DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.09.22
K2O含量对CaO-Al2O3-MgO-FexO-SiO2系熔体黏度及析出相的影响
候朋涛1,王丽君2,3,刘仕元2,张建坤4,周国治2,3
(1. 北京科技大学 冶金与生态工程学院,北京 100083;
2. 北京科技大学 钢铁协同创新中心,北京 100083;
3. 北京科技大学 钢铁冶金新技术国家重点实验室,北京 100083;
4. 赞比亚谦比希铜冶炼有限公司,基特韦 23558)
摘 要:采用旋转柱体法研究在1175~1400 ℃温度区间内,K2O含量对CaO-Al2O3-MgO-FexO-SiO2系熔体黏度的影响,并结合XRD和SEM分析了熔渣冷却过程中各物相的析出行为。同时,采用FactSage软件计算了该体系析出相总量及析出温度,与实验结果进行对比和分析。结果表明:当熔渣中K2O含量低于1%(质量分数)时,由于碱性氧化物的网络破坏作用,熔渣黏度降低,但是随着K2O含量的继续增加,熔渣黏度呈现先升高后降低的趋势,黏度最大值出现在n(K2O)/n(Al2O3)>1的区域。同时,熔渣的黏度随温度的下降而升高,且黏度随温度变化时会出现骤增的转折点,当到达“转折点”温度时,熔渣的黏度会迅速升高,这主要是由橄榄石相的析出造成。
关键词:K2O含量;黏度;FactSage软件;析出相
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-09-1929-07 中图分类号:G142.71 文献标志码:A
由于单一产区的铜矿石无法满足ISA炉冶炼的需求,因此铜锍冶炼企业矿石来源渠道繁杂,造成了冶炼稳定性差。研究熔渣成分变化对熔渣性质的影响,对于合理配矿,保证生产顺行具有重要的意义。在造锍熔炼过程中,FexO和SiO2的含量占熔渣总质量的80%(质量分数)左右,同时熔渣中还含有一定量的CaO、Al2O3、MgO和碱金属氧化物(K2O)。
国内对于相关熔渣体系的研究仅限于CaO、Al2O3、MgO、FexO和SiO2构成三元、四元或者五元体系[1-7],在铜冶炼过程中,虽然碱金属在熔渣中的含量比较低,但是碱金属会加快炉衬的侵蚀,影响炉料顺行,同时对熔渣黏度的影响也十分显著。目前,国内关于碱金属对熔渣黏度的研究,主要集中在含Na2O体系熔渣的研究[8-13]。国内外关于K2O对熔渣性质的研究的报道[14-25],主要集中在CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2体系及其子体系中。目前,有关报道中所研究体系的成分变化范围与本研究中熔渣有较大差别,同时,K2O对CaO-Al2O3-MgO-FexO-SiO2熔渣黏度的研究还未见报道。
针对某厂的实际生产条件,K2O含量较高时,在造锍熔炼过程中会生成高熔点的白榴石相,影响冶炼正常进行。为进一步确定,熔渣中K2O含量变化时,是否会造成高熔点白榴石相的析出,以及对熔渣黏度的影响。本文作者研究K2O含量对CaO-Al2O3-MgO- FexO-SiO2系熔渣体系黏度以及熔渣冷却过程中析出物相的影响。
1 实验
1.1 渣料准备
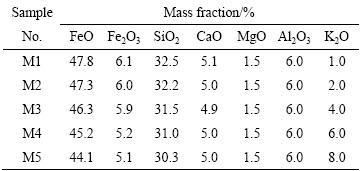
实验采用分析纯Fe、Fe2O3、SiO2、Al2O3、MgO、CaCO3和 K2CO3配制合成渣。其中,“FeO”由Fe和Fe2O3粉体按摩尔比1:1混匀在n(CO)/n(CO2)=1在1300 ℃恒温12 h制备[26]。SiO2、Al2O3、MgO和CaCO3分别在1000 ℃下焙烧10 h,其中CaO由CaCO3受热分解制备。为了减少挥发,K2O以K2CO3的形式配入渣中。将预先制备FeO和CaO以及其他试剂按表1所示,用玛瑙研钵充分研磨均匀后,压样,进行黏度测定,所有样品中的m(SiO2)/m(Fe)=0.8。
表1 试验渣样的组成
Table 1 Compositions of experimental slags
1.2 黏度测定
黏度实验采用旋转柱体法测定,仪器为东北大学生产的 RTW/10 型熔体物性测定仪,装置如图1(a)。测量前,黏度仪在室温下利用标准蓖麻油校准。在本研究中,采用U型硅钼棒电阻炉进行加热,热电偶采用预先由三级标准热电偶校正的双Pt-Rh热电偶(PtPh6- PtPh30),热电偶顶端紧贴坩埚底部。测试用钼材质的黏度锤和坩埚,黏度锤尺寸如图1(b)所示。为了保证熔渣成分,避免氧化,在氧化铝炉管的顶端安装特制的法兰。测试过程在氩气气氛保护下进行,氩气经净化后,以0.5 L/min由炉底通入,从炉管上部的法兰口导出。每次测试称取170 g样品放入钼坩埚中,将钼坩埚置于炉体恒温带内,接通冷却水,开启设备电源。按设定程序升温至1400 ℃熔化渣样,降温测量,温度梯度为50 ℃。每到一个温度恒温30 min,确保熔渣温度均匀。
1.3 表征手段
样品经研磨后,采用X射线衍射仪(XRD)进行物相分析(管压 40 kV,管流 40 mA,铜靶 Kα,λ=1.54178 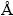 ,扫描范围2θ为10°~90°,扫描速率 10 (°)/min)。将样品经过冷镶磨平抛光处理后,表面喷金 120 s 处理,采用 MLA250型扫描电电子显微镜(SEM)观察其显微形貌。
,扫描范围2θ为10°~90°,扫描速率 10 (°)/min)。将样品经过冷镶磨平抛光处理后,表面喷金 120 s 处理,采用 MLA250型扫描电电子显微镜(SEM)观察其显微形貌。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 温度对黏度的影响
图2所示为不同K2O含量下CaO-Al2O3-MgO- FexO-SiO2系熔体黏度与温度的关系。由图2可知,随温度的降低,黏度升高,存在一个转折温度,黏度发生突变。高于转折温度,熔体黏度随温度变化不大,均小于0.3 Pa·s,熔渣具有良好的流动性;低于转折温度,熔体黏度值突增,熔渣流动性恶化。
由图2(b) 可知,在转折温度以上,熔渣黏度与温度的倒数符合阿伦尼乌斯方程。根据lnη-1/T的线性关系,可以通过图2(b)线性回归计算得到各成分熔渣的粘流活化能,将其结果列于表2。 K2O含量从0增加到1%(质量分数),粘流活化能逐渐降低;K2O含量从1%增加到6%,熔渣的粘流活化能逐渐增加,K2O含量从6%增加到8%时,粘流活化能逐渐降低。
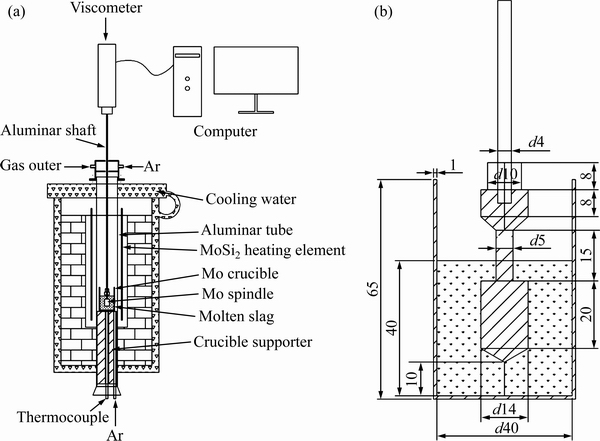
图1 黏度测定装置图
Fig. 1 Schematic illustrations of apparatus for viscosity measurement (a) and dimensions of crucible and bob (b) (Unit: mm)
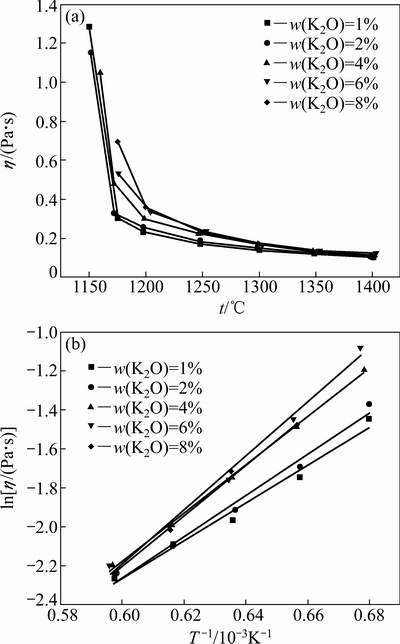
图2 不同K2O含量下熔渣黏度与温度的关系
Fig. 2 Relationship between temperature and viscosity of slags with different contents of K2O
表2 不同K2O含量对熔渣黏度活化能的影响
Table 2 Effect of K2O on viscous activation energy of slags
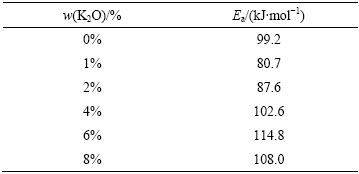
当温度高于转折温度时,熔体属于牛顿流体。温度对黏度的影响可以从分子流动性角度解释,在相对较低的温度下分子的移动缓慢,这是由于聚合体之间接触紧密,从而导致黏度很高。随着温度的升高,熔体各分子获得更高的动能,分子间间距增大,分子运动的阻力减少,分子更容易地移动,因此,黏度较低[27]。但是温度低于转折温度,熔体中开始有固相析出,使熔体的流动阻力增大,从而使黏度突然增大。
2.2 K2O含量对黏度的影响
图3所示为K2O含量对CaO-Al2O3-MgO-FexO- SiO2系熔渣黏度的影响。K2O含量对熔渣黏度的影响比较复杂,且随着温度的降低,K2O对熔渣黏度的影响越显著。加入1%的K2O时,熔渣的黏度首先减低;随K2O含量的增加,熔渣的黏度开始上升,当K2O含量超过4%时,熔渣的黏度趋于平缓或稍许下降。
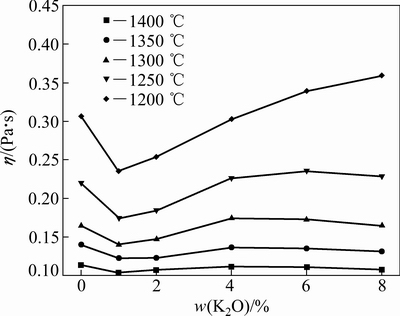
图3 K2O含量对CaO-Al2O3-MgO-FexO-SiO2熔渣黏度的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of K2O on viscosities of CaO-Al2O3-MgO- FexO-SiO2 System
在硅铝酸盐熔体中,K2O对熔体结构有两个方面的影响。其一,作为网络修饰体,提供O2-,使复杂的硅酸盐网络的聚合度降低,如式(1) ~ (3)所示[28]。
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)

 (3)
(3)
碱金属氧化物如K2O 和 Na2O加入到熔体后,释放出的自由氧离子可以修饰硅酸盐网络结构,生成 [Si2O7]6-和[SiO4]4-单体,从而导致随着K2O含量的增加熔渣的黏度降低。
其二,K2O的另一个作用如式(4)所示[29],可以改变铝酸盐的结构:
 (4)
(4)
虽然K2O可以分离出自由氧离子,但是由于K+离子的电荷补偿效应,K2O还可以促使[AlO4]5-四面体结构的形成,作为熔渣结构的网络形成体[30-32]。
当加入1%的K2O时,可能是由于K2O的量过低,不足以进行电荷补偿,但是K2O可以释放出K+和O2-,一定程度上破坏了熔渣网络结构,从而使熔渣的黏度降低;当继续加入K2O后,促使[AlO4]5-四面体结构的形成进入硅酸盐网络,使熔渣的聚合度增加,从而使熔渣黏度增大。体系中Al2O3的摩尔浓度为4.1%,当K2O的浓度为6%(摩尔浓度为4.5%)时,熔体中Al3+全部参与方程(4)反应;随着K2O含量的增加(n(K2O)/n(Al2O3)>1),K2O又开始作为网络修饰体,使硅酸盐网络的聚合度降低,从而使熔渣黏度减小。这一熔渣黏度随K2O变化的现象在SUKENAGA等[14]、SOKENGA等[24]和KIM等[17]的研究中也有报道。
2.3 FactSage计算结果比较
图4所示为在转折温度(1200 ℃)以上时利用FactSage软件Viscosity模块计算得到的黏度值与实验值的对比[33]。在转折温度以上计算值与实验值基本符合,平均偏差在6.5%左右。由于FactSage的适用范围为单一液相的熔体,而不适用于固液两相共存的熔体。因此,FactSage可以用来估算高于转折温度熔渣的黏度值,对低于熔点的情况,则应慎重选择。
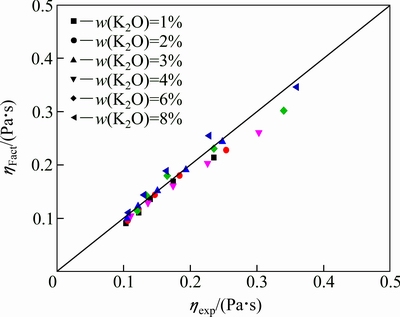
图4 实验测定的黏度值(ηexp)与FactSage计算值(ηFact)的比较
Fig. 4 Viscosities comparison between experimental data and calculated values by FactSage
2.4 物相分析
2.4.1 熔体物相组成
由于该渣系的结晶能力很强,淬冷时无法获得完全高温玻璃相。但是在冷却过程中,物相的演变也可以间接地反映出降温过程该渣系的物相析出顺序和析出相的形态变化[34-35]。
图5和6所示分别为从1400 ℃淬冷样品的XRD谱和SEM像。图5表明4组不同K2O含量的渣样其物相基本相同,主要为橄榄石相,且在橄榄石相中并未发现K2O的存在,K2O保留在基底玻璃相中。图6的SEM结果与XRD结果基本一致,并未发现有白榴石相析出。镁、铁橄榄石之间可以完全固溶,结晶相是钙镁橄榄石、 镁橄榄石以及钙橄榄石的固溶相。白榴石的熔点在1686 ℃左右,白榴石应该更易析出,但是并没有发现有白榴石相生成,因此,在熔炼过程中当造渣反应完成后,白榴石相不易在熔渣中析出。冶炼中出现的白榴石相可能是矿物熔化过程中产生。
2.4.2 熔体橄榄石相含量
图7所示为FactSage计算不同K2O含量的熔渣冷却过程中橄榄石相析出结果。其中析出相是多元固溶橄榄石相,包括2FeO·SiO2、MgO·FeO·SiO2和2MgO·SiO2,以及少量MgO·CaO·SiO2、CaO·FeO·SiO2和2CaO·SiO2。随着K2O含量在1%~8%范围内增加,橄榄石相的析出温度逐渐降低,在1150~1180 ℃窄范围内变化,而且析出量也随着K2O含量的增加而下降。计算的结果也证实了熔渣在低于1200 ℃时(含K2O高于4%时转折温度)黏度突然升高的原因,即开始有固相析出。虽然液相中固相的含量较少,但熔体不再符合牛顿流体的特性,熔体黏度增大。
从橄榄石的析出量来看,相同温度下,随着K2O含量的升高,橄榄石相的总量在下降, K2O在一定程度上内具有抑制橄榄石相的析出量的作用。但是在实际生产中,通过K2O来控制橄榄石相的析出作用有限,由于橄榄石相的析出对温度更加敏感,因此,调控温度是避免橄榄石相析出的主要措施。
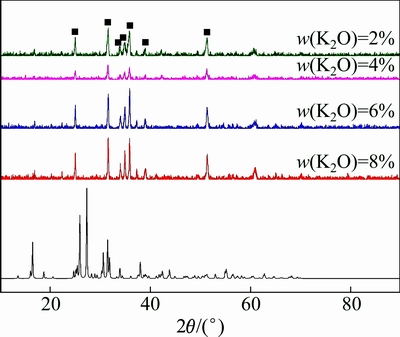
图5 不同K2O含量渣样的XRD谱
Fig. 5 XRD patterns of quenched slag samples
3 结论
1) 当熔渣中K2O低于1%(质量分数)时,熔渣的黏度降低,但是随着K2O含量的增加,熔渣的黏度先升高然后降低,黏度最大的点出现在n(K2O)/n(Al2O3)>1的区域。
2) 熔渣的黏度随温度变化时会出现突然升高的转折点,这是由于该温度下熔体中橄榄石相的析出造成的。虽然该温度下各组分之间熔体内的固相量很少,且相差不大,但熔体不再符合牛顿流体的特性,黏度骤增。
3) 渣样冷却过程中析出相主要为钙镁铁固溶的橄榄石相。橄榄石相的析出量对温度变化表现的特别敏感,在造锍熔炼过程中应严格控制炉膛的温度在1200 ℃以上。K2O具有抑制橄榄石相的析出总量的效果。
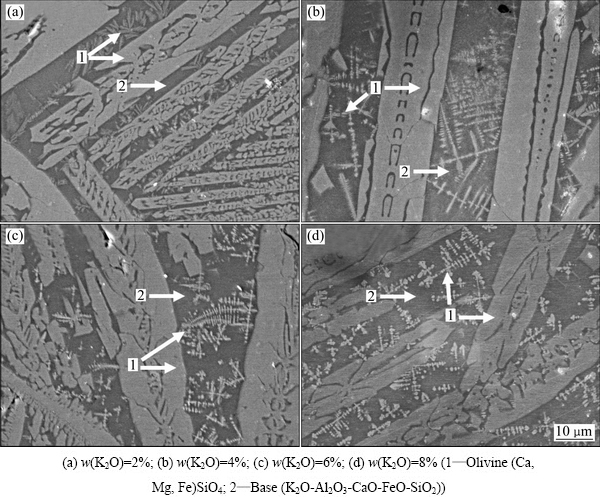

图6 不同K2O含量渣样的SEM谱
Fig. 6 SEM images of quenched slag samples
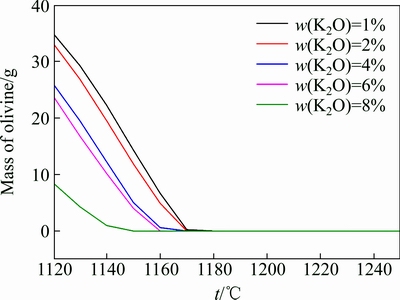
图7 熔渣在冷却过程中橄榄石相的析出与温度的关系
Fig. 7 Relationship between precipitated phases of olivine and temperature in process of cooling
REFERENCES
[1] 黄翠环. CaO-SiO2-MgO-FeOx四元氧化物体系热力学性质的计数[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2010.
HUANG Cui-huan. Thermodynamic property calculation on CaO-SiO2-MgO-FeOx system[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2010.
[2] 辛雪倩. CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-FeOx四元氧化物体系热力学性质研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2011.
XIN Xue-qian. Study on thermodynamic properties of the CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-FeOx quaternary system[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2011.
[3] 高运明, 王少博, 杨映斌, 杨创煌, 洪 川. FeO含量对SiO2- CaO-Al2O3-MgO(-FeO)酸性渣熔化温度的影响[J]. 武汉科技大学学报, 2013, 36(3): 161-165.
GAO Yun-ming, WANG Shao-bo, YANG Ying-bin, YANG Chuang-huang, HONG Chuan. Influence of Fe0 content on the melting temperature of SiO2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO(-FeO) acid slag[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2013, 36(3): 161-165.
[4] 张淑会. CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO-FeO五元渣系热力学性能的研究[D]. 唐山: 河北理工学院, 2003.
ZHANG Shu-hui. Study on thermodynamics property of CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO-FeO slags[D]. Tangshan: Hebei University of Technology, 2003.
[5] 曾德文, 李作刚, 刘海霞, 张传福. FeO-SiO2-CaO-MgO系高镁炉渣黏度的测定[J]. 中南工业大学学报, 1997, 28(4): 343-346.
ZENG De-wen, LI Zuo-gan, LIU Hai-xia, ZHANG Chuan-fu. Viscosity determination of high magnesium content slag FeO-SiO2-CaO-MgO system[J]. Journal of Central South University, 1997, 28(4): 343-346.
[6] 张传福, 王 智, 曾德文, 谭鹏夫. FeO-MgO-SiO2系黏度的研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 1998(3): 45-47.
ZHANG Chuan-fu, WANG Zhi, ZENG De-wen, TAN Peng-fu. Viscosity of FeO-MgO-SiO2 system: A study[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 1998(3): 45-47.
[7] 曾德文, 李作刚, 刘海霞, 张传福. FeO-SiO2-CaO-MgO系高镁炉渣黏度的测定[J]. 中南工业大学学报, 1997, 18(4): 343-346.
ZENG Dewen, LI Zuo-gan, LIU Hai-xia, ZHANG Chuan-fu. Viscosity determination of high magnesium content slag of FeO-SiO2-CaO-MgO system[J]. Journal of Central South University, 1997, 18(4): 343-346.
[8] 刘承军, 姜茂发. CaO-SiO2-Na2O-CaF2-Al2O3-MgO渣系的黏度和结晶温度[J]. 东北大学学报, 2002, 23(7): 656-659.
LIU Cheng-jun, JIANG Mao-fa. Viscosity and crystallization temperature of CaO-SiO2-Na2O-CaF2-Al2O3-MgO system[J]. Journal of Northeastern University, 2002, 23(7): 656-659.
[9] 何 峰, 平财明, 郑媛媛, 乔 勇. (Na2O-Al2O3) /B2O3对高硼硅酸盐玻璃黏度和热学性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2013, 32(6): 1022-1025.
HE Feng, PING Cai-ming, ZHANG Yuan-yuan, QIAO Yong. Influence of (Na2O-Al2O3)/B2O3 on viscosity and thermal properties of silica-rich[J]. Borosilicate Glasses Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 32(6): 1022-1025.
[10] 佟志芳, 乔家龙, 陈 涛. 炉渣组分对CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2- MgO-Na2O渣系黏度的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2016, 16(2): 189-196.
TONG Zhi-fang, QIAO Jia-long, CHEN Tao. Effect of composition on viscosity of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2-MgO-Na2O system slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2016, 16(2): 189-196.
[11] 韩秀丽, 张翼飞, 刘 磊, 冯运莉, 刘丽娜. Na2O对保护渣黏度和渣膜矿相结构的影响[J]. 铸造技术, 2016, 37(5): 957-960.
HAN Xiu-li, ZHANG Yi-fei, LIU Lei, FENG Yun-li, LIU Li-na. Influence of Na2O on viscosity of mold flux and mineralogical structure of flux film[J]. Foundry Technology, 2016, 37(5): 957-960.
[12] 程金树, 李淑晶, 杨 飞. Na2O对LAS微晶玻璃高温黏度及析晶的影响[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2010, 32(22): 44-47.
CHENG Jin-shu, LI Shu-jing, YANG Fei. Effect of Na2O on high temperature viscosity and crystallization behavior of lithium aluminum silicate glass-ceramic[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2010, 32(22): 44-47.
[13] 刘承军, 朱英雄, 姜茂发, 王云盛. CaO-SiO2-Na2O-CaF2- Al2O3- MgO保护渣系的Al2O3吸收速率和黏度[J]. 炼钢, 2001, 17(3): 42-46.
LIU Cheng-jun, ZHU Ying-xiong, JIANG Mao-fa, WANG Yun-sheng. Al2O3 absorption rate and viscosity of system CaO-SiO2-Na2O-CaF2-Al2O3-MgO[J]. Steelmaking, 2001, 17(3): 42-46.
[14] CHEN M, ZHAO B. Viscosity measurements of the SiO2-K2O-CaO system relevant to biomass slags[J]. Fuel, 2016, 180: 638-644.
[15] WIESNER V L, VEMPATI U K, BANSAL N P. High temperature viscosity of calcium-magnesium-aluminosilicate glass from synthetic sand[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2016, 124: 189-192.
[16] HIGO T, SUKENAGA S, KANEHASHI K, SHIBATA H, OSUGI I. Effect of potassium oxide addition on viscosity of calcium aluminosilicate melts at 1673-1873 K[J]. ISIJ International, 2014, 54(9): 2039-2044.
[17] KIM W H, SOHN I, MIN D J. A study on the viscous behaviour with K2O additions in the CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-MgO-K2O quinary slag system[J]. Steel Research International, 2010, 81(9): 735-741.
[18] LIU M, ZHOU H Q, ZHU H K, YUE Z X, ZHAO J X. Microstructure and dielectric properties of Ca-Al-B-Si-O glass/Al2O3 composites with various alkali oxides contents[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(10): 2733-2739.
[19] POOLE J P. Low-temperature viscosity of alkali silicate glasses[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1949, 32(7): 230-233.
[20] KADOGAWA Y, YAMATE T. Viscosity of mixed-alkali lead silicate glasses in the softening region[J]. Journal of the Society of Materials Science Japan, 1974, 23(245): 104-108.
[21] DAVIES J, MOON J T, TRAICE F B. Alkalis in the blast furnace[J]. Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1978, 5(4): 151-161.
[22] ZHANG Y S, SUN W, LI Z J. Preparation and microstructure characterization of poly-sialate-disiloxo type of geopolymeric cement[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2009, 16(6): 906-913.
[23] BOCKER C, AVRAMOV I,  C. Viscosity and diffusion of barium and fluoride in Na2O/K2O/Al2O3/SiO2/BaF2 glasses[J]. Chemical Physics, 2010, 369(2): 96-100.
C. Viscosity and diffusion of barium and fluoride in Na2O/K2O/Al2O3/SiO2/BaF2 glasses[J]. Chemical Physics, 2010, 369(2): 96-100.
[24] SUKENAGA S, SAITO N, KAWAKAMI K, NAKASHIMA K. Viscosities of CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-(R2O or RO) melts[J]. ISIJ International, 2006, 46(3): 352-358.
[25] ZHANG G H, CHOU K C. Measuring and modeling viscosity of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 (-K2O) melt[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2012, 43(4): 841-848.
[26] VIDACAK B, SICHEN D, SEETHARAMAN S. An experimental study of the viscosities of Al2O3-CaO-“FeO” slags[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2001, 32(4): 679-684.
[27] ROHINDRA D R, LATA R A, COLL R K. A simple experiment to determine the activation energy of the viscous flow of polymer solutions using a glass capillary viscometer[J]. European Journal of Physics, 2012, 33(5): 1457.
[28] WASEDA Y, TOGURI J M. The structure and properties of oxide melts[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 1998.
[29] SANO N, LU W, RIBOUD P V. Advanced physical chemistry for process metallurgy[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 1997.
[30] MYSEN B O, VIRGO D, KUSHIRO I. The structural role of aluminum in silicate melts-a Raman spectroscopic study at 1 atmosphere[J]. American Mineralogist, 1981, 66(7/8): 678-701.
[31] METALS I O. 3rd international conference on molten slags and fluxes[M]. Glasgow: University of Strathclyde, 1989.
[32] HWA L G, HWANG S L, LIU L C. Infrared and Raman spectra of calcium alumino-silicate glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1998, 238(3): 193-197.
[33] BALE C W, CHARTRAND P, DEGTEROV S A, ERIKSSON G, HACK K. FactSage thermochemical software and databases[J]. Calphad, 2002, 26(2): 189-228.
[34] 刘 柳, 闫红杰, 周孑民, 高 强, 张振杨. 氧气底吹铜熔池熔炼过程的机理及产物的微观分析[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(7): 2116-2124.
LIU Liu, YAN Hong-jie, ZHOU Jie-min, GAO Qiang, ZHANG Zhen-yang. Mechanism of copper smelting process by oxygen bottom blowing and microanalysis of smelting products[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(7): 2116-2124.
[35] 孙铭良, 黄克雄, 李新海. 炼铜炉渣的显微分析与渣含铜[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1998, 8(1): 106-112.
SUN Ming-liang, HUANG Ke-xiong, LI Xin-hai. Microanalysis for slag of copper matte smelting and loss of copper in slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1998, 8(1): 106-112.
Influence of K2O on viscosities and precipitated phase of CaO-Al2O3-MgO-FexO-SiO2 slags
HOU Peng-tao1, WANG Li-jun2,3, LIU Shi-yuan2, ZHANG Jian-kun4, CHOU Kuo-chih2,3
(1. School of Metallurgical and Ecological Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. Collaborative Innovation Center of Steel Technology, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China.
4. Chambishi Copper Smelter Limited, ZhangKitwe 23558, Zambia)
Abstract: The viscosities of CaO-Al2O3-MgO-FexO-SiO2 slags with different K2O contents were measured using the rotating cylinder method in the temperature range from 1175 ℃ to 1400 ℃. The quenched slag samples were also characterized by XRD and SEM to identify the precipitated phases during the cooling process. Meanwhile, the theoretical calculation on precipitated phases was carried out on the platform of Factsage with the Equilibrium Moduls. The results show that the viscosity decreased when K2O is less than 1% (mass fraction). With increasing K2O content, viscosity increases firstly and then decreases. The maximum value of viscosity occurs when the mole ratio of K2O and Al2O3 is larger than 1. During cooling, the viscosity increases, and at the critical temperature, the viscosity enlarges suddenly, which is caused by the precipitation of the fayalite.
Key words: K2O content; viscosity; FactSage software; precipitated phase
Foundation item: Project (2014M560046) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Project (51474141) supported by National Natural Science of China
Received date: 2016-07-26; Accepted date: 2017-01-16
Corresponding author: WANG Li-jun; Tel: +86-15210906865; E-mail: lijunwang@ustb.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:中国博士后科学基金委资助项目(2014M560046);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51474141)
收稿日期:2016-07-26;修订日期:2017-01-16
通信作者:王丽君,副教授,博士;电话:15210906865;E-mail:lijunwang@ustb.edu.cn