DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.05.11
温度对镍和铜电接触微动性能的影响
刘新龙,蔡振兵,刘善邦,彭金方,朱旻昊
(西南交通大学 牵引动力国家重点实验室 摩擦学研究所,成都 610031)
摘 要:选用两种典型的电接触材料(镍、紫铜)进行从室温到高温下(室温~300 ℃)以及10 N载荷的电接触微动试验,采用3D形貌仪和SEM对磨痕形貌进行分析。结果表明:温度对接触电阻的影响显著。在室温环境下,两种材料的接触电阻均处在一个稳定的值;随着温度的上升(室温~100 ℃),镍的接触电阻急剧上升,而铜的接触电阻相对稳定,随着温度上升至300 ℃,两种材料的接触电阻均发生剧烈变化。接触区域的氧化磨屑生成和堆积是导致接触电阻急剧上升的主要原因。
关键词:微动;接触电阻;接触斑点;温度;电接触
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-05-0944-11 中图分类号:TG146.4 文献标志码:A
电接触是指2个导电材料因带电接触而产生的一种状态[1]。电接触是所有电力电子线路中不可或缺的重要组成部分,其可靠性极为重要。由于载荷类型[2-3]、接触方式[4]、接触面积[5]、环境状态[6]的差异,材料种类繁多,因而电接触存在极为复杂的物理、化学过程。电接触材料的基本要求是:1) 良好的导电导热性能[7];2) 低的接触电阻和温升;3) 抗熔焊和抗环境介质污染[8]。而环境是主要的影响因素之一[9]。电接触的质量与水平对设备与系统的可靠性有着重要的影响。电接触学属于交叉学科。它将物理、力学、电学、材料、化学、环境等多个学科的概念和理论应用于电连接可靠性问题,形成电接触理论。电接触是电子、通信、控制、电力系统中存在着普遍现象。如果接触点发生故障,则可能影响到整个系统的可靠运行。由此引出了电接触的稳定性、寿命等与可靠性相关的研究内容[10-11]。而接触电阻是电连接的一个基本、主要的参数。电接触的材料、结构、制造工艺、工作环境都有密切关系[9]。
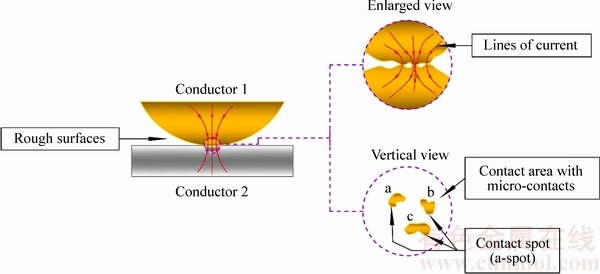
图1 电接触的定义
Fig. 1 Definition of electrical contact
电接触的定义如图1所示:理论上接触的两个导体,由于接触表面存在初始粗糙度,实际接触的区域是如图1放大图所示的微小触点,这些实际接触的区域称为“接触斑点”(Contact spot,a-spot)[12]。电流通过这些所谓的接触斑点时必然发生收缩,这样就引起了接触电阻的变化[13]。
1 实验
镍[14]和铜[15]都是常用的电接触材料,目前对上述两种材料研究较多,但是针对温度变化(室温~300 ℃)对其接触电阻影响的研究较少,为了深入对2种材料电接触性能的研究,确定温度变化导致接触电阻变化的机理与影响因素,改良与优选电接触材料,故选取镍和铜作为试验研究对象,所选材料具体性能参数如表1所列。
表1 材料性能参数
Table 1 Characteristics of selected materials
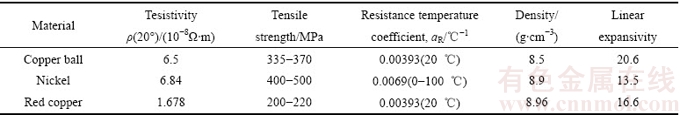
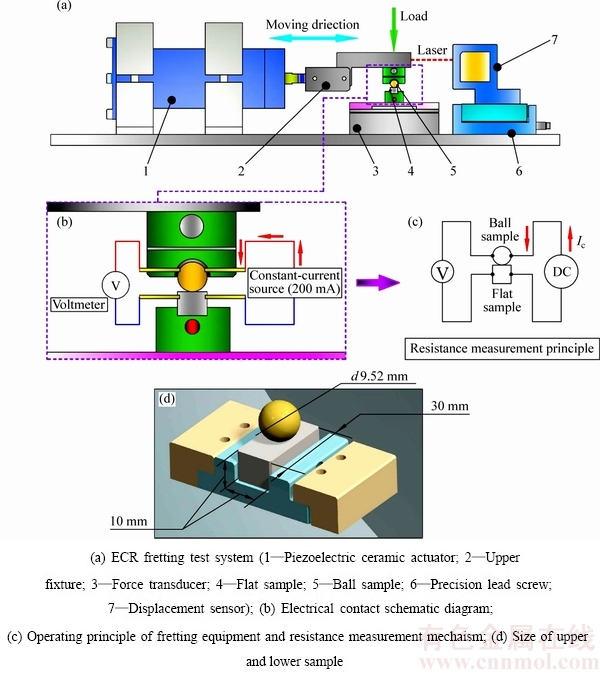
图2 实验装置示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagrams of experimental device
本实验研究借助由西南交通大学摩擦学研究所研制的1台电接触微动试验机。试验机主要包括驱动装置、加载装置以及数据采集系统,具体如图2所示。驱动装置(见图2(a))由压电陶瓷驱动,加载系统采用砝码加载,数据采集系统包括:二维载荷传感器、位移传感器、NI数据采集卡。而接触电阻的测量则采用经典的四线法接线方式测量[16] (见图2(b)~(c))。试验中选用铜球(Cu:60.5%~63.5%;Fe:0.01%;Pb:0.08%;P:0.15%;So:0.005%;Bi:0.002%和Zn:Bal)/平面接触作为研究对象,接触副的具体尺寸如图2(d)所示。为了消除材料接触表面的初始粗糙度对实验结果产生干扰,所选材料的接触面都预先经过抛光处理。其中:触点压力设置为定载荷10 N,触点电流为20 mA,温度变化范围为室温、100 ℃、200 ℃、300 ℃。试验数据通过NI采集卡储存至PC机中显示及后处理。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 两种接触副的摩擦因数
两种材料的摩擦因数(COF)和平均摩擦因数如图3所示,可见两种材料的摩擦因数受温度的影响明显:(a) 镍的摩擦因数随着温度的升高而降低,当温度从室温上升至300 ℃时,摩擦所因数从0.83降至0.5;(b) 铜的摩擦因数并未随着温度的上升而降低,而是随着温度的上升而升高,当温度从室温上升至300 ℃时,摩擦因数从0.33上升至0.75,其中100 ℃和200 ℃时摩擦因数值相似。
2.2 两种接触副的接触电阻
图4所示为两种材料的接触电阻,图5所示为每2000个循环取一次平均值的平均电阻。从图4可以看出:(a) 在室温环境下,镍的接触电阻从3~31 mΩ之间变化,随着温度从100 ℃上升300 ℃,镍的接触电阻从530 mΩ 急剧上升至1450 mΩ。镍的平均电阻在室温环境下相对稳定,而随着温度上升至300 ℃,平均接触电阻从4000次循环开始上升,在8000次循环时达到峰值1002.24 mΩ;(b) 铜的接触电阻在室温和100 ℃环境下都相对较为稳定,变化范围从1.65~129 mΩ之间变化,当温度上升至200 ℃时,铜的最大接触电阻增至501 mΩ,而3种温度下(RT、100 ℃、200 ℃)平均接触电阻较为相似,只在试验末期开始发生明显差异,其中200 ℃达到245.41 mΩ;当温度上升至300 ℃时,接触电阻达到峰值(为1476 mΩ),平均接触电阻也急剧上升。
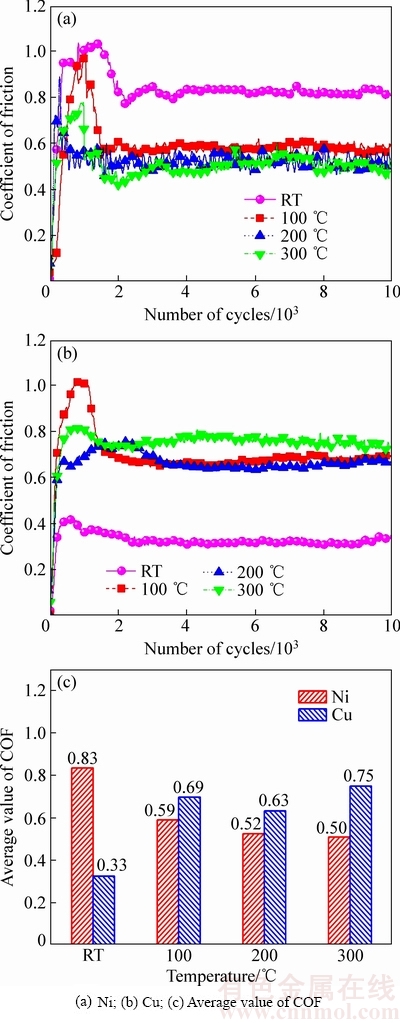
图3 两个摩擦副的摩擦因数和平均摩擦因数
Fig. 3 COF and average value of COF of two contact pairs

图4 两个摩擦副的接触电阻
Fig. 4 ECR of two contact pairs

图5 两个摩擦副的平均接触电阻
Fig. 5 Statistical resistance of two contact pairs

图6 两个摩擦副的导电性能
Fig. 6 Electric conductivity of two contact pairs
为研究两种材料接触电阻稳定性与使用寿命,选取1 Ω、2 Ω作为接触电阻两个临界阈值[17]。并根据材料的接触电阻是否超出临界阈值作为材料电接触性能的评估依据。图6所示为两种材料在试验中,接触电阻瞬时值达到两个峰值(1000 mΩ,2000 mΩ)所需的循环次数,其中铜在室温(RT)以及100 ℃下接触电阻瞬时值最大值不足300 mΩ,故在室温和100 ℃只选取100 mΩ和200 mΩ作为考察铜材料的两个瞬时电阻峰值。从图6(a)中可知,在4种环境下,镍达到1000 mΩ的循环次数是8040、5419、5552、4432。达到2000 mΩ的循环次数是8050、6068、5787、2638;由图6(b)可知,铜在200 ℃和300 ℃环境下达到1000 mΩ的循环次数是7642、7813,达到2000 mΩ的循环次数是7798、7874。由此可以得到以下分析:1) 镍的接触电阻达到瞬时峰值的循环次数相比铜要小得多,这说明镍作为电接触材料,其使用寿命比铜短,其接触电阻相比铜要更大。2) 在200 ℃、300 ℃环境下,铜的瞬时接触电阻在试验末期才可达到1000 mΩ、2000 mΩ峰值。这说明铜作为电接触材料,在一定温度下具有相对较长的使用寿命。
2.3 微动运行工况分析
两种材料的运行工况微动图(摩擦力(Ft)-位移幅值(D))曲线[18]如图7所示,由图7可知:1) 在室温环境下,两种材料的微动区域都处在完全滑移区;2) 随着温度上升至100 ℃,镍的微动工况处在混合区,与此同时铜的微动工况时处在部分滑移区;3) 300 ℃环境下 ,镍的微动运行工况仍然处在混合区;而铜的微动运行工况处在部分滑移区。总而言之:室温环境下,两种材料的微动运行工况都在滑移区,而在高温环境下,两种材料的接触表面发生剧烈的变化,微动运行工况也在部分滑移和混合区之间转变。

图7 微动运行工况图与平均接触电阻
Fig. 7 Fretting sliding condition (FSC) and statistical resistance
2.4 磨损机制与接触电阻的关系
图8所示为高温环境下接触电阻达到峰值时的磨损机制原理图以及对应的等效电路图。图8(a)所示为磨损机制示意图。在图8(b)中,Rb代表球试样的接触电阻,Rd代表氧化磨屑(见图8(c))的电阻,Rp代表平面试样的接触电阻,“a”和“b”代表微动区域不同的接触点。球试样的往复运动等效于电路图(见图8(b))开关“S”交替接通触点“a”和“b”,此时的瞬时接触电阻阻值正好对应图8(d)中的“a”和“b”两个峰值点。
材料在高温下产生的氧化磨屑粘附在接触表面将会引起两个导体接触电阻的剧变甚至直接导致电路开路[19],因为金属氧化物一般具有极大的电阻甚至直接氧化成绝缘体[20-21],如氧化镍就是典型的绝缘体[22]。氧化镍的物理性质也随温度的变化而变化。温度的升高,其密度和电阻增加[23-24]。图9所示为微动区域的SEM形貌图和EDX结果:在室温环境下:镍的磨损区域周围有少量磨屑堆积,黄色区域内有明显犁沟磨痕,此区域的主要成分为镍和从球试样转移到平面试样的铜。而铜平面试样的微动区域未见明显磨屑,磨痕边界也未见磨屑堆积;在300 ℃下,镍的磨损区域有大量磨屑堆积并形成“第三体”(见图9(e)黄色区域),“第三体”的主要成分应是镍的氧化物以及铜的氧化物。此时铜的磨痕宽度较室温下要更长,在微动区域仍未见明显磨屑,微动区域主要是铜及其的氧化物。
综上所述:接触电阻与磨损机制的关系可以总结为3个阶段:1) 稳定阶段—微动区域开始发生轻微磨损,但是不足以改变接触电阻;2) 上升阶段—微动区域发生明显犁沟、剥层、磨损等现象,直接导致接触面积变小,接触斑点增加;3) 波动阶段—微动区域磨屑堆积形成“第三体”[25],并且萌生裂纹、开始发生的严重材料缺失。
两种材料的微动区形貌与接触电阻的关系如图10 (室温)和图11 (300 ℃)所示,由图中可知:
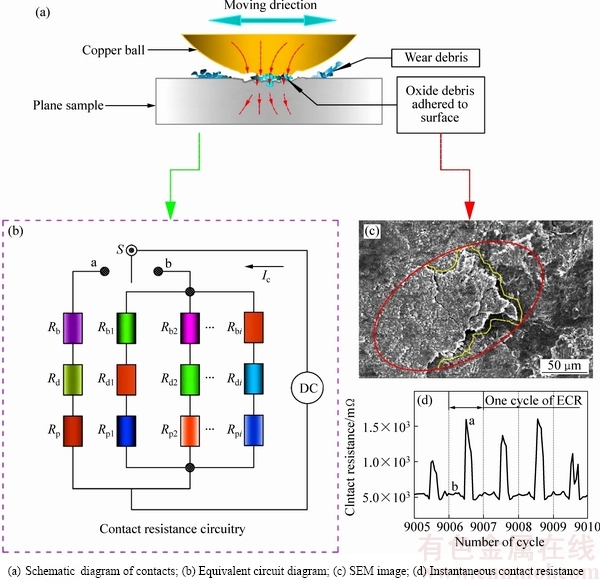
图8 高温环境下的磨损机制和等效电路图
Fig. 8 Schematic diagram of degradation mechanisms and contact resistance circuitry under elevated temperature

图9 磨痕形貌以及成分分析
Fig. 9 Wear track morphologies and EDX of two contact pairs
1) 室温下,镍的接触副表面都有深度为10 μm左右的磨痕凹坑,其中球试样表面有若干类似于图10(b)中的触点“b”,接触点“b”和平面试样接触导致接触电阻上升如图10(c)所示;铜接触副的微动区也检测到凹坑,球表面凸起的“b”点由若干个微小触点聚集而成,“b”点与铜平面试样接触而形成图10(f)中两个接触电阻峰值(6.34 mΩ和1.7 mΩ)。
2) 300 ℃下,镍表面检测到由氧化磨屑堆积成的触点“a”(见图11(b)),如上述的接触电阻与磨损机制的关系:触点“a”与球接触并形成接触斑点,导致接触电阻急剧上升至峰值1361.4 mΩ(见图11(c))。同理,铜的接触区域存在大量如“a”和“d”以及“b”和“c”的触点。在单次循环试验中,这类凸起的触点交替接触形成接触斑点,导致出现如图10(f)所示的两个接触电阻峰值(420.58 mΩ和345.77 mΩ)。

图10 室温下两种材料的3维/2维轮廓与接触电阻的关系
Fig. 10 Relationship between ECR and 3D/2D profiles for two contact pairs under RT
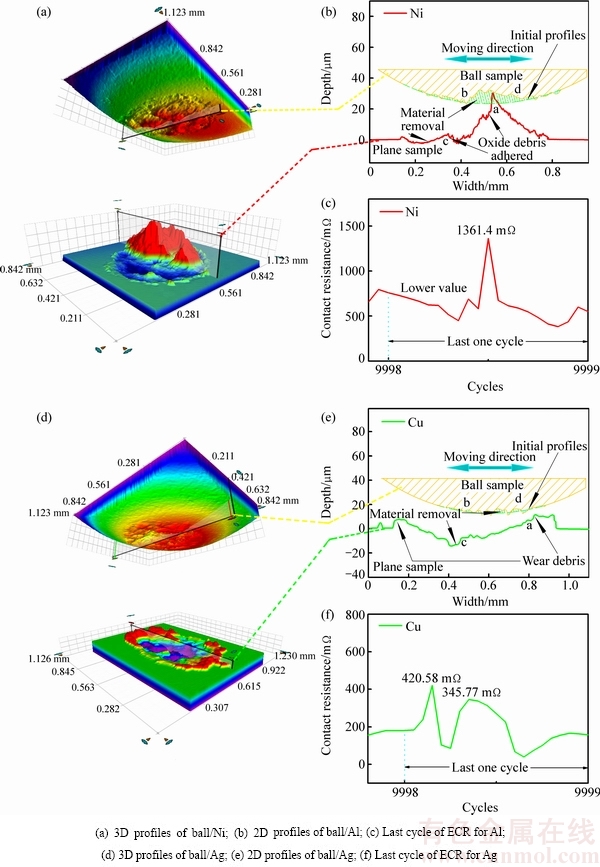
图11 300 ℃下两种材料的3维/2维轮廓与接触电阻的关系
Fig. 11 Relationship between ECR and 3D/2D profiles for two contact pairs under 300 ℃
3 结论
1) 室温环境下,金属材料的接触电阻较为稳定,微动磨损导致接触表面状况发生改变并增加金属的接触电阻。
2) 高温环境下,金属材料接触表面损伤更加剧烈。金属氧化物堆积在接触区域形成阻值极大的接触斑点,是导致接触电阻急剧上升的根本原因。
REFERENCES
[1] 堵永国, 张为军, 胡君遂. 电接触与电接触材料(二)[J]. 电工材料, 2005(3): 42-46.
DU Yong-guo, ZHANG Wei-jun, HU Jun-sui. Electrical contact and electrical contact materials (2)[J]. Electrical Engineering Materials, 2005(3): 42-46.
[2] NARAYANAN T S N S, PARK Y W, LEE K Y. Fretting-corrosion mapping of tin-plated copper alloy contacts[J]. Wear, 2007, 262: 228-233.
[3] TAHERI P, HSIEH S, BAHRAMI M. Investigating electrical contact resistance losses in lithium-ion battery assemblies for hybrid and electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(15): 6525-6533.
[4] WU C P, YI D Q, WENG W, LI S H, ZHOU J M. Influence of alloy components on arc erosion morphology of Ag/MeO electrical contact materials[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(1): 185-195.
[5] TAHERI P, HSIEH S, BAHRAMI M. Investigating electrical contact resistance losses in lithium-ion battery assemblies for hybrid and electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196: 6525-6533.
[6] 郭凤仪, 娄晓妹, 李本君, 李 雷, 石立志. 滑动电接触磨损量最小的最佳载荷实验[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报, 2012, 31(1): 81-84.
GUO Feng-yi, LOU Xiao-mei, LI Ben-jun, LI Lei, SHI Li-zhi. Optimum normal load when minimum wear loss of electrical sliding contact[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University, 2012, 31(1): 81-84.
[7] 范金铎, 李勇军, 吕保国, 张晓辉. 新型弱电触点材料——微异型复合触点带[J]. 机电元件, 2001, 21(3): 21-26.
FAN Jin-duo, LI Yong-jun, Lü Bao-guo, ZHANG Xiao-hui. New type of weak current contact material——Micro special shaped composite contact zone[J]. Electromechanical Components, 2001, 21(3): 21-26.
[8] 周怡琳, 章继高. 触点镀金材料的自然腐蚀和电接触特性研究[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2001, 20(4): 11-13.
ZHOU Yi-lin, ZHANG Ji-gao. Gold plated contacts material natural corrosion and electrical contact properties[J]. Electronic Components & Material, 2001, 20(4): 11-13.
[9] 许 军, 李 坤. 电接触的接触电阻研究[J]. 电工材料, 2011(1): 10-13.
XU Jun, LI Kun. The research on resistance of electrical contact[J]. Electrical Engineering Materials, 2011(1): 10-13.
[10] SHIRI S G, ABACHI P, POURAZARANG K, RAHVARD M M. Preparation of in-situ Cu/NbC nanocomposite and its functionally graded behavior for electrical contact applications[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(3): 863-872.
[11] XIE X L, ZHANG L, XIAO J K, QIAN Z Y, ZHANG T, ZHOU K C. Sliding electrical contact behavior of AuAgCu brush on Au plating[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(9): 3029-3036.
[12] ANTLER M. Electrical effects of fretting connector contact materials: A review[J]. Wear, 1985, 106: 5-33.
[13] DANKS D. Tribology of electrical contacts[M]. US: Springer, 2013.
[14] SONG J, KOCH C. Wear patterns and lifetime of electric contacts[C]//Electrical Contacts. Orlando: IEEE, 2008: 238-244.
[15] NARAYANANT S, PARK Y W, LEE K Y. Fretting-corrosion mapping of tin-plated copper alloy contacts[J]. Wear, 2007, 262(1/2): 228-233.
[16] REN W, WANG P, SONG J, ZHAI G. Effects of current load on wear and fretting corrosion of gold-plated electrical contacts[J]. Tribology International, 2014, 70(70): 75-82.
[17] LIN X Y, XU L J, SHAO Y C, LUO G P, ZHANG H X. Research on fretting resistance and fretting wear property of Ni-Au contact pair[C]//Electrical Contacts (Holm). Minneapolis: IEEE, 2011: 1-6.
[18] LISKIEWICZ T, NEVILLE A, ACHANTA S. Impact of corrosion on fretting damage of electrical contacts[C]//Montreal: IEEE Holm Conference on, 2006: 257-262.
[19] KANGY L, JEONG D K, KIM J H. Simulational study of electrical contact degradation under fretting corrosion[J]. Tribology International, 2011, 44(12): 1651-1658.
[20] MENNICKE C, HE M Y, CLARKE D R, SMITH J S. The role of secondary oxide inclusions (“pegs”) on the spalling resistance of oxide films[J]. Acta Materialia, 2000, 48(11): 2941-2949.
[21] HWANG D Y, YONG M K, PARK D Y, YOO B, SHIN D H. Corrosion resistance of oxide layers formed on AZ91 Mg alloy in KMnO4, electrolyte by plasma electrolytic oxidation[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(23): 5479-5485.
[22] BRUYERE J C, CHAKRAVERTY B K. Switching and negative resistance in thin films of nickel oxide[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1970, 16(1): 40-43.
[23] JIN Y O, SAINT-JOHN D, PODRAZA N, JACKSON T N, HORN M W. High temperature coefficient of resistance molybdenum oxide and nickel oxide thin films for microbolometer applications[J]. Optical Engineering, 2015, 54(3): 037101.
[24] KOBAYASHI Y, FUJIWARA Y. Cerium conversion coating on electroless nickel-phosphorus substrate and its high-temperature oxidation resistance[J]. Journal of the Surface Finishing Society of Japan, 2004, 55(10): 677-681.
[25] HANNEL S, FOUVRY S, KAPSA P, VINCENT L. The fretting sliding transition as a criterion for electrical contact performance[J]. Wear, 2001, 249(9): 761-770.
Effect of elevated temperature on fretting wear of nickel and copper under electric contact
LIU Xin-long, CAI Zhen-bing, LIU Shan-bang, PENG Jin-fang, ZHU Min-hao
(Tribology Research Institute, Traction Powder State Key Laboratory, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China)
Abstract: The fretting wear behavior of two typical materials (nickel and red copper) and contacts at elevated temperatures (from RT to 300 ℃) and normal loads (10 N) is addressed. The morphology and wear surface was analyzed by 3D profile and SEM. The results show that elevated temperature significantly affected the contact resistance. At room temperature (RT), electrical contact resistance (ECR) remains stable of two materials for several thousand fretting cycles. With the increase of temperature (from RT to 100 ℃), the ECR of red copper seems stable under elevated temperature, while the ECR of nickel is easily affected by elevated temperature. The ECR of two contacts rises sharply under 300 ℃. Oxide debris accumulation at the contact areas is the key of rising and fluctuating ECR under electrical contact fretting wear.
Key words: fretting; contact resistance; contact spot; temperature; electric contact
Foundation item: Projects(51375407, 51575459, U1530136, 51627806) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2017-03-10; Accepted date: 2017-07-01
Corresponding author: ZHU Min-hao; Tel: +86-13808007296; E-mail: zhuminhao@swjtu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51375407,51575459,U1530136,51627806)
收稿日期:2017-03-10;修订日期:2017-07-01
通信作者:朱旻昊,教授,博士;电话:13808007296;E-mail:zhuminhao@swjtu.cn