文章编号:1004-0609(2009)12-2083-07
电磁铸造对Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金微观组织及
晶内固溶度的影响
王少华1,杨守杰2,房灿峰1,王剑钊1,戴圣龙2,张兴国1
(1. 大连理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,大连 116024;
2. 北京航空材料研究院,北京 100095)
摘 要:分别采用电磁铸造和普通连铸技术制备Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金,研究电磁场对合金显微组织、合金元素晶内固溶度的影响。结果表明:采用电磁铸造技术制备的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金具有良好的表面质量和内部组织;电磁场显著提高合金元素在晶内的固溶度,减小了微观偏析程度。相对于普通连铸,电磁铸造法制备的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金的晶粒平均尺寸从68 mm减小到53 mm,Zn、Mg和Cu元素的晶内相对溶质固溶度分别由56%、62%和25%提高到79%、74%和44%。
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金;电磁铸造;普通连续铸造;显微组织;相对溶质固溶度
中图分类号:TG1460.2 文献标识码: A
Effects of electromagnetic casting on as-cast microstructures and
solid solubility inside crystals of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy
WANG Shao-hua1, YANG Shou-jie2, FANG Can-feng1, WANG Jian-zhao1, DAI Sheng-long2, ZHANG Xing-guo1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China;
2. Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Beijing 100095, China)
Abstract: Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr aluminum alloys were prepared by electromagnetic casting (EMC) and direct chill casting (DCC), respectively. The effects of electromagnetic field on as-cast microstructure and alloy elements solid solubility inside crystals of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr aluminum alloy were investigated. The results show that the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy billets prepared by EMC have better surface qualities, microstructures and higher solid solubility inside crystals of alloy elements. The degree of microsegregation in the EMC billet decreases. Compared with the DCC specimens, the average grain size of the EMC specimens decreases from 68 μm to 53 μm, moreover, the relative intracrytalline solubilities of elements Zn, Mg and Cu increase from 56%, 62% and 25% to 79%, 74% and 44%, respectively.
Key words: Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy; electromagnetic casting; direct chill casting; microstructure; relative intracrytalline solubility
Al-Zn-Mg-Cu系铝合金属于超高强变形铝合金,具有高的比强度和比刚度、较好的耐腐蚀性和热加工性能等优点,是运载火箭、宇宙飞船和空间站等航天器的主体结构材料,也是导弹、战斗机等武器系统的关键结构材料之一,因此广泛应用于航空航天及军事工业[1-6]。随着超高强变形铝合金研究的不断深入以及对性能要求的不断提升,合金元素含量也越来越高,例如B96Ц合金的合金元素含量可达15%(质量分数),Zn含量最高可达9%。目前,此类合金铸锭的制备多采用普通连铸技术(Direct chill casting, DCC),合金元素在晶内固溶不充分,以共晶化合物形式存在于晶界或偏聚形成粗大第二相。在随后形变热处理过程中,仅有少部分发生回溶,大部分仍残存在晶界,呈链状分布,严重影响合金的韧性。由于微观组织具有强烈的“遗传性”,是决定材料最终力学性能和物理性能的重要因素。因此,选用先进的铸造技术来提高铸态组织中合金元素的晶内固溶度,降低晶界处共晶化合物的数量和尺寸,有利于材料加工后综合性能的提升。
由前苏联学者GETSELEV开发的[7-8]电磁铸造技术(Electromagnetic casting, EMC)是先进的无模半连续铸造技术,可以有效提高连铸坯表面质量并细化显微组织[9-11],但关于其对合金元素晶内固溶度影响的研究却鲜有报道。本文作者采用电磁铸造和普通连铸技术制备了Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金,对比研究了两种连铸技术对合金连铸锭显微组织、合金元素晶内固溶度的影响。
1 实验
实验中,Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金是以高纯Al(99.99%,质量分数,下同)、Zn(99.9%)、Mg(99.9%)以及Al-50%Cu、Al-4%Zr中间合金为原料在熔化炉中配制而成,熔炼过程中采用熔剂覆盖保护和750 ℃氩气除气精炼,采用电磁铸造和普通连铸技术制备d174 mm Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金连铸坯。其中,电磁铸造工艺参数为:电源功率20 kW,浇注温度720 ℃±10 ℃,冷却水流量1.85 m3/h,稳定拉坯速度2 mm/s;除施加电磁场外,普通连铸采用相同工艺参数。在熔炼、浇注成型过程中,严格控制杂质元素含量。Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金连铸坯化学成分如表1所示。
表1 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloys (mass fraction, %)
分别在两种连铸方法制备的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr铸锭的边缘和中心部位取样,磨制、抛光、腐蚀,制备金相试样。腐蚀液采用凯氏溶液(95%H2O、1.5%HCl、1%HF和2.5%HNO3,体积分数)。显微组织采用莱卡MEFS型多功能金相显微镜和岛津JSM-M5600LN型扫描电镜观察。采用与扫描电镜配套的Oxford型能谱分析仪测定晶间第二相元素组成。在X射线衍射仪(XRD6000XD-3A)上进行相分析。
分别在DCC和EMC铸锭横截面上1/2半径处取样。为了消除成分偏差的影响,首先通过XRF-1800型X射线荧光光谱分析仪分别确定试样的化学成分。对每个试样分别选取6个晶粒,采用EPMA-1600型电子探针分析测定晶粒内部微区的合金元素含量,计算取平均值,再对主要合金元素进行面扫描及线扫描分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 显微组织
图1所示为两种连铸技术制备的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭横截面上的显微组织。从图1中可以看出,无论是DCC铸锭的中心还是边部位置,晶粒形状不规则,大小不均匀,并且中心晶粒尺寸稍大于边部,整个铸锭范围内晶粒平均尺寸为68 mm。无论是EMC铸锭的边部还是中心,显微组织均为细小、呈近球形的等轴晶,晶粒平均尺寸减小到53 mm。两种铸锭的XRD谱如图2所示。两种铸锭的相组成一致,主要为固溶体基体α(Al),η(MgZn2)相和θ(Al2Cu)相。但是,DCC铸锭XRD中η(MgZn2)相和θ(Al2Cu)相所对应的衍射峰强度较EMC铸锭中相同物相的衍射峰强度要大,说明EMC铸锭中的η(MgZn2)相和θ(Al2Cu)相较DCC铸锭中的有所减少,固溶在铝基体内部的合金元素则有所增加。
图3所示为Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金DCC铸锭晶界处共晶组织和晶内第二相粒子的形貌。晶界共晶组织中的A点和第二相粒子B点的能谱分析如表2所列。两点成分基本一致,均为θ(Al2Cu)相。在EMC铸锭中也发现了同样的组织,只是尺寸较小,数量也很少。
表2 普通铸造Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭中晶界组织及第二相成分分析
Table2 Composition analysis of grain boundary microstructure and second-phase in DCC Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy billets

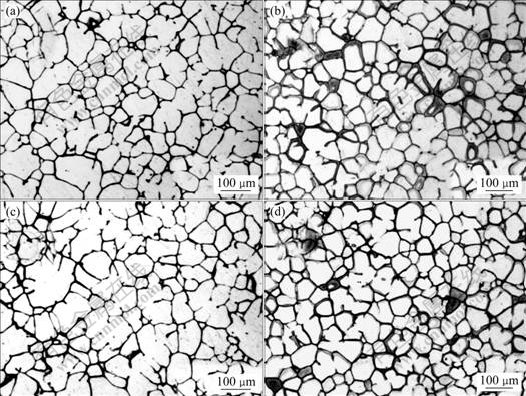
图1 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭的微观组织
Fig.1 As-cast microstructures of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy billets: (a) Edge of DCC billets; (b) Center of DCC billets; (c) Edge of EMC billets; (d) Center of EMC billets
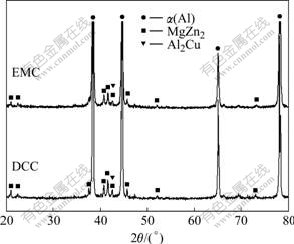
图2 普通铸造与电磁铸造Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭的XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD patterns of DCC and EMC Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy billets
普通连续铸造过程中,由于熔池内温度场、溶质场不均匀,形核核心少,铸锭内部易以枝晶的方式生长。此时,在晶间和二次枝晶臂根部充盈富集大量溶质元素的熔体,在凝固过程中易形成粗大晶间非平衡化合物。电磁铸造过程中,磁场的引入增大了注入熔体在熔池内形成的大环流,使得液穴内温度均匀,熔体内部溶质场和温度场分布趋于均匀,糊状区面积减小、厚度趋于均一。增加了凝固前沿的温度梯度, 使糊状区整体趋向于同时凝固,晶粒尺寸趋于一致 化[12]。伴随的电磁搅拌加速了过热的驱散并打碎枝晶臂,熔断脱落的枝晶臂在熔体中又可成为新的异质形核核心,并重新分布于过热的液体中,最终整个液体中悬浮晶核的数量倍增,这样形成的铸坯组织从边缘到铸锭中心为均匀分布的等轴晶。
普通连铸过程中,连铸坯壳和结晶器直接接触存在着相对的滑动摩擦,表面存在大量的划痕;另外,初期凝固坯壳在冷却过程中的体积收缩导致铸坯与结晶器壁之间产生气隙,使得界面热阻迅速增加,界面换热能力大幅下降,内部过热金属会使坯壳发生部分重熔,枝晶间低熔点物质在凝固壳收缩压力和熔融金属静压力的共同作用下,渗透到铸锭表面形成偏析瘤。电磁铸造过程中,液体金属仅依靠电磁力约束以“半悬浮”状态无模连续成型,而且金属液直接在冷却水的作用下快速冷却凝固,避免了二次重熔[13-14],使得铸坯表面光整。电磁铸造与普通连续铸造法制备的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭表面质量如图4所示。
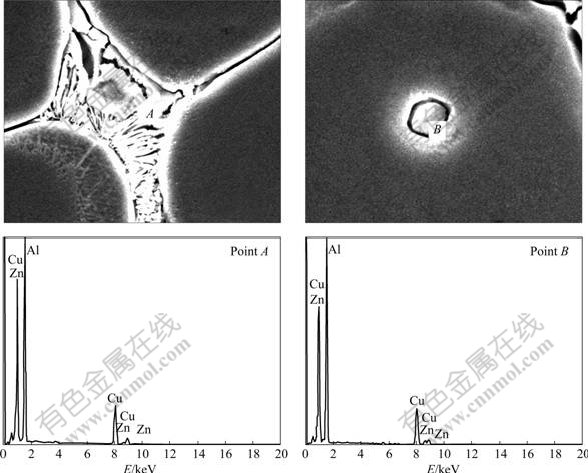
图3 普通连铸Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭晶界处组织与第二相的形貌及能谱分析
Fig.3 Energy spectrum analysis of grain boundary microstructure and second-phase in DCC Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy billets
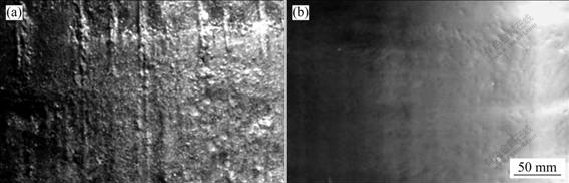
图4 普通连续铸造(DCC)与电磁铸造(EMC)铸锭的表面质量
Fig.4 Surface qualities of DCC and EMC billets: (a) DCC billet; (b) EMC billet
2.2 合金元素晶内相对固溶度
图5和6所示为两种连铸技术制备的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭中主要合金元素EPMA面分析和线分析。在普通连铸和电磁铸造的铸锭中,合金元素Zn、Mg和Cu在晶粒尺度内分布不均匀,主要表现为:合金元素Zn、Mg和Cu的谱线在晶界处都存在着尖锐的峰值(见图6),说明晶界处元素浓度较高,晶粒内分布相对较少;Cu元素在晶界处的偏析最为严重,这是由于在合金凝固过程中Cu极易偏聚在晶界形成非平衡的共晶化合物或者偏聚形成难溶的第二相粒子。DCC铸锭中,Zn和Mg在晶内有少量固溶,大部分以共晶组织的形态分布在晶界处,晶粒内部和晶界间存在较大的浓度梯度;EMC铸锭中,Cu元素的分布仍有较大的浓度梯度,合金元素Zn、Mg则在晶界偏聚的现象有所减轻,增加了在铝基体晶粒中以固溶态形式存在的数量,晶粒尺度内分布更为均匀,铸锭的微观偏析得到改善。这与图2中 XRD的分析结果相符。
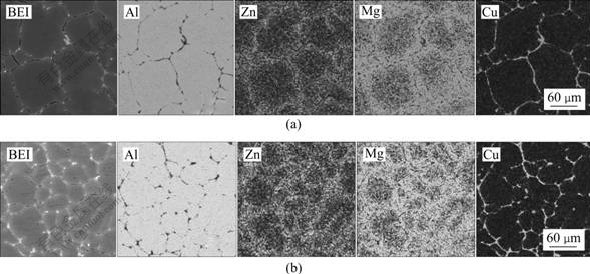
图5 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭的主元素面扫描分析
Fig.5 Mapping analyses of main alloy elements in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy billets: (a) DCC billet; (b) EMC billets
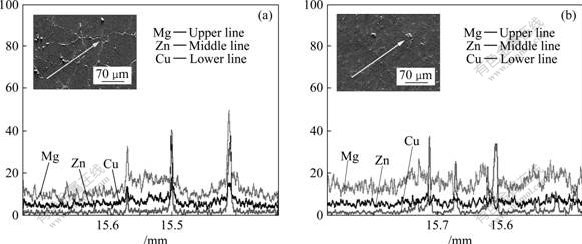
图6 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭的主元素线扫描分析
Fig.6 Line analyses of main alloy elements in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy billets: (a) DCC billet; (b) EMC billets
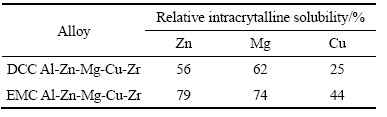
为定量表征出合金元素在晶内的固溶程度,从而准确地得出电磁铸造方法在提高合金元素晶内固溶程度的作用,并为将来进行的热处理工艺提供参考,本文采用合金元素晶内相对溶质固溶度(元素A晶内相对溶质固溶度=晶内元素A含量/合金样品元素A含量)来表征两种连铸技术对铸锭中主要合金元素晶内固溶程度的影响,计算结果如表3所列。DCC铸锭中元素Zn、Mg和Cu的晶内相对溶质固溶度较小,分别为56%、62%和25%;而在EMC铸锭中元素Zn、Mg和Cu的晶内相对溶质固溶度显著提高,分别为79%、74%和44%。
表3 主要合金元素的晶内相对溶质固溶度
Table 3 Relative intracrytalline solubility in grain of main alloy elements
在普通连铸过程中,金属液首先依靠结晶器壁冷却成初期凝固坯壳。由于凝固时金属体积收缩,凝固壳与结晶器壁之间形成气隙,气隙使连铸过程的系统导热系数迅速下降,随后铸锭下移由二冷水直接冷却成型。由于冷却强度不高,液穴中结晶核心少,导致枝晶生长期长,溶质元素析出多,在最终凝固阶段高浓度溶质以共晶化合物的形式在晶界处凝固析出,所以不利于溶质元素在晶粒内部的固溶。而在电磁铸造过程中,由于液体金属仅依靠电磁力约束成型,和感应器之间没有任何的物理接触,直接由冷却水冷却凝固成型,冷却强度大于普通连铸[15];提高了凝固前沿的过冷度从而大量形核,趋于同时凝固,结果大量的溶质元素来不及扩散至后凝固的熔体中而直接固溶在晶粒内部。此过程可以结合图7所示的普通连铸与电磁铸造过程凝固界面附近合金溶质元素分布示意图加以解释。熔体在凝固过程中,高浓度溶质元素聚集在凝固界面附近的液态部分(边界层),由于凝固速度快,液态边界层的对流不充分,仅靠扩散作用无法使液态金属内溶质元素均匀混合,导致大部分的合金元素没有足够的时间和条件传输到晶界处最终形成化合物,而是直接固溶在晶粒内部,提高了合金元素在晶内的固溶度。电磁铸造技术提高了冷却强度,同时也增大了凝固过程中熔体内的有效分配系数ke。BOTON、PRIM和SLICHTER导出的有效分配系数ke的数学表达式[16]为

在电磁铸造过程中,由于冷却强度大,凝固速度增大,因而凝固界面的移动速度增大,即e-Rδ/D项减少,表明有效分配系数ke=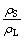 增大,即固相中元素浓度增加。
增大,即固相中元素浓度增加。
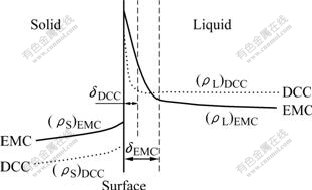
图7 凝固界面处溶质元素分布
Fig.7 Distribution of solute element in area of solidification surface
另外,磁场的引入增大了注入熔体在熔池内形成的大环流,熔体内部溶质场和温度场分布趋于均匀,糊状区面积减小、厚度趋于均一。糊状区的变化使得枝晶前沿的温度梯度增加,糊状区整体趋向于同时凝固,形成尺寸均匀、近球形的等轴晶组织。等轴晶组织铸锭各晶粒间成分相近,并且相对而言具有较为均匀的微区成分,弥散了溶质元素在晶粒内部的分布,促进了溶质元素的固溶,从而消除了以枝晶方式生长过程中对合金溶质元素固溶的不利影响,提高了合金溶质元素的固溶度。
相关文献报道[17-18],在交变电磁场以及较大的冷却速度作用下,该系列铝合金在凝固过程中的液相线温度和固相线温度均升高,且固相线温度升高幅度相对更大,使得结晶温度区间相对变小,从而缩短了合金元素在液固两相区的停留时间,减少了溶质元素偏聚形成粗大的金属间化合物和晶界非平衡化合物的数量,起到了提高合金元素晶内含量的作用。
综上所述,电磁铸造在改善Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸态微观组织,强制合金元素晶内固溶,减小微观偏析方面作用显著。
3 结论
1) 电磁铸造技术明显细化了Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金连铸坯的显微组织,减少了晶界析出相的尺寸和数量,从而获得了细小均匀的铸态显微组织。相对比普通连铸,平均晶粒尺寸从68 mm减小到53 mm;电磁铸造显著改善了Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金连铸锭的表面质量。
2) 电磁铸造明显减小了Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr合金铸锭内的微观偏析程度并提高了元素Zn、Mg和Cu晶内相对溶质固溶度,与普通连铸坯比较,分别由56%、62%和25%提高到79%、74%和44%。
REFERENCES
[1] 李成功, 巫世杰, 戴圣龙, 杨守杰. 先进铝合金在航空航天工业中的应用与发展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(Al Special): 14-21.
LI Cheng-gong, WU Shi-jie, DAI Sheng-long, YANG Shou-jie. Application and development of advanced aluminum alloy in aerospace industry[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(Al Special): 14-21.
[2] 陈昌麒. 超高强铝合金的发展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(Al Special): 22-27.
CHEN Chang-qi. Development of ultrahigh-strength aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(S1): 22-27.
[3] ADACHI H, OSAMURA K, OCHIAI S. Mechanical property of nanoscale precipitate hardening aluminum alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2001, 44(8): 1489-1492.
[4] LI Zhi-hui, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHANG Yong-an, ZHU Bao-hong, WANG Feng, LIU Hong-wei. Investigation on strength, toughness and microstructure of an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy pre-stretched thick plates in various ageing tempers[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(4): 2021-2027.
[5] CHEN K H, FANG H C, ZHANG Z, CHEN X. Effect of Yb, Cr and Zr additions on recrystallization and corrosion resistance of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 497(1/2): 426-431.
[6] DIXIT M, MISHRA R S, SANKARAN K K. Structure–property correlations in Al 7050 and Al 7055 high-strength aluminum alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 478: 163-172
[7] 曹志强, 张兴国, 金俊泽. 电磁铸造技术及其发展[J]. 轻金属, 1995, (10): 51-53.
CAO Zhi-qiang, ZHANG Xing-guo, JIN Jun-ze. Electromagnetic casting technology and its development[J]. Light Metals, 1995, (10): 51-53.
[8] GETSELEV Z N. Casting in an electromagnetic field[J]. J Metals, 1971, 23(10): 38-39.
[9] PRITCHETT T R. Electromagnetic casting of aluminum alloy[J]. Light Metal Age, 1981, 39: 12-16.
[10] EVANS J W. The use of electromagnetic casting for Al alloys and other metals[J]. JOM, 1995, 47(5): 38-41.
[11] 曹志强, 张兴国, 贾 非, 郝 海, 金俊泽. 电磁铸造铝合金锭的力学性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2002, 16(6): 635-639.
CAO Zhi-qiang, ZHANG Xing-guo, JIA Fei, HAO Hai, JIN Jun-ze. Mechanical property of aluminum alloy ingot by electromagnetic casting[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 16(6): 635-639.
[12] 房灿峰. 高性能镁合金电磁改性技术研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2006.
FANG Can-feng. Research on electromagnetic modified technology of high-performance magnesium alloy[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2006.
[13] 李玉梅, 张兴国, 贾 非, 曹志强, 金俊泽. 铝合金电磁连铸技术的基础研究[J]. 铸造技术, 2002, 23(2): 111-114.
LI Yu-mei, ZHANG Xing-guo, JIA Fei, CAO Zhi-qiang, JIN Jun-ze. Fundamental study on electromagnetic continuous casting aluminium alloy[J]. Foundry Technology, 2002, 23(2): 111-114.
[14] 郝 海, 金俊泽, 张兴国. 电磁铸造中的感应热研究[J]. 铸造, 1998, 47(8): 5-9.
HAO Hai, JIN Jun-ze, ZHANG Xing-guo. Study on induction heat in electromagnetic casting[J]. China Foundry, 1998, 47(8): 5-9.
[15] 张兴国. 电磁铸造技术的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2001: 53-65.
ZHANG Xing-guo. Studies of electromagnetic casting technology[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2001: 53-65.
[16] 胡赓祥, 蔡 珣. 材料科学基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2004. 6. 267.
HU Geng-xiang, CAI Xun. Materials science foundation[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2004. 6. 267.
[17] 张 勤, 班春燕, 崔建忠, 巴启先, 路贵民, 张北江. CREM法半连铸Al合金过程中电磁场对溶质元素固溶的影响机理[J]. 物理学报, 2003, 52(10): 2642-2648.
ZHANG Qin, BAN Chun-yan, CUI Jian-zhong, BA Qi-xian, LU Gui-min, ZHANG Bei-jiang. The forced solution mechanism of alloying agents of 7075 alloy as-cast ingot under the effects of electromagnetic field[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2003, 52(10): 2642-2648.
[18] 曹禄华, 于家康. 用电子探针测定铝合金在定向凝固过程中的溶质分配系数[J]. 分析测试技术与仪器, 1996, 2(3): 44-47.
CAO Lu-hua YU Jia-kang. Characterization of solute distribution coefficient in aluminum alloys during directional solidification by EPMA[J]. Analysis and Testing Technology and Instruments, 1996, 2(3): 44-47.
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2005CB623705);国家自然科学基金资助项目(50875031)
收稿日期:2009-02-03;修订日期:2009-07-15
通信作者:张兴国,教授,博士;电话:0411-84706183;E-mail: zxgwj@dlut.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)