文章编号:1004-0609(2011)06-1292-07
纵向强磁场对Al-0.85%Cu合金定向凝固
界面稳定性和形态的影响
李 茂,任维丽,任忠鸣,李 喜,钟云波,邓 康
(上海大学 材料科学与工程学院,上海 200072)
摘 要:研究纵向稳恒强磁场在定向凝固Al-0.85%Cu(质量分数)合金平面晶-胞晶转变过程中,对界面失稳程度及胞晶形貌的影响。结果表明:随着磁场强度的增加,界面失稳程度先变小后变大,最后又变小;磁场强度为1 T时,界面失稳程度最大,胞晶间距先减小后增大;磁场强度为4 T时,胞晶间距达到最小值;同时,磁场也使得胞晶形貌变得不规则。采用磁阻尼效应和热电磁对流(TEMC)相互竞争的机制来解释相关现象。
关键词:Al-0.85%Cu;定向凝固;强磁场;界面稳定性;磁阻尼;热电磁对流
中图分类号:TG111.4 文献标志码:A
Effect of high longitudinal magnetic field on interface stability and morphology of directionally solidified Al-0.85%Cu alloy
LI Mao, REN Wei-li, REN Zhong-ming, LI Xi, ZHONG Yun-bo, DENG Kang
(School of Material Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China)
Abstract: The effect of steady high longitudinal magnetic field on the interface stability and cellular morphology of Al-0.85%Cu (mass fraction) alloys was studied. The results show that the degree of interface stability changes from high to low and then to high again, at last from high to low with increasing the magnetic field intensity. When the strength of the magnetic field is 1 T, the instable interface is the most obvious. With increasing the strength of the magnetic field, the cellular spacing decreases firstly, reaches its least value at 4 T magnetic field, and then increases. At the same time, the cellular morphology changes to irregular. The experimental phenomena were analyzed according to competition of convection damping effect and thermo-electromagnetic convection effect with the magnetic field.
Key words: Al-Cu alloy; directional solidification; high magnetic field; interface stability; magneto-hydrodynamic effect; thermoelectro-magnetic convection
磁场能够影响晶体的生长过程、约束晶体的排列方向、有效地抑制导电流体中的热溶质对流、耦合热电效应形成热电磁对流[1],进而对凝固组织和性能产生影响。近年来,随着超低温技术和超导技术的进 步,获得10 T左右的强磁场已不难实现,这为研究强磁场下的凝固过程控制提供了可能。日本大阪大学Yasuda教授及东北大学的王恩刚研究了强静磁场对偏晶合金Cu-Pb[2-3]和包晶合金 Pb-Bi、Sn-Cd组织[2]的影响规律。本文作者所在的研究组对强静磁场对典型凝固组织的影响进行研究[4-10],发现在强静磁场下凝固固溶体合金的枝晶组织形态以及共晶和包晶组织的形貌均发生了变化。在固溶体Al-4.5%Cu(质量分数)合金的定向凝固生长过程中,磁场使得该合金由胞晶到枝晶转变所对应的生长速率减小;共晶合金Pb-Sn 和 Al-Al2Cu在强静磁场下凝固时,其宏观组织出现偏析区域和共晶层片间距减小。COLLIE等[11]用线性稳定性理论研究了二元合金定向凝固中磁场对界面不稳定性的影响,结果显示垂直磁场的施加增加了对流存在时界面不稳定所需的临界浓度。
组织形态及成分偏析的变化与固液界面的稳定性有密切的关系。任忠鸣等[12]初步研究了强磁场对定向凝固Al-Cu合金界面稳定性的影响。在此基础上,本文作者进一步研究磁场强度对固液界面失稳程度以及胞晶形态的影响。
1 实验
实验装置如文献[8]所示,主要由超导磁体、水冷套、加热炉、LMC冷却池及伺服抽拉系统所组成。超导强磁体可以产生纵向的均匀静磁场,磁感应强度在0~14 T连续可调。定向凝固为Bridgman-Stockbarger炉,使用镍铬电阻丝加热,用WZK-??型智能温控仪表和K型镍铬-镍硅热电偶控制温度,精度为±1 ℃。设定炉膛中心的温度为900 ℃,温度梯度的测量采用测量固/液界面前沿温度曲线的方法,再通过公式GL=ΔT/ΔS,计算温度梯度。其中GL为固液界面前沿液相中的温度梯度;ΔT为温度的变化;ΔS为距离的变化。本实验所测定的温度梯度为46.1 ℃/cm。冷却介质为液态Ga-In-Sn合金。实验材料是采用纯度均为99.99%的Al和Cu,在感应炉中按比例熔融获得Al-0.85%Cu合金,并用直径为3.5 mm的石英管吸铸,经打磨后将合金棒装在长为200 mm、内径为3.5 mm的刚玉管中以备实验。实验时按预定拉速进行定向凝固,并在达到稳定段后迅速下拉使液体部分进入冷却池Ga-In-Sn合金中淬火,以保留固液界面生长状态。在所得定向凝固试样的固液界面上下处截取金相试样,分别沿平行于和垂直于生长方向剖开,经镶嵌、预磨、抛光后腐蚀,并用金相显微镜观察和分析组织。
2 实验结果
2.1 强磁场对固液界面稳定性的影响
图1所示为施加不同磁场下试样在抽拉速度为0.5 μm/s和1 μm/s时的纵向显微组织。由图1可以看出,有无磁场作用下,0.5 μm/s抽拉速度下对应的显微组织界面均保持稳定。当抽拉速度升高到1 μm/s时,凝固组织都从平面晶转变到胞晶,1 μm/s时,平界面都已失稳。但是,随着磁场强度的增加,界面失稳程度表现出先减弱后增强,最后又减弱的演变过程。没有施加磁场时,固液界面处仅有零星的破缺;施加0.4 T的磁场时,固液界面处几乎没有破缺;1 T磁场时,界面上形成了不规则的胞晶,且胞晶发生分枝;4 T磁场时,失稳程度进一步降低,界面上出现比较密集的破缺;10 T时,界面处的这种破缺程度进一步降低。图2所示为与图1相对应的抽拉速度为1 μm/s时,界面以下稳恒区处的横向显微组织。 进一步验证了界面失稳程度随磁场强度的变化规律。
2.2 强磁场对胞晶形貌及其间距的影响
图3所示为不同磁场强度下试样在2 μm/s拉速时固液界面的纵向显微组织。图3(a)所示为未施加磁场的固液界面形貌,其为典型的规则胞状晶生长界面,胞晶成较笔直的无分枝的棒状。当施加磁场后,胞状形状变得不规则。1 T磁场时,胞晶沿生长方向的直线度发生了明显的变化,胞晶端部出现了明显的分叉形态,且组织变得不连续,胞晶尖端并非都在界面上,呈现竞争生长的趋势;4 T磁场时,胞晶分枝程度进一步变大;6 T以上磁场时,胞晶组织分枝的程度又减小。这说明磁场有使得胞晶组织变得不规则的作用。
图4所示为与图3相对应固液界面处的横向显微组织。可以看出,随着磁场强度的增加,胞晶组织由规则的多边形状变得混乱。施加磁场之后,胞状晶间距变小,在4 T磁场时,达到极小值,胞状晶间距与磁场强度的对应关系如图5所示。
3 分析与讨论
目前普遍认同的强静磁场对金属合金定向凝固过程的影响机理主要集中在两个方面:一是磁阻尼(Magneto-hydrodynamic damping,MHD)效应;二是热电磁对流(Thermoelectro-magnetic convection,TEMC)效应。磁阻尼是由于导电流体在磁场中运动产生感应电流,感应电流与外加磁场相互作用产生一个与运动方向相反的洛伦兹力(σeυ×B)×B,抑制了流动。它能够阻碍与磁场方向不平行的流动,从而影响边界层的溶质传输,如图6(a)所示。热电磁对流是由于熔体和晶体的热电因子不同,且二者之间存在温度梯度,从而产生了热电流。热电流与磁场相互作用产生一个洛仑兹力JTE×B,这个力将驱动凝固界面附近的熔体在一定区域内流动,从而产生了热电磁对流,如图6(b)所示。它能够使界面处的流动加剧,促进溶质的传输。
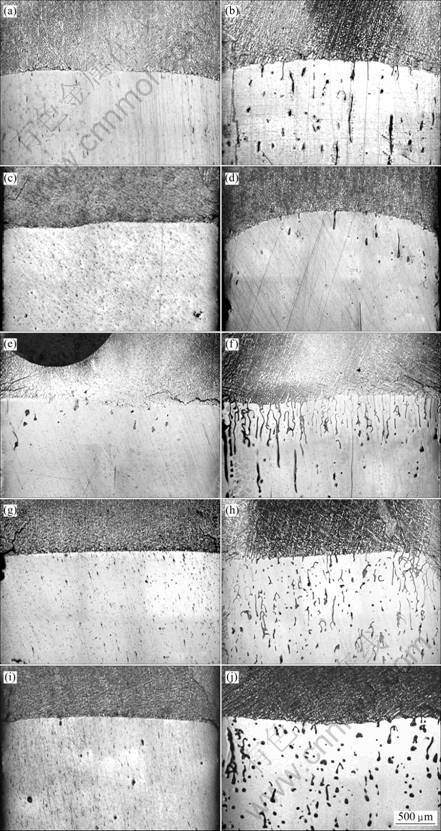
图1 不同磁场强度和抽拉速率下Al-0.85%Cu固-液界面处的纵向显微组织
Fig.1 Longitudinal microstructures near solid-liquid interface of directionally solidification Al-0.85%Cu alloy at different magnetic fields and growing rates: (a) 0 T, 0.5 μm/s; (b) 0 T, 1 μm/s; (c) 0.4 T, 0.5 μm/s; (d) 0.4 T, 1 μm/s; (e) 1 T, 0.5 μm/s; (f) 1 T, 1 μm/s; (g) 4 T, 0.5 μm/s; (h) 4 T, 1 μm/s; (i) 10 T, 0.5 μm/s; (j) 10 T, 1 μm/s
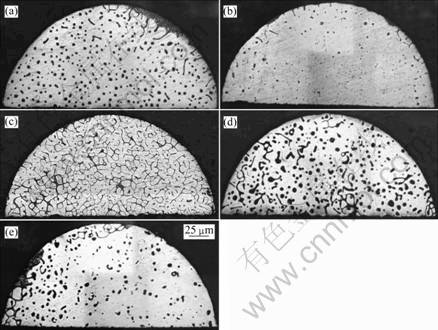
图2 不同磁场强度下Al-0.85%Cu在 1 μm/s时固-液界面处的横向显微组织
Fig.2 Transverse microstructures in solid- liquid interface of directionally solidification Al-0.85%Cu alloy at growing rate of 1 μm/s with different magnetic fields: (a) 0 T; (b) 0.4 T; (c) 1 T; (d) 4 T; (e) 10 T
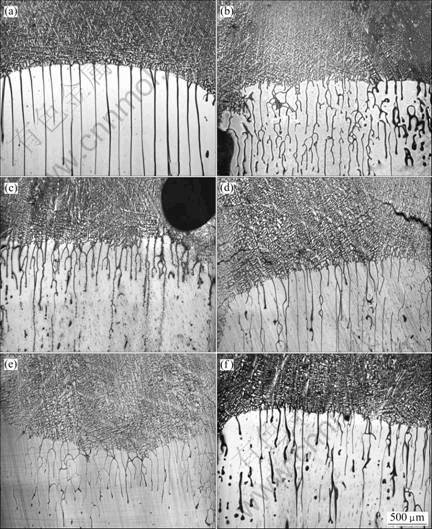
图3 不同磁场下Al-0.85%Cu在2 μm/s时固-液界面处的纵向显微组织
Fig.3 Longitudinal microstructures near solid-liquid interface of directional solidification Al-0.85%Cu alloy at growing rate of 2 μm/s with various magnetic fields: (a) 0 T; (b) 1 T; (c) 4 T; (d) 6 T; (e) 8 T; (f) 10 T
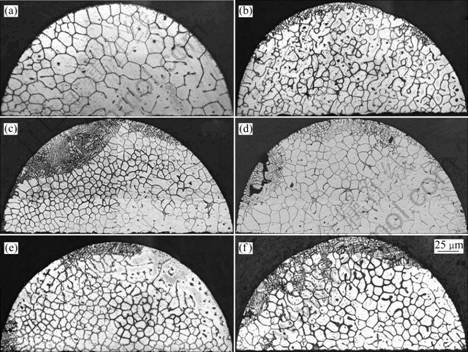
图4 不同磁场下Al-0.85%Cu在2 μm/s时固液界面处的横向显微组织
Fig.4 Transverse microstructures in solid-liquid interface of directionally solidification Al-0.85%Cu alloy at growing rate of 2 μm/s with various magnetic fields: (a) 0 T; (b) 1 T; (c) 4 T; (d) 6 T; (e) 8 T; (f) 10 T
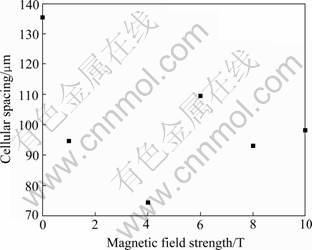
图5 2 μm/s拉速下胞状晶间距与磁场强度的关系
Fig.5 Relationship between cellular spacing and magnetic field strength at growing rate of 2 μm/s
由上述可知,热电磁力(JTE×B)与B成正比,磁阻尼力[(σeυ×B)×B]与B 2成正比,因此,热电磁力和磁阻尼力表现出竞争作用关系,二者之间存在一个临界的磁场强度,当磁场强度高于临界值时,则产生显著的磁阻尼现象。有研究表明,当表征磁阻尼作用大小
的参数哈特曼数(Hartmann,Ha= ,其中,σe
,其中,σe
为电导率; 为粘度;L0为流动的特征尺寸)为10[13]时,对应的磁感应强度即为磁场的临界值。
为粘度;L0为流动的特征尺寸)为10[13]时,对应的磁感应强度即为磁场的临界值。

图6 磁阻尼效应和胞晶间的热电磁对流效应
Fig.6 Magneto-hydrodynamic damping(a) and thermoelectro- magnetic convection in cellular area(b)
3.1 磁场对界面失稳程度的影响
由成分过冷判据可获得Al-0.85%Cu在无磁场条件下平界面失稳的临界G/Vcri值:
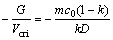 (1)
(1)
式中:m为液相线斜率;k为溶质分配系数;D为液相中Cu的扩散系数;G为界面处的平均温度梯度;C0为合金的初始浓度。
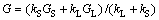 (2)
(2)
由界面处热量守恒得
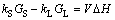 (3)
(3)
式中:?H为单位体积熔化热;V为生长速度。由于低速下V?H远远小于kLGL(kSGS),所以kSGS≈kLGL,由于kS≈2kL,G=(2/3)GL,物性参数如表1所列,代入其值,得到平界面稳定的临界值为GL/Vcri=6.788,由于GL=46.1 ℃/cm,所以Vcri=0.68 μm/s。实验结果表明,没有施加磁场时,界面失稳发生在0.5~1.0 μm/s之间,两者基本吻合。
表1 Al-Cu的物性参数[14]
Table 1 Physical parameters of Al-Cu alloy
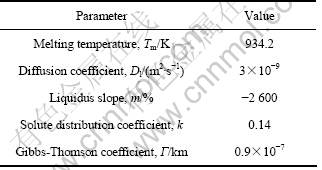
由成分过冷判别式可知,界面失稳程度与合金的m、k、C0有关,LI[12]通过考察磁场对平衡分配系数k、液相线斜率m的影响发现,10 T的强磁场对k和m的影响不大,因此,界面失稳程度将与界面前沿液体的溶质浓度有很大的关系。蔡丽霞等[15]和TRIVIDE等[16]的研究都发现,对流能降低界面前沿溶质的浓度,减小成分过冷度,从而提高了平界面的稳定性。施加0.4 T的磁场,在坩锅尺寸范围内产生了强烈的热电磁对流,且热电磁对流起主导作用,使得界面失稳程度减弱。当磁场强度增加到1 T,磁阻尼效应明显[17],坩埚尺寸内的热电磁对流被抑制,界面处的成分过冷度增加,界面失稳程度又变大。 进一步增加磁场强度,可能增加了界面能,使得固液界面又趋于稳定。目前,并没有这方面的理论与实验研究,有待于进一步验证。
3.2 磁场对胞晶形貌及其间距的影响
胞状凝固中胞晶间距可以自行调整以减小成分过冷到一个最低值。如果条件发生改变使得胞状晶端部附近的成分过冷度超过保持稳定的极小值,将要形成扰动,且这种扰动还要发展,即分枝越来越多,以期减小该处的间距。由Hartmann数可知,Hartmann数与流动的特征尺寸L0成正比,而坩埚尺寸比胞晶尺寸大得多,同样达到使得TEMC被抑制的Hartmann数10时,对于坩埚尺度所需磁场,要小于胞晶尺度的。因此,当磁场强度为1~4 T时,虽然坩埚尺度范围内的TEMC被抑制,但胞晶尺寸范围内的TEMC仍然存在,它与磁阻尼效应相互竞争,改变了胞晶尖端溶质的分布及局部的成分过冷度,胞晶尖端为了满足成分过冷最小的需求,使得胞晶发生分枝,胞晶间距减小,胞晶形态变得不规则。当磁场强度大于4 T时,胞晶尺寸范围内的TEMC较磁阻尼效应更加微弱,磁阻尼占主导作用,胞晶间距又增加,如图7所示。

图7 胞晶形貌及间距随磁场强度增加的变化趋势
Fig.7 Change trend of cellular morphology and spacing as magnetic field strength increasing
4 结论
1) 随着磁场强度的增加,固-液界面失稳程度表现出先减弱后增强,最后又减弱的趋势。
2) 施加磁场后,多边形的规则胞晶形貌变得不规则。随磁场强度的增加,胞晶间距先减小后增大,在4 T时,胞晶间距达到最小值。
REFERENCES
[1] KHINE Y Y, WALKER J S. Thermoelectric magnetohydrodynamic effects during Bridgman semiconductor crystal growth with a uniform axial magnetic field[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1998, 183: 150-158.
[2] YASUDA H, OHNAKA I, KISHIO K. Effect of magnetic field on solidification in Cu-Pb monotectic alloy[J]. ISIJ international, 2003, 43(6): 942-949.
[3] 张 林, 王恩刚, 左小伟, 赫冀成. 强磁场对Cu-80%Pb过偏晶合金凝固组织的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2008, 44(2): 165-171.
ZHANG Lin, WANG En-gang, ZUO Xiao-wei, HE Ji-cheng. Effect of high magnetic field on solidified structure of Cu-80%Pb hypermonotectic alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2008, 44(2): 165-171.
[4] REN Zhong-ming, LI Xi, SUN Yan-hui, DENG Kang, ZHONG Yun-bo. Influence of high magnetic field on peritectic transformation during solidification of Bi-Mn alloy[J]. Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 2006, 30: 277-285.
[5] ZHU Wei-wei, REN Zhong-ming, REN Wei-li, DENG Kang, ZHONG Yun-bo. Effect of high magnetic field on the unidirectionally solidification Al-Al2Cu eutectic crystal orientations and the induced microstructures[J]. Materials Science and Engneering A, 2006, 441: 181-186.
[6] LI Xi, REN Zhong-ming, FAUTRELLE Y. Effect of a vertical magnetic field on the dendrite morphology during Bridgman crystal growth of Al-4.5wt%Cu[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2006, 290: 571-575.
[7] 李 喜, 任忠鸣, 孙延辉, 王 俊, 余建波, 任维丽. 纵向强磁场对定向凝固Al-4.5%Cu合金显微组织的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2006, 42(2): 147-152.
LI Xi, REN Zhong-ming, SUN Yan-hui, WANG Jun, YU Jian-bo, REN Wei-li. Effect of high longitudinal magnetic field on the microstructure of directionally solidified Al-4.5%Cu alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 42(2): 147-152.
[8] 孙延辉, 任忠鸣, 李 喜, 王洪亮, 王 俊, 邓 康. 强磁场对Al-4.5%Cu合金枝晶生长行为影响的初步研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 2005, 15(9): 1148-1152.
SUN Yan-hui, REN Zhong-ming, LI Xi, WANG Hong-liang, WANG Jun, DENG Kang. Effect of high magnetic field on the dendrite growth behavior during Al-4.5%Cu directional solidification[J]. Progress in Nature Science, 2005, 15(9): 1148-1152.
[9] 马娟平, 任忠鸣, 邓 康, 李 喜, 吴 琼. 强磁场对定向凝固Pb-Sn共晶生长影响的初步研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 2004, 14(7): 110-114.
MA Juan-ping, REN Zhong-ming, DENG Kang, LI Xi, WU Qiong. Effect of high magnetic field on the eutectic growth during Pb-Sn directional solidification[J]. Progress in Nature Science, 2004, 14(7): 110-114.
[10] 余建波, 任忠鸣, 邓 康, 任维丽, 李 喜, 王 俊. 强磁场与交流电叠加对纯铝凝固组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(1): 92-97.
YU Jian-bo, REN Zhong-ming, DENG Kang, REN Wei-li, LI Xi, WANG Jun. Effects of simultaneously imposing high magnetic field and alternative current on solidification structures of pure aluminum[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(1): 92-97.
[11] CORIELL S R, CORDES M R, BOETTINGER W J. Convective and interfacial instabilities during unidirectional solidification of a binary alloy[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1980, 49: 13-28.
[12] LI Xi, FAUTRELLE Y, REN Zhong-ming. Effect of a high magnetic field on the morphological instability and irregularity of the interface of a binary alloy during directional solidification[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57: 1689-1701.
[13] LEHMANN P, MOREAU R, CAMEL D, BOLCATO R. Modification of interdendritic convection in directional solidification by a uniform magnetic field[J]. Acta Mater, 1998, 46(11): 4067-4079.
[14] FORNARO O, PALACIO H A. Planar to cellular transition during directional solidification of Al-0.5wt.% Cu[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1997, 36(4): 439-445.
[15] 蔡丽霞, 金蔚青, 潘志雷, 刘照华, 梁歆桉. 对流效应和溶质浓度对KNbO3晶体界面形貌稳定性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2001, 16(4): 609-614.
CAI Li-xia, JIN Wei-qing, PAN Zhi-lei, LIU Zhao-hua, LIANG Xin-an. Effect of convection and solute concentration on the morphological instability of KNbO3 crystal[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(4): 609-614.
[16] TRIVEDI R, MIYAHARA H, MAZUMDER P, SIMSEK E, TEWARI S N. Directional solidification microstructures in diffusive and convective regimes[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2001, 222: 365-379.
[17] LI Xi, Annie Gagnoud, REN Zhong-ming, FAUTRELLE Y. Rene moreau investigation of thermoelectric magnetic convection and its effect on solidification structure during directional solidification under a low axial magnetic field[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(7): 2180-2197.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学青年基金资助项目(50701031);长江学者和创新团队发展计划资助项目(IRT0739);上海市科委项目(071005103,08dj1400404,08DZ1130100)
收稿日期:2009-07-22;修订日期:2011-05-15
通信作者:任忠鸣,教授,博士;电话:021-56331102;E-mail: zmren@mail.shu.edu.cn