Study on bioleaching of refractory gold ore (Ⅰ)——Mechanism on bioleaching of pyriteby Thiobacillus ferrooxidans
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2001年第5期
论文作者:闵小波 柴立元 陈为亮 张传福 黄伯云 邝中
文章页码:784 - 789
Key words:mechanism; pyrite bioleaching; Thiobacillus ferrooxidans
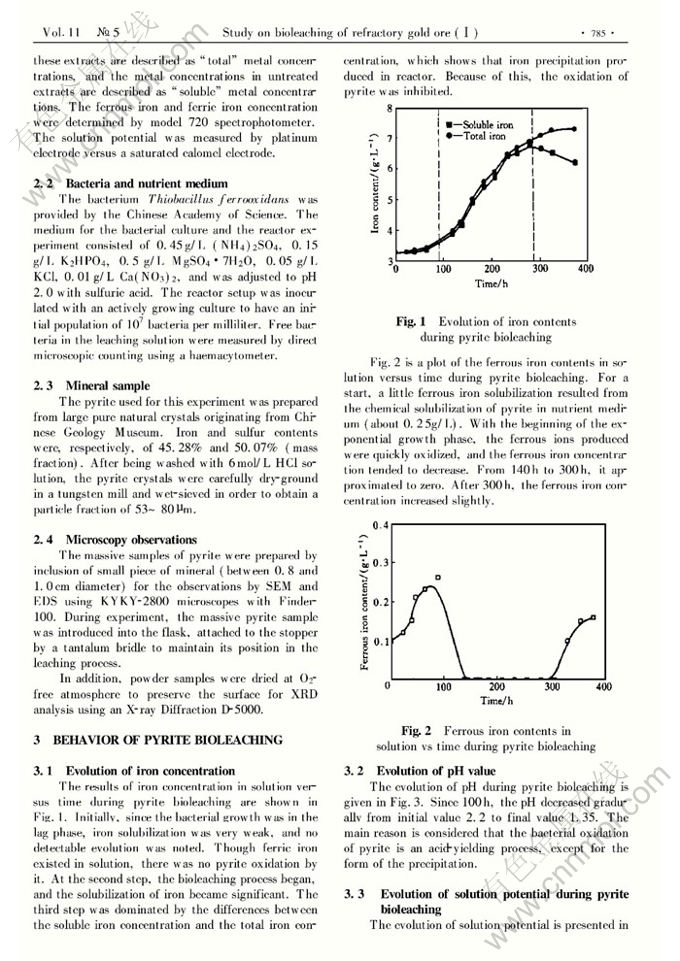
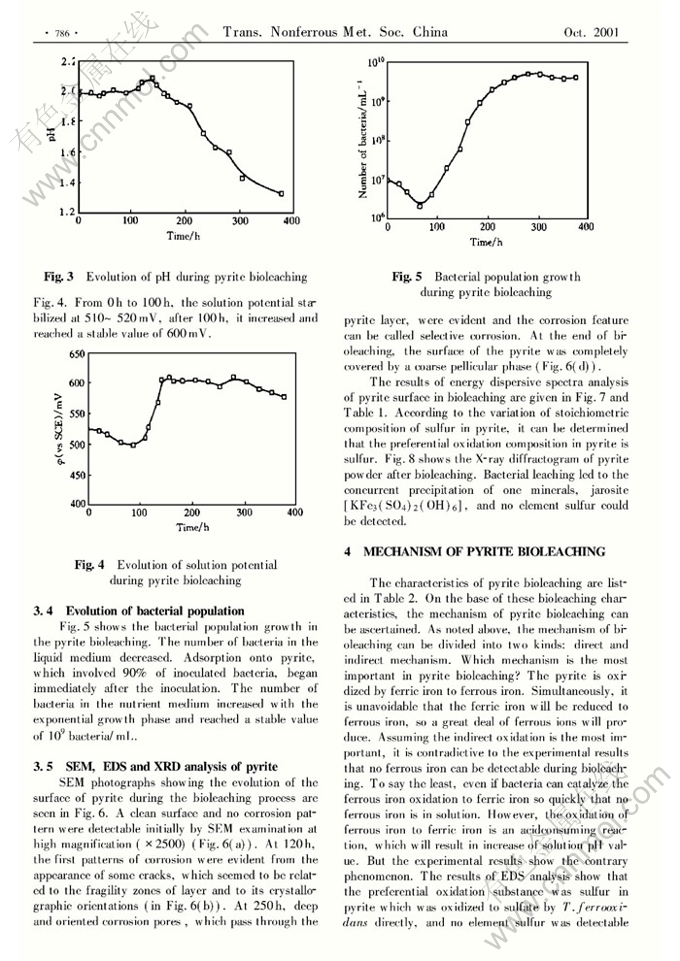
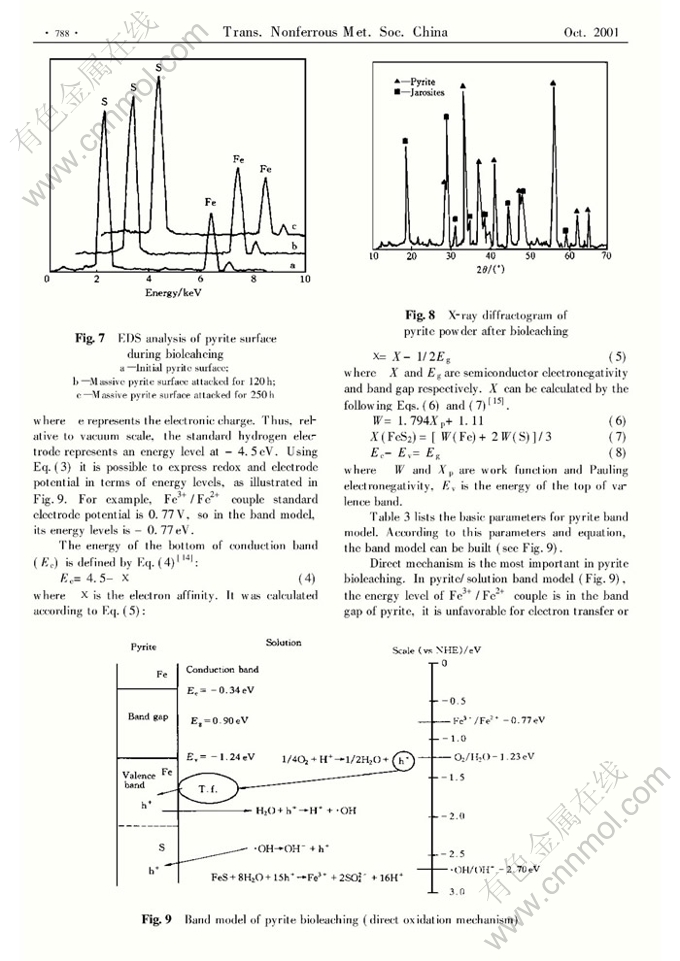
Abstract: The variation of main parameters including ion concentration, pH value, potential and biomass was examined in bioleaching pyrite. The pH value of the solution decreased obviously. Most of T. ferrooxidans adhered to the surface of pyrite. The surface properties of pyrite and leached products were determined by SEM, EDS and XRD. Pyrite was corroded selectively by T.ferrooxidans and sulfur in pyrite was leached preferentially. The primary product for bioleaching pyrite was jarosite. Based on these results, it can be found that pyrite is oxidized mainly through the dir, ect role of T.ferrooxidans. A band model for bioleaching pyrite was built, by which the bioleaching process was explained theoretically. The model shows that the holes, which are injected into the valence band of pyrite through adhered T. ferrooxidans , result from dissolved oxygen in the solution.
 .
.