high temperature molten salts (t>400 ℃), intermediate temperature molten salts (100 ℃ Application of high temperature molten salts in high temperature lithium batteries (HTLBs, also called as lithium thermal batteries) is one of the representative cases. The HTLBs have long been used for military purposes [4-7]. They are reliable, rugged and robust. Recently, the application of HTLBs for geothermal and oil/gas borehole power sources is increasingly attracting the attention. The goal is to use the heat of borehole to keep the electrolytes in the molten state, thus the use of internal pyrotechnic systems of the HTLBs can be eliminated. However, this would require the electrolytes which melt and keep thermal stability at the intermediate temperatures, especially under 300 ℃ [3,5]. In this frame, the traditional alkali metal halides, belonging to the high temperature molten salts, such as LiCl-KCl [8,9] and LiF-LiCl-LiBr [5], cannot be applied in HTLBs in the absence of the internal pyrotechnic systems due to their high melting points. Thus, investigations in the fields of new molten salts electrolytes have seen tremendous increase in popularity. Introduction of the Cs and Rb cations into the alkali halide electrolytes seemed to be a beneficial attempt and was expected to lower the melting temperatures; however, the high cost of the Cs and Rb halides made them unattractive with commercialization [3]. The iodide-based electrolytes [7,10,11], which possess low melting points, could be considered a promising alternative; however, the issues of high cost, sensitivity toward oxidation by oxygen and hygroscopic character, may limit the commercial manufacturing [3,5]. Compared with the alkali halide electrolytes, the nitrate-based electrolytes appear to be promising for use as electrolytes in HTLBs because of their much lower melting points, but the protective passivation layer of Li2O would be disrupted when the operating temperature is elevated to a certain value, which would result in unacceptable hazards to the battery and the nearby equipments [12]. Thus, investigations in the fields of novel electrolytes which melt under 300 ℃ are of great importance for HTLBs as geothermal and oil/gas borehole power sources. A number of organics with low melting points are potential candidates for HTLBs and some of which have been studied for possible applications in HTLBs [3,5]. The bis (trifluoromethy- lsulfonyl) amide (TFSI) anion is well-known as one of the major anions producing molten salt electrolytes with low melting points [13-19]. MA et al [20] have previously reported a molten salt electrolyte based on the LiTFSI and CF3SO3K (KTf). The LiTFSI/KTf mixture, at the molar ratio of 1:1, has the eutectic temperature of 160 ℃ and could be thermally stable under 300 ℃. This mixture was expected to be used at intermediate temperatures. The present work is concerned with the investigation of the electrochemical behavior of lithium incorporated into aluminum in the LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte at 240 ℃ (as Li-Al alloys are commonly used as anodes in HTLBs, we estimated the ability of the LiTFSI/KTf molten salt to be used as the electrolyte with Al working electrode). A variety of electrochemical techniques are used including cyclic voltammetry, chronopotentiometry and chronoamperometry. The morphology, and crystal structure of the fresh Al and electrochemical formed Li-Al alloy are characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD), respectively. 2 Experimental The preparation of the LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte at the molar ratio of 1:1 has been described elsewhere [20]. The working electrode was an aluminum wire with a high purity (99.99%) and a diameter of 1.38 mm. In some experiments, the aluminum foil (99.999% pure) was used as the working electrode which had an area of 1 cm2 exposed to the LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte. The spectroscopically pure graphite rod was used as the counter electrode. The platinum wire with a diameter of 0.3 mm was used as the pseudo-reference electrode. The potential of this electrode was calibrated with the Li/Li+ dynamic electrode. Detailed information about the preparation of the Li/Li+ dynamic electrode can be found in Ref. [21]. All potentials given in this work are referred to this Li/Li+ dynamic potential. The cyclic voltammetry, chronopotentiometry and chronoamperometry experiments were carried out with an AutoLab PGSTAT 30 electrochemical workstation in a homemade experimental apparatus, as presented in Fig. 1. The cyclic voltammetry was conducted in the potential range of 3-0 V at a scan rate of 100 mV/s. The chronoamperometry experiments were performed at the potentials of 150, 125, 100, 75 and 50 mV, and the current densities of 1.0, 2.5 and 5.0 mA/cm2 were employed for the galvanostatic deposition and stripping of Li measurements. All electrochemical measurements were carried out under argon atmosphere. Fig. 1 Schematic representation of experimental apparatus for electrochemical measurements: 1—Thermocouple; 2—Counter electrode (spectroscopically pure graphite rod); 3—Working electrode (aluminum wire or aluminum foil); 4— Pseudo- reference electrode (calibrated with Li/Li+ dynamic electrode); 5—Pyrex cell; 6—LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte The morphologies of the fresh Al and the electrochemically formed Li-Al alloy were determined by SEM (Hitachi S-4700), using Cu Ka radiation. X-ray diffraction was carried out with a Thermo ARL SCINTAG X’TRA at room temperature, using a Cu Ka radiation source under the voltage of 45 kV and the current of 40 mA. The XRD patterns were recorded with the step size of 0.04° at the speed of 2.4 (°)/min. 3 Results and discussion 3.1 Cyclic voltammetry Figure 2 shows a typical cyclic voltammogram of the reduction/oxidation reaction of lithium on the aluminum electrode, recorded at a scan rate of 100 mV/s at 240 ℃. During the forward sweep, current starts increasing at about 0.25 V which could be ascribed to the reduction of Li+ and resulted in the formation of Li-Al alloy. As seen from Fig. 2, a remarkable feature is the appearance of a hysteresis in the cathodic current when the direction of sweep was reversed, which could be attributed to a nucleation process of crystal growth [22]. There is no second oxidation peak in the anodic current. It differs from the previously reported result that three couples of oxidation/reduction reversible peaks could be observed for the aluminum electrode in the alkali metal halide melts and each couple of reversible peaks were associated to a Li-Al alloy phase transition [23-25]. Therefore, it is considered that only one of the Li-Al phases is reversible for aluminum electrode in LiTFSI/KTf molten salt. The cyclic voltammetry is regarded as a semi-quantitative tool and can be considered a rapid charge-discharge cycle. Thus, the efficiency of lithium recoveries could be calculated to be about 85% based on the rapid charge-discharge cycle, and arrived at a constant value of about 95% after several cycles. Fig. 2 Cyclic voltammogram of aluminum electrode in LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte at 240 ℃ and 100 mV/s 3.2 Coulombic efficiency From a battery viewpoint, the technique of charge-discharge cycles at constant current densities is probably a better one to check the electrochemical performance of aluminum in LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte. A typical chronopotentiometric curve recorded at a constant current density of 1 mA/cm2 is shown in Fig. 3. A marked polarization at the beginning of the reduction curve is a characteristic feature of the formation of new Li-Al alloy phase. This polarization is inferred that the initial formation of the new Li-Al alloy on the aluminum surface is difficult and needs additional power to accomplish this process. This phenomenon also could be found in the following cycles at various current densities. The smooth reduction curve indicates that the process of lithium incorporation in aluminum substrate was stable. The potential drop in the middle of the chronopotentiometric curve is due to the polarization caused by the alternation of current direction, and the final sharp decrease of potential could be ascribed to the exhaustion of lithium in the Al electrode. Fig. 3 Typical chronopotentiometric curve recorded during galvanostatic cycle experiment at 1 mA/cm2 and 240 ℃ Previous reports [26,27] have discussed that the efficiency of the lithium recoveries from aluminum is less than 100% due to the formation of Li-Al alloys. This phenomenon is the so-called “retention capacity” of Li-Al alloys. Normally, the “retention capacity” would result in very poor lithium recoveries in the first cycle. A similar result was obtained in our study, as presented in Fig. 4. The efficiency of the lithium recoveries can be determined from the ratio of time for oxidation to time for reduction by constant current measurements. The aluminum electrode was subjected to several cycles at the current densities of 1.0, 2.5 and 5.0 mA/cm2. At constant current densities, the coulombic efficiency could be calculated from the ratio of the time for stripping of lithium to the time of deposition of lithium. At the current density of 1 mA/cm2, the coulombic efficiency is about 81% in the first cycle, and reaches an almost constant value in the third cycle. It is noteworthy that the coulombic efficiency decreases when the current density increases, and the coulombic efficiency tends to be the constant value after several cycles at the current densities of 2.5 and 5.0 mA/cm2. It is noticeable that the processes of lithium incorporation in aluminum are also free from dendrites at the current densities of 1.0, 2.5 and 5.0 mA/cm2 during charge-discharge cycles. Fig. 4 Coulombic efficiency of anodic stripping of Li on Al electrode at 240 ℃ and various current densities 3.3 XRD and SEM micrographs To prove the existence of Li-Al alloy after the charge-discharge cycles, an aluminum electrode was transferred from the cell for XRD and SEM measurements. Figure 5 shows XRD patterns of unused Al and electrochemically formed Li-Al specimens. Three peaks with a value of 2θ around 38.4°, 44.8° and 78.2° can be assigned to planes (111), (200) and (311) of Al, respectively. There are additional peaks at 40.3°, 43.2°, 50.4° and 74.1° which correspond to the Li-Al composition. SEM images of Al and electrochemically formed Li-Al alloy are shown in Fig. 6. The surface of the pure Al foil is smooth and cracks cannot be found, as presented in Fig. 6(a). The charge-discharge cycles in the LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte led to a significant change in the surface image from the original one. It is shown that the cracks are distributed over the surface of the electrochemically formed Li-Al alloy in Fig. 6(b). The cracks may be caused by the gradual increase of the electrode volume during the formation of Li-Al alloy. Fig. 5 XRD patterns of Al (a) and electrochemically formed Li-Al alloy (b) at 1 mA/cm2 and 240 ℃ Fig. 6 SEM images of Al (a) and electrochemically formed Li-Al alloy (b) at 1 mA/cm2 and 240 ℃ 3.4 Mechanism of lithium incorporation into Al electrode More insight into the mechanism of Li incorporation into Al matrix can be attained from an analysis of chronoamperometry measurements which have been proved to be a convenient technique for the investigation of lithium reduction on the aluminum substrate. A typical chronoamperogram observed at a fresh Al electrode in the LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte is shown in Fig. 7. Two distinct regions (A and B) in the chronoamperogram could be observed. The initial part (A) of the reduction curve is characterized by a rapid decrease in the current to a minimum value. This could be ascribed to the double-layer charging, and is more probably due to the insertion of lithium into aluminum matrix for the formation of a-phase Li-Al alloy [28,29]. Fig. 7 Chronoamperogram on aluminum electrode in LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte at 240 ℃ The curves of current density (J) vs negative square root of time (t-1/2) for the incorporation of Li into Al are presented in Fig. 8(a). The linearity of the curves indicates that this process is diffusion control. The diffusion coefficient of lithium penetration in aluminum for the formation of a-phase Li-Al alloy can be calculated from the Cottrell equation: where F denotes the Faraday constant; ct is the saturated concentration of lithium in the a-phase Li-Al alloy; c0 is the initial lithium concentration in aluminum; D is the diffusion coefficient. The charge transfer number n is equal to 1 and c0 is assumed to be zero. Then Eq. (1) can be simplified to Thus the diffusion coefficient D is 1.8×10-10 cm2/s which is calculated from the curve of the imposed potential of 125 mV at 240 ℃. This experimental value of D is lower than the value (D=4.0×10-10 cm2/s) obtained at 450 ℃ in the LiCl-KCl melt [30], but higher than that (D=2.4×10-11 cm2/s) obtained at 20 ℃ in 1 mol/L LiClO4/PC solution [28]. This is in good agreement with the trend that the diffusion coefficient D gradually increases with the increase of temperature. The following part (B) of the cathodic chronoamperogram shows a slower increase in current, which should correspond to the formation and growth of the nuclei on the surface. The curves of current density (J) vs the square root of time (t1/2) are depicted in Fig. 8(b). It is shown that the curves are linear at the various potentials, which may provide the evidence for the instantaneous three-dimensional nucleation [31]. As we know, the instantaneous three-dimensional nucleation theory has been developed for the electrodeposition in which the substrate electrode itself does not change. Thus, the process of lithium incorporation into aluminum remains dubious and needs further investigations. Fig. 8 Portions of cathodic chronoamperograms on aluminum electrode in LiTFSI/KTf molten salt electrolyte at 240 ℃: (a) Initial current decay region; (b) Current increase region 4 Conclusions 1) The initial steps of lithium incorporation into aluminum appear to involve a nucleation process. The incorporation of lithium into aluminum is uniform and smooth. 2) The coulombic efficiency is very low in the first cycle and arrives the constant values after several cycles at the current densities of 1.0, 2.5 and 5.0 mA/cm2. 3) The incorporation of lithium into aluminum for the formation of a-phase Li-Al alloy is limited by its diffusion coefficient. The diffusion coefficient of lithium incorporation into aluminum was measured to be 1.8×10-10 cm2/s. References [1] Ito Y, Nohira T. Non-conventional electrolytes for electrochemical applications [J]. Electrochim Acta, 2000, 45: 2611-2622. [2] Galiński M, Lewandowski A, St?pniak I. Ionic liquids as electrolytes [J]. Electrochim Acta, 2006, 51: 5567-5580. [3] Masset P, Guidotti R A. Thermal activated (“thermal”) batteries technology. Part II: Molten salt electrolytes [J]. J Power Sources, 2007, 164: 397-414. [4] Guidotti R A, Masset P. Thermal activated (“thermal”) batteries technology. Part I: An overview [J]. J Power Sources, 2006, 161: 1443-1449. [5] Guidotti R A, Reinhardt F W, Odined J. Overview of high-temperature batteries for geothermal and oil/gas borehole power sources [J]. J Power Sources, 2004, 136: 257-262. [6] Butler P, Wagner C, Guidotti R, Francis I. Long-life, multi-tap thermal battery development [J]. J Power Sources, 2004, 136: 240-245. [7] Masset P, Schoeffert S, Poinso J Y, Poignet J C. LiF-LiCl-LiI vs. LiF-LiBr-KBr as molten salt electrolyte in thermal batteries [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2005, 152(2): A405-A410. [8] Kaun T D, Nelson P A, Reday L, Vissers D R, Henriksen G L. High temperature lithium/sulfide batteries [J]. Electrochim Acta, 1993, 38: 1269-1287. [9] Singh P, Guidotti R A, Reisner D. AC impedance measurements of molten salt thermal batteries [J]. J Power Sources, 2004, 138: 323-326. [10] Masset P, Henry A, Poinso J Y, Poignet J C. Ionic conductivity measurements of molten iodide-based electrolytes [J]. J Power Sources, 2006 160: 752-757. [11] Masset P. A promising alternative for thermal batteries [J]. J Power Sources, 2006, 160: 688-697. [12] Miles M H, McManis G E. Effect of temperature and electrolyte composition on the lithium-boron alloy anode in nitrate melts: Passivating films on solid and liquid lithium [J]. Electrochim Acta, 1985, 30: 889-897. [13] Sun J, Forsyth M, MacFarlane D R. Room-temperature molten salts based on the quaternary ammonium ion [J]. J Phys Chem B, 1998, 102: 8858-8864. [14] MacFarlane D R, Meakin P, Sun J, Amini N, Forsyth M. Pyrrolidinium imides: A new family of molten salts and conductive plastic crystal process [J]. J Phys Chem B, 1999, 103: 4164-4170. [15] Hu Y S, Li H, Huang X J, Chen L Q. Novel room temperature molten salt electrolyte based on LiTFSI and acetamide for lithium batteries [J]. Electrochem Commun, 2004, 6: 28-32. [16] Fernicola A, Croce F, Scrosat B, Watanabe T, Ohno H. LiTFSI-BEPyTFSI as an improved ionic liquid electrolyte for rechargeable lithium batteries [J]. J Power Sources, 2007, 174: 342-348. [17] Hagiwara R, Tamaki K, Kubota K, Goto T, Nohira T. Thermal properties of mixes alkali bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amides [J]. J Chem Eng Data, 2008, 53: 355-358. [18] Kubota K, Nohira T, Goto T, Hagiwara R. Ternary phase diagrams of alkali bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amides [J]. J Chem Eng Data, 2008, 53: 2144-2147. [19] Watara A, Kubota K, Yamagata M, Goto T, Nohira T, Hagiwara R, Ui K, Kumagai N. A rechargeable lithium metal battery operating at intermediate temperatures using molten alkali bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide mixture as an electrolyte [J]. J Power Sources, 2008, 183:724-729. [20] Ma C A, Tu X H, Chu Y Q, Zhao F M, Zhu Y H. Thermal and electrochemical performance of binary molten salt electrolyte based on LiTFSI and CF3SO3K [J]. Electrochem Solid-State Lett, 2009, 12(4): A88-A90. [21] Kasajima T, Nishikiori T, Nohira T, Ito Y. Electrochemical behavior of hydride ion in a LiBr-KBr-CsBr eutectic melt [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2003, 150: E403-E408. [22] CARPIO R A, KING L A. Deposition and dissolution of lithium-aluminum alloy and aluminum from chloride-satuated LiCl-AlCl3 and NaCl-AlCl3 melts [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1981, 128: 1510-1517. [23] Fung Y S, Inman D, White S H. Studies of the kinetics of the lithium/aluminium electrode in molten LiCl-KCl by linear sweep voltammetry [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1982, 12: 669-680. [24] Park S H, Winnick J, Kohl P A. Investigation of the lithium couple on Pt, Al, and Hg electrodes in lithium imide-ethyl methyl sulfone [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2002, 149: A1196-A1200. [25] Kasajima T, Nishikiori T, Nohira T, Ito Y. Electrochemical window and the characteristics of (α+β) Al-Li alloy reference electrode for a LiBr-KBr-CsBr eutectic melt [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2004, 151: E335-E339. [26] Amezawa K, Ito Y. The single-electrode peltier heats of Li-Al alloy electrodes in LiCl-KCl eutectic system [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1994, 141: 3096-3103. [27] Besenhard J O. Cycling behaviour and corrosion of Li-Al electrodes in organic electrolytes [J]. J Electroanal Chem, 1978, 94: 77-81. [28] Geronov Y, Zlatilva P, Staikov G. The secondary lithium-aluminum electrode at room temperature. II: Kinetics of the electrochemical formation of the lithium-aluminium alloy [J]. J Power Sources, 1984, 12: 155-165. [29] Baranski A S, Fawcett W R. Formation of lithium-aluminum alloys at an aluminum electrode in propylene carbonate [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1982, 129: 901-907. [30] Melendres C A. Kinetics of electrochemical incorporation of lithium into aluminum [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1977, 124: 650-655. [31] Rolland P, Mamantov G. Electrochemical reduction of Al2Cl7- ions in chloroaluminate melts [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1976, 123: 1299-1303. 屠晓华1,2,3,褚有群2,马淳安2 1. 嘉兴学院 生物与化学工程学院,嘉兴 314001; 2. 浙江工业大学 应用化学系,绿色化学合成技术国家重点实验室培育基地,杭州 310032; 3. 嘉兴市化工清洁工艺重点实验室,嘉兴 314001 摘 要:采用循环伏安、计时电位和计时电流等电化学测试技术考察LiTFSI/KTf熔盐电解质中锂在铝电极上的电化学行为。结果表明:在该熔盐中,锂在铝电极上的电化学还原过程伴随着锂铝合金的成核过程,锂在铝电极上的嵌入过程平缓、稳定。恒电流充放电循环实验发现,首次循环的库仑效率很低,这主要归结于Li-Al合金对锂元素的持留能力。通过XRD和SEM表征了充放电前后铝电极的物相组成和表面形貌。计时电流实验发现,锂原子嵌入铝电极中形成a-Li-Al合金的过程受锂在铝基体内的扩散步骤控制,且该扩散系数为1.8×10-10 cm2/s。 关键词:熔盐;铝电极;循环伏安;库仑效率;成核过程 (Edited by YANG Hua) Foundation item: Project (70510011) supported by Scientific Research Starting Foundation of Jiaxing University, China; Project (84209001B3) supported by Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Clean Chemical Process of Jiaxing, China Corresponding author: MA Chun-an; Tel/Fax: +86-571-88320830; E-mail: science@zjut.edu.cn DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61346-0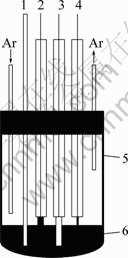


![]() (1)
(1)![]() (2)
(2)
LiTFSi/KTf熔盐电解质中锂在铝电极上的电化学行为

