KOH亚熔盐法分解钒渣的动力学分析
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第5期
论文作者:刘挥彬 杜 浩 王大卫 王少娜 郑诗礼 张 懿
文章页码:1489 - 1500
关键词:钒渣;尖晶石;亚熔盐法;动力学分析;分解;活化能
Key words:vanadium slag; spinel; sub-molten salt method; kinetics analysis; decomposition; activation energy
摘 要:开发了一种常压下用KOH亚熔盐介质氧化分解钒渣的新工艺,并考察了反应温度、碱矿质量比、粒度、搅拌速率等工艺参数对钒铬浸出的影响。结果表明,反应温度、碱矿比是最重要的影响因素;在反应温度180 °C、碱矿质量比4:1、搅拌速率700 r/min、通氧气流量1 L/min的条件下,反应进行300 min后钒、铬的浸出率分别达到了95%和90%。动力学分析表明,钒渣在KOH亚熔盐介质中的氧化分解遵循缩核模型,并受内扩散控制。钒铬尖晶石分解反应的表观活化能分别为40.54和50.27 kJ/mol。
Abstract: A novel process was developed for the decomposition of vanadium slag using KOH sub-molten salt under ambient pressure, and the effects of reaction temperature, alkali-to-ore mass ratios, particle size, and stirring speed on vanadium and chromium extraction were studied. The results suggest that the reaction temperature and KOH-to-ore mass ratio are more influential factors for the extraction of vanadium and chromium. Under the optimal reaction conditions (temperature 180 °C, initial KOH-to-ore mass ratio 4:1, stirring speed 700 r/min, gas flow 1 L/min, and reaction time 300 min), vanadium and chromium extraction rates can reach up to 95% and 90%, respectively. Kinetics analysis results show that the decomposing process of vanadium slag in KOH sub-molten salt can be well interpreted by the shrinking core model under internal diffusion control. The apparent activation energies for vanadium and chromium are 40.54 and 50.27 kJ/mol, respectively.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1489-1500
Hui-bin LIU1,2,3, Hao DU1, Da-wei WANG4, Shao-na WANG1, Shi-li ZHENG1, Yi ZHANG1
1. National Engineering Laboratory for Hydrometallurgical Cleaner Production Technology, Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China;
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China;
3. China ENFI Engineering Corporation, Beijing 100038, China;
4. School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing 100083, China
Received 8 May 2012; accepted 25 November 2012
Abstract: A novel process was developed for the decomposition of vanadium slag using KOH sub-molten salt under ambient pressure, and the effects of reaction temperature, alkali-to-ore mass ratios, particle size, and stirring speed on vanadium and chromium extraction were studied. The results suggest that the reaction temperature and KOH-to-ore mass ratio are more influential factors for the extraction of vanadium and chromium. Under the optimal reaction conditions (temperature 180 °C, initial KOH-to-ore mass ratio 4:1, stirring speed 700 r/min, gas flow 1 L/min, and reaction time 300 min), vanadium and chromium extraction rates can reach up to 95% and 90%, respectively. Kinetics analysis results show that the decomposing process of vanadium slag in KOH sub-molten salt can be well interpreted by the shrinking core model under internal diffusion control. The apparent activation energies for vanadium and chromium are 40.54 and 50.27 kJ/mol, respectively.
Key words: vanadium slag; spinel; sub-molten salt method; kinetics analysis; decomposition; activation energy
1 Introduction
Due to its excellent physical properties such as high tensile strength, hardness, and fatigue resistance, vanadium is widely used as alloying material in the iron and steel making industries [1]. The consumption of vanadium in the iron and steel industries accounts for about 85% of the total vanadium-bearing products worldwide [2,3]. Vanadium is also widely used to make advanced functional materials such as magnetic materials, superconducting materials, aircraft engine materials, nuclear reactors, and other applications [4-6].
Vanadium-bearing slag is one of the most important resources for vanadium production, and about 58% vanadium compounds are produced using vanadium slag worldwide [7]. Usually, utilizing vanadium slag as raw materials, vanadium compounds are extracted via pyrometallurgical approaches. Roasting of vanadium slag with sodium salts is currently the most popular extraction process [8]. Sodium salt roasting process mainly consists of sodium salt roasting, water leaching, solution purification, and vanadium precipitation [9,10]. However, this process suffers from low vanadium extraction efficiency and release of toxic gases such as chlorine and hydrochloric acid, causing serious environmental pollutions [11,12]. In order to solve the toxic gas release problems, process based on the roasting of vanadium slag with calcium salts was developed, but the high-energy consumption and low vanadium extraction efficiency limit the application of such process [13]. Acid leaching is another process to recover vanadium from vanadium slag. In this process acids such as nitric or sulfuric acid are used as leaching agents, and the vanadium in the slag can be converted to 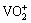 and VO2+ ions and dissolved in the acid solution. Unfortunately, this technology has low leaching kinetics and produces a large amount of impurities in the leaching solution, which were difficult to be separated [14-16].
and VO2+ ions and dissolved in the acid solution. Unfortunately, this technology has low leaching kinetics and produces a large amount of impurities in the leaching solution, which were difficult to be separated [14-16].
Further, the vanadium slag usually contains 3%-6% chromium (III) oxide in the form of chromium spinel, which is more stable than vanadium spinel thermodynamically. Consequently, the chromium compounds in the vanadium slag cannot be recovered at vanadium roasting temperatures, a large amount of chromium containing tailings were produced, threating the environment significantly. [17]. In this regard, it is necessary to develop a new and cleaner production process to improve the vanadium yield and recover chromium simultaneously with low energy consumption.
Recently, a novel method called sub-molten salt (SMS) technology [18] has been developed by the Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences [19]. The core of this new process is continuous liquid-phase oxide (LO) of vanadium slag in a sub-molten salt medium under atmospheric pressure. Sub-molten salt is an unconventional reaction medium, which is characterized by high alkaline concentration (usually above 50%), high boiling point, high ionic strength, and has been successfully applied to treating amphoteric ores to extract valuable metals, such as Cr, Al, Ti, Nb, Ta and other amphoteric metals [20-25]. In comparison with the traditional sodium salt roasting technology, which operates at 850 °C, the reaction temperature in the new method can drop to 180-250 °C, significantly decreasing the energy consumption. The extraction rates of vanadium and chromium can reach up to 95% and 90%, respectively, which is superior to the traditional technology (in the salt roasting technology, the conversion rate is 80% for vanadium and only 10% for chromium [26]). The SMS process has attracted extensive attention from both academia and vanadium processing industries, and a pilot scale demonstration plant utilizing this process is under construction in Hebei Province, China, now.
The LO technology exhibits excellent prospects in improving resource utilization efficiency and eliminating environmental pollutions. However, systematic studies regarding the LO technology to extract vanadium and chromium from vanadium slag have rarely been reported, and much fundamental work needs to be done. Therefore, in this work, the leaching process of vanadium slag using KOH SMS was investigated, and various operation parameters were examined to study the influence of temperature, the mass ratio of alkali-to-ore, the particle size, and the stirring speed on the decomposition of vanadium slag. Moreover, the phase identification and transformation of the slag were also investigated.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
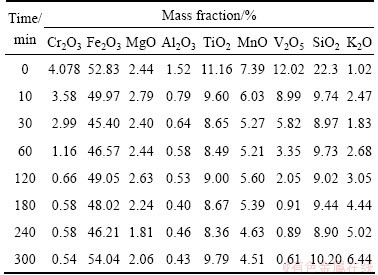
The vanadium slag used in this study was obtained from Chengde Iron and Steel Corporation, China. The sample was dried overnight at 110 °C to remove moisture. The dried samples were then ground and sieved. The chemical compositions of particles with different sizes are presented in Table 1. The results show that in general the content of V2O5 increases as the particle size decreases, and the increase in V2O5 content becomes negligible when the particle size is less than 75 μm. So, particles with size less than 75 μm were selected for further studies. The mineralogical analysis of the samples is shown in Fig. 1. From Table 1 and Fig. 1, it is clear that vanadium slag mainly consists of vanadium- chromium spinels (FeV2O4, FeCr2O4), quartz (SiO2) and fayalite (Fe2SiO4).
The potassium hydroxide used in this work is of analytical grade and obtained from Beijing Chemical Company. Distilled water was used throughout the experiments.
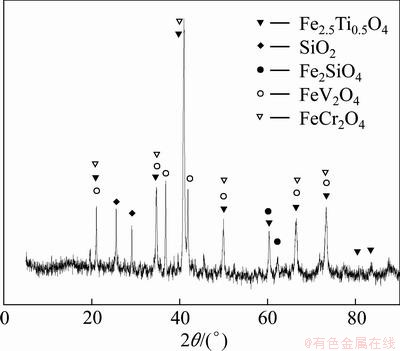
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of vanadium slag
Table 1 Chemical compositions of vanadium slag with different particle sizes
2.2 Apparatus and procedures
All experiments were performed in a 500 mL SUS316 stainless steel reactor equipped with a thermometer and a mechanical stirrer. The temperature was controlled by a programmable temperature controller, with a precision of ±2 K. The flow rate of oxygen was controlled by a flow meter. A schematic drawing of the experimental apparatus is shown in Fig. 2.
For each run, KOH was dissolved with water to make a 70%-75% solution, and the vanadium slag was prepared. The solution was heated at a rate of 12 K/min. When the temperature reached the pre-set value and then remained stable, the oxygen or air flow was passed continuously through the reactor to provide an oxidizing atmosphere for the system under atmospheric pressure. Then a predetermined amount of vanadium slag was added into the reactor through the feed inlet port on the lid of reactor. The slurry was intensively stirred under atmospheric pressure to maintain reaction for a period of time. At the end of the reaction, the oxygen or air flow was replaced by N2 and the slurry was diluted and cooled by adding water into the reactor. The diluted slurry was then filtered to obtain a solid residue for Cr and V content analysis. All experimental data were the average of two or three parallel experiments, and the extraction rate of vanadium was calculated by
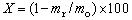 (1)
(1)
where X is the extraction rate of vanadium, mr and mo are the mass of vanadium in the residue and the mass of vanadium in the original vanadium slag, respectively. Similar approach has also been used for the analysis of chromium extraction rate.
The vanadium slag and residue were analyzed using an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer (ICP-AES, PE Optima 5300DV, Perkin Elmer) and the phases were examined with X-ray diffraction (XRD, Phillips PW223/30). SEM images of the vanadium slag and the residue were obtained with a SEM equipment (JEOL, Japan). The particle size distribution of the residue was measured by a laser particle size analyzer (Mastersizer 2000).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Physicochemical properties of MeOH solutions
In this work, instead of NaOH, KOH sub-molten salt was chosen as the reaction medium for the decomposition of vanadium slag due to the superior physiochemical properties of KOH solution in comparison with NaOH solution. Figure 3 shows the relation between the boiling point and the concentration of MeOH (Me denotes as K or Na) solutions [27]. As can be seen in Fig. 3, the boiling point of MeOH solution increases with the solution concentration, and at the same concentration, the boiling point of KOH solution is significantly higher than that of NaOH solution when the MeOH concentration is greater than 50%, suggesting that the reaction can be operated at higher temperatures in KOH medium under ambient pressure, and a relatively high temperature is beneficial for the oxidation of vanadium slag by providing faster reaction kinetics.
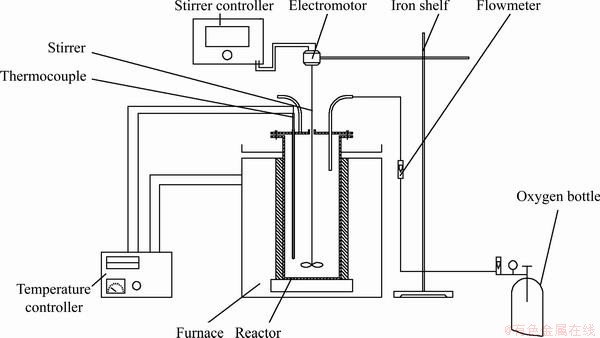
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of experimental apparatus
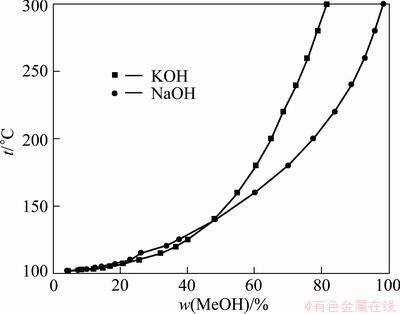
Fig. 3 Relationship between boiling point and concentration of MeOH solution in atmosphere pressure [27]
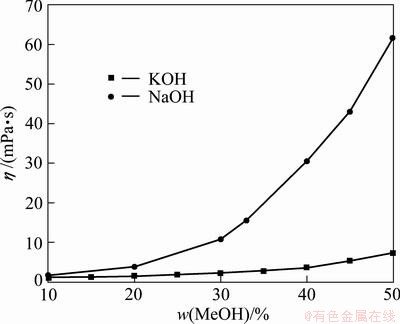
Fig. 4 Comparison of viscosities of NaOH and KOH solutions at 298 K [28]
The viscosities of KOH and NaOH solutions are compared at 298 K [28], and the results are plotted in Fig. 4. As can be seen in Fig. 4, the viscosity increases monotonically with the alkaline concentration, the viscosity of KOH solution is substantially lower than that of corresponding NaOH solution at the same concentration, and the relatively low viscosity favors oxygen diffusion and mass transfer, which is beneficial for the decomposition of vanadium slag.
Further, the oxygen diffusion coefficients [29,30] are presented in Fig. 5. D(O2) values in both KOH and NaOH solutions decrease with the increase of concentration, and D(O2) in KOH solution is always higher than that in corresponding NaOH solution, confirming that the lower viscosity solution is in favor of the oxygen diffusion.
According to the previous studies, oxygen plays an important role in oxidizing the spinels. SUN et al [31] studied the oxidation decomposition of chromite ore in KOH-KNO3-H2O binary sub-molten salt system and found that during the reaction, oxygen was an important reactant, playing an important role in oxidizing Cr3+ to water soluble Cr6+. And they indicated that enhancing oxygen transportation in the system could effectively intensify the decomposition of chromium spinels. Moreover, oxygen dissolved into KOH-KNO 3-H2O melt system could convert to reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as O,  , and O2- to intensify the oxidation of Cr3+. JIN et al [32] reported the effects of ROS in SMS system and they suggested that the superoxide and peroxide ions were stable in basic medium and exhibited high oxidizing activities.
, and O2- to intensify the oxidation of Cr3+. JIN et al [32] reported the effects of ROS in SMS system and they suggested that the superoxide and peroxide ions were stable in basic medium and exhibited high oxidizing activities.
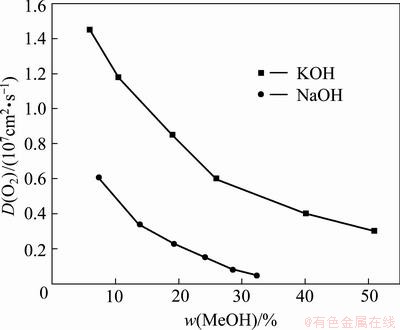
Fig. 5 Oxygen diffusion coefficients in NaOH [29] and KOH [30] solutions at 298 K
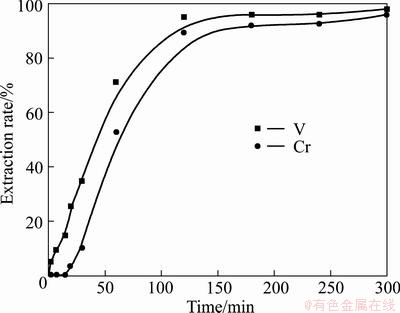
Fig. 6 Relationship between extraction rate of vanadium or chromium and reaction time in KOH sub-molten salt
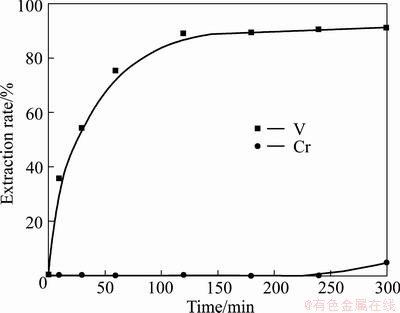
Fig. 7 Relationship between extraction rate of vanadium or chromium and reaction time in NaOH sub-molten salt
In summary, KOH shows superior physiochemical properties to NaOH, and is therefore expected to exhibit better reactivity in the decomposition of vanadium slag. To validate the above conclusion, a test was performed. Under reaction conditions of temperature 210 °C, MeOH-to-ore mass ratio 4:1, alkaline concentration 75%, stirring speed 700 r/min, and gas flow 1 L/min, the decomposition efficiencies of vanadium slag in KOH and NaOH medium were compared, and the results are plotted in Fig. 6 and Fig. 7. It can be seen that the vanadium extraction rates obtained are almost the same in both media. However, there is a significant difference of chromium extraction rates in the two media, and about 90% extraction rate is obtained in KOH medium while almost zero in NaOH medium. The substantial difference between V and Cr extraction rates in KOH and NaOH media is due to the fact that chromium spinel is thermodynamically more stable than vanadium spinel [17,26,31], requiring a more oxidative medium to achieve full oxidation. And as previously discussed, KOH is superior to NaOH in many physicochemical properties, especially in terms of providing a more oxidative reaction medium due to the better oxygen solubility and transportation efficiency [32] and therefore is chosen as the medium for oxidizing vanadium and chromium spinels.
3.2 Reaction mechanisms
Vanadium slag mainly contains spinels (FeV2O4, FeCr2O4), quartz (SiO2) and fayalite (Fe2SiO4). Earlier reports have revealed that the spinel particles were randomly dispersed in fayalite phase and silicon- containing phase is one of the major reasons impeding the oxidation of spinel [33,34]. Thus, the fayalite phase should firstly be decomposed before the vanadium and chromium spinels were oxidized [17]. In KOH SMS medium, due to its high alkalinity, fayalite and quartz could readily react with KOH and O2. Followed by the dissolution of fayalite, vanadium and chromium spinels are exposed to the reaction medium for further reactions. In the presence of oxygen, the vanadium and chromium spinels will be rapidly decomposed and oxidized to produce water soluble potassium vanadate and potassium chromate.
3.3 Effect of agitation
In order to improve the extraction rates of vanadium and chromium, it is desirable to apply intense agitation to forming homogenous suspension and allowing efficient mixing of particles in the reaction medium. The effects of agitation on the extraction of vanadium and chromium were investigated in 75% KOH solution at 180 °C with alkali-to-ore mass ratio of 4:1. The stirring speed was from 100 to 900 r/min, and the results are shown in Figs. 8 and 9. In Figs. 8 and 9, it is observed that the extraction rates of vanadium and chromium firstly increase with the increase of the stirring speed due to the improved transportation of reactants in the medium. Further, when the stirring speed is higher than 700 r/min, the influence of external mass transfer becomes negligible, and the extraction rates of vanadium and chromium become independent of stirring speed. Similar observation has also been reported by LIU et al [35] and the results showed that the extraction rate of titanium increased with the increase of the stirring speed due to the mass transportation with strong agitation. Therefore, a stirring speed of 700 r/min was chosen for further experiments.
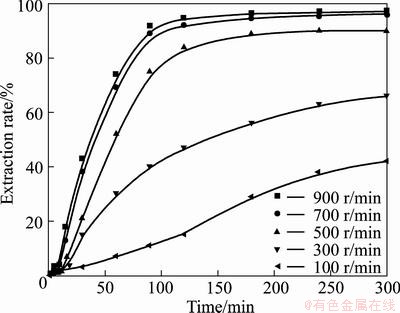
Fig. 8 Effect of stirring speed on vanadium extraction rate
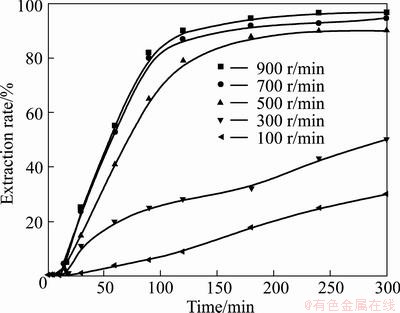
Fig. 9 Effect of stirring speed on chromium extraction rate
3.4 Effect of KOH-to-ore mass ratio
The amount of KOH used during the reactions is also an important factor influencing the mass transportation. The effects of alkali-to-ore mass ratios on the extraction of vanadium and chromium were investigated under conditions of temperature 180 °C, 75% KOH solution, stirring speed 700 r/min, and gas flow 1 L/min. The alkali-to-ore mass ratios of 3:1, 4:1 and 5:1 were examined, and the results are shown in Figs. 10 and 11. The results demonstrate that the extraction rates of vanadium and chromium increase with the increase of alkali-to-ore mass ratios from 3:1 to 4:1, which is attributed to the fact that the increase of the alkali-to-ore mass ratio decreases the viscosity of the slurry, favoring the mass transportation of the reactants in the system. Further, the increase of the alkali-to-ore mass ratios from 4:1 to 5:1 does not provide further improvement for the dissolution of vanadium slag as suggested by the negligible enhancement of vanadium and chromium extraction rates. Moreover, regardless of the difference in alkali-to-ore mass ratio, the extraction rates of both vanadium and chromium can reach up to 90% after 4 h, suggesting that the adjustment of the alkali-to-ore mass ratio can only change the reaction kinetics and has little effect on the reaction thermodynamics. Furthermore, it is noticed that when the alkali-to-ore mass ratio is less than 3:1, the system becomes too viscous to be mechanically stirred, and therefore it has not been investigated. Similar observation has also been reported by LIU el al [35] and their results suggested that the extraction rate of titanium increases with the increase of KOH-to-ore mass ratio because of the decrease of the suspension density and viscosity of the system. In view of the above discussion, the ratio of 4:1 is thus recommended for the following experiments.
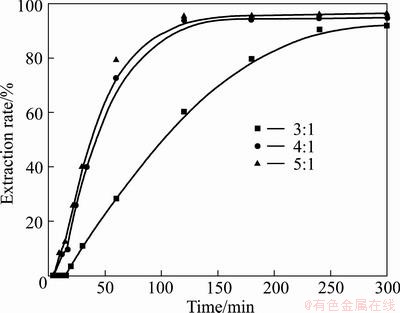
Fig. 10 Effect of KOH-to-ore mass ratio on vanadium extraction rate
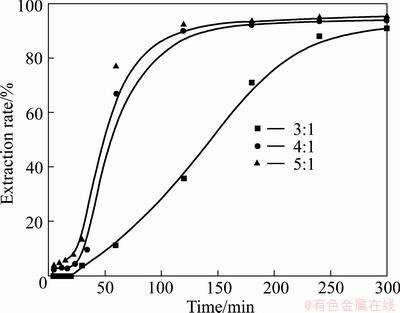
Fig. 11 Effect of KOH-to-ore mass ratio on chromium extraction rate
3.5 Effect of particle size
The dependence of vanadium and chromium extraction efficiency on particle size of vanadium slag particles was examined in 75% KOH solution at 180 °C with alkali-to-ore mass ratio of 4:1 with 48-75, 75-96, 96-150, and 150 μm, and the results are shown in Figs. 12 and 13. Figures 12 and 13 show that the extraction rate improves significantly when the particle size is less than 96 μm, and further reduction in particle size does not improve the extraction of vanadium and chromium. It is known that the specific surface area of particles increases as the particle size decreases. The increase of solid reactant surface area promotes the contact between vanadium slag and the KOH sub-molten salt, thus improves the reaction efficiency. Similar observation has also been reported by LIU el al [35], and the results suggested that the particle size of ilmenite had a significant effect on the decomposition of ilmenite and the extraction rate of titanium is inversely proportional to the average diameter of the initial particles. However, the sustained decrease of the particle size leads to the increase in viscosity of the sub-molten system, which is bad for the O2 transmission. And O2 transmission is critical for the oxidation of vanadium and chromium. Thus, when the particle size is reduced to less than 96 μm, further reduction in particle size does not improve the extraction rates of vanadium and chromium. However, the energy consumption for grinding particles is inversely proportional to the particle size, and it would be more valuable to perform experiments utilizing particle with similar size to that from industrial batch production, which is 75-96 μm. Thus, the particle size less than 75 μm was chosen for further studies.
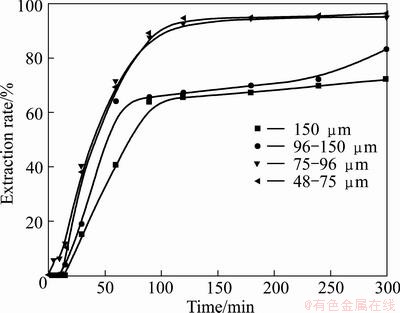
Fig. 12 Effect of particle size on vanadium extraction rate
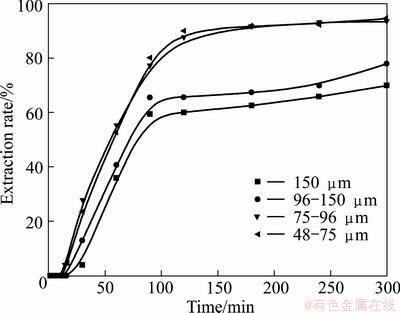
Fig. 13 Effect of particle size on chromium extraction rate
3.6 Effect of temperature
As shown in Figs. 14 and 15, the increase of temperature can accelerate the oxidation of vanadium and chromium spinels. From Fig. 14, it can be observed that at temperature lower than 165 °C, the vanadium extraction rate after 120 min is less than 56%, while at 180 °C the extraction rate is nearly 90%. In Fig. 15, at temperature below 165 oC, the chromium extraction rate after 180 min is less than 52%, but at 180 °C the extraction rate is nearly 86%. This is because increasing the temperature will not only accelerate the oxidation, but also decrease the viscosity of the medium, and consequently increase the oxygen solubility and diffusion efficiency, favoring the decomposition reactions [36]. Similar temperature dependency of chromium extraction efficiency on temperature has been reported by ZHENG el al [25]. Further, at temperature of 150 °C, the extraction rate of vanadium is 84% after 360 min, while only 62% for chromium, indicating that chromium spinel is more stable than vanadium, which is in good agreement with previous thermodynamics analysis [17]. When temperature is above 180 °C, the extraction rates of vanadium and chromium do not show a significant increase with temperature, and thus the temperature of 180 °C is recommended for further studies.
From the above analyses, it is found that the effect of reaction temperature on the extraction of vanadium and chromium is much more significant than that of the other three factors. The results of factorial experiments suggested that the increase of temperature, KOH-to-ore mass ratio, stirring speed, and decrease of vanadium slag particle size are beneficial for the extraction of vanadium and chromium. Under the optimal conditions of temperature 180 °C, initial KOH-to-ore mass ratio 4:1, stirring speed 700 r/min, and gas flow 1 L/min, extraction rates of vanadium and chromium can reach up to 95% and 90% after 300 min, respectively.
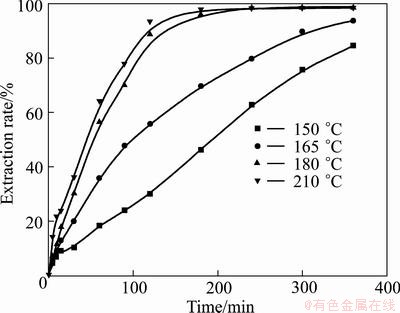
Fig. 14 Effect of temperature on vanadium extraction rate
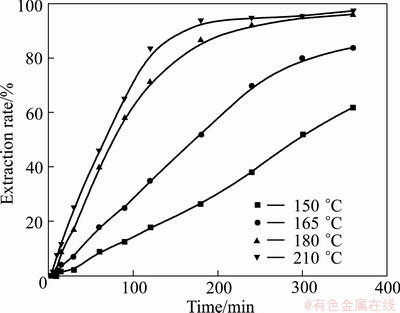
Fig. 15 Effect of temperature on chromium extraction rate
3.7 Kinetics analysis
The extraction of vanadium and chromium was analyzed with the shrinking core model under the assumption that the ore is homogeneously spherical solid phase [17].
In order to determine the kinetics, three established kinetic models [17,37] were usually used, and expressed by the following equations.
1) Liquid boundary layer diffusion control
X=kt (2)
2) Solid product layer diffusion control
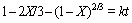 (3)
(3)
3) Surface reaction control
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
where X is the extraction rate of vanadium or chromium, k is the overall rate constant, μ is the stoichiometric coefficient, M is the molecular mass of the solid reactant, D is the diffusion coefficient, cA is the KOH concentration, ρ is the density of the particle and r is the radius of vanadium slag particle.
To reveal the controlling step of the vanadium extraction, the conversion data of vanadium at 165 °C in Fig. 14 were fitted into Eqs. (2), (3) and (4) shown in Fig. 16. The results show that both Eq. (3) and Eq. (4) fit the experimental data perfectly. Therefore, it is clear that both surface reaction and diffusion of solid product layer are controlling steps for the vanadium oxidation reaction. Further analysis of particle size effect (Fig. 12) suggests that for particles larger than 96 um, after fast extraction during the first 100 min, the extraction rate of vanadium reaches plateau, and increases slowly with reaction time possibly due to the formation of thick product layer (Fig. 13), inhibiting the diffusion of reactants. In this regards, it is reasonable to describe the vanadium extraction reaction as mainly being controlled by the solid product layer diffusion. Any measure that can improve the inner mass transfer in the residue layer, such as the increase of temperature and decrease of the particle size, would enhance the decomposition [31].
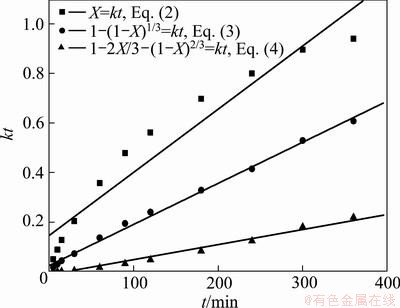
Fig. 16 Vanadium extraction rate vs time fitted by three kinetics equations at 165 °C
The extraction rates of vanadium at different temperatures are fitted in Fig. 17, and the value of k is obtained, where k is the reaction rate constant corresponding to the slopes of the straight lines. Then the specific apparent activation energy can be calculated based on the Arrhenius equation shown in Fig. 18:
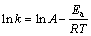 (6)
(6)
where Ea is the apparent activation energy, A is the pre-exponential factor, and R is the molar gas constant.
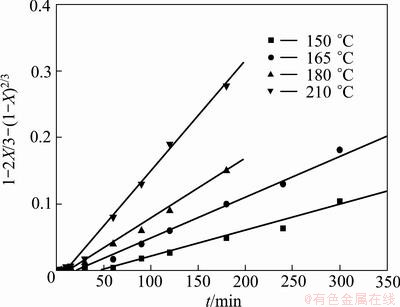
Fig. 17 Plot of extraction kinetics of vanadium at various reaction temperatures
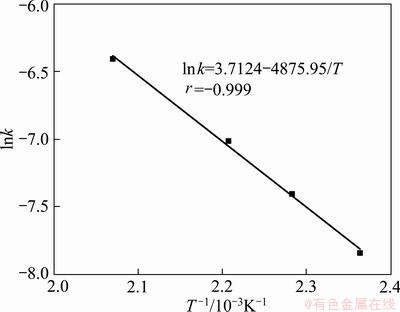
Fig. 18 Natural logarithm of reaction rate constant versus reciprocal temperature of vanadium
The apparent activation energy of vanadium extraction is calculated to be 40.54 kJ/mol. Because the solid product layer diffusion control model fits the experiment data perfectly and the value of Ea is relatively low, it is plausible to propose that the oxidation extraction of vanadium is controlled by mass diffusion in the product (residue) layer.
Similarly, to reveal the controlling step of the chromium extraction, the extraction rates of chromium at 165 °C in Fig. 15 are also fitted into Eqs. (2)-(4), as shown in Fig. 19. The results show that both Eqs. (3) and (4) give very good linear relationships, but the latter gives better linear correlation with the correlation coefficient of 0.999.
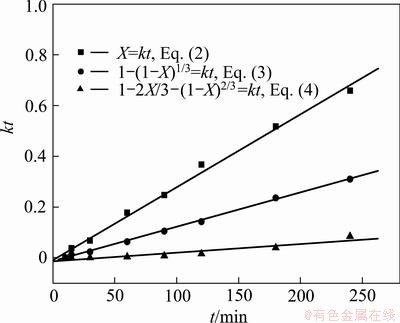
Fig. 19 Chromium extraction rate vs time at 165 °C fitted by three kinetics equations
Because both vanadium and chromium exist as spinel, their extraction kinetics in KOH SMS shares similarity. Previous analysis of vanadium suggests that mass diffusion in the product (residue) layer is the controlling step. So the extraction of chromium is also expected to be controlled by internal diffusion. However, due to the fact that the chromium spinel is more difficult to be oxidized than vanadium as previously discussed, the extraction of chromium is thus believed to be controlled by both surface reaction and solid product layer diffusion, and the former has a more significant effect.
Then extraction rates of chromium at different temperatures are fitted in Fig. 20 and the apparent activation energy of chromium extraction is calculated to be 50.27 kJ/mol (Fig. 21). The value is higher than that of vanadium, indicating that the extraction of chromium is controlled by both surface reaction and solid product layer diffusion.
3.8 XRD and SEM analysis of residue
The phase changes of vanadium slag with time are shown in Fig. 22. The diffraction patterns of fayalite and quartz phase quickly disappear after reaction for 15 min, suggesting that silicon-rich phases easily dissolve in KOH sub-molten salt. However, the decomposition of vanadium and chromium spinels proceeds progressively. The spinels can be completely oxidized after 4 h, as indicated by the vanishing of spinel structural diffraction peaks. The typical composition of residues at different time is listed in Table 2. In comparison with Table 1, the vanadium and chromium contents are obviously decreased to below 0.7% (in terms of their oxides), and the tailing mainly contains ferric oxides.
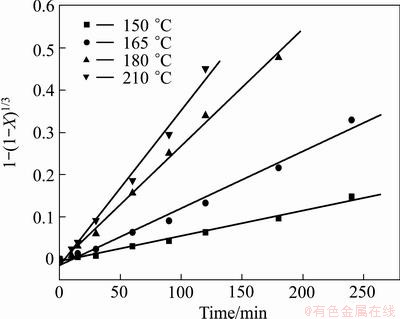
Fig. 20 Plot of extraction kinetics of chromium at various reaction temperatures
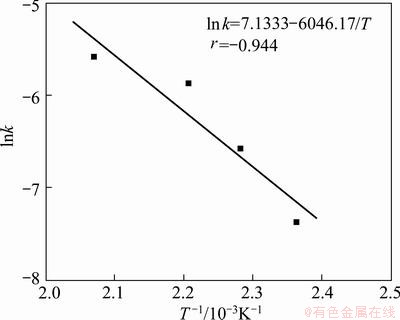
Fig. 21 Natural logarithm of reaction rate constant vs reciprocal temperature of chromium
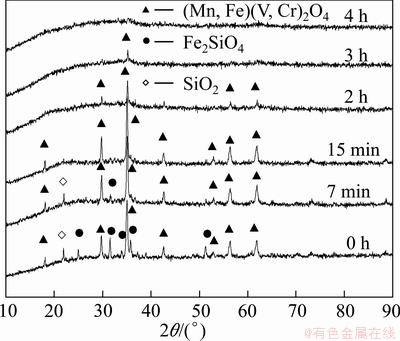
Fig. 22 XRD patterns of residues at different time
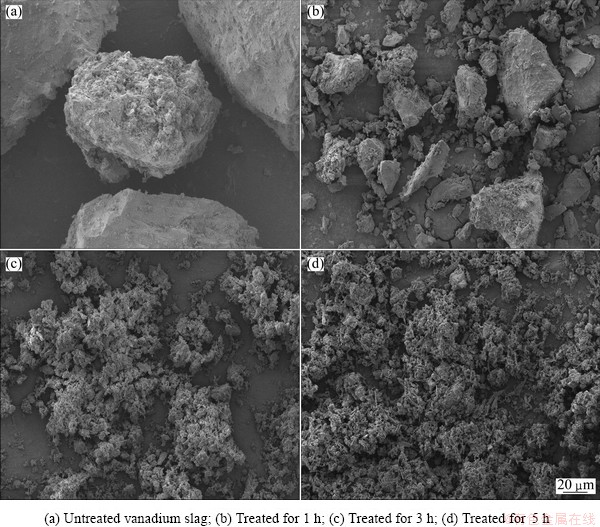

Fig. 23 SEM images of residues at different time
Table 2 Chemical composition of residues at different time
The SEM images of the vanadium slag particles treated at 180 °C are shown in Fig. 23. It can be seen that the untreated slag particles are featured as compact solids with smooth surface, and the surface becomes rough and porous after 1 h due to the decomposition reactions. Finally, the spinel particles are destroyed by the sub-molten salt and tiny ferric oxide particles are formed in the residues.
4 Conclusions
1) Under the optimal conditions of temperature 180 °C, initial KOH-to-ore mass ratio 4:1, stirring speed 700 r/min, and gas flow 1 L/min, vanadium and chromium extraction rates can reach up to 95% and 90% after 300 min, respectively.
2) Various parameters for the extraction of vanadium and chromium were investigated. The increase of temperature, mass ratio of KOH-to-ore, stirring speed, and decrease of vanadium slag particle size are beneficial for the extraction of vanadium and chromium.
3) The kinetics study reveals that decomposing process of vanadium slag in KOH sub-molten salt is well interpreted with the shrinking core model under internal diffusion control. The apparent activation energies of vanadium and chromium dissolution are 40.54 and 50.27 kJ/mol, respectively.
4) XRD analysis shows that vanadium and chromium spinels are oxidized after the decomposition of fayalite and quartz phase.
References
[1] MOSKALYK R R, ALFANTAZI A M. Processing of vanadium: A review [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003, 16(8): 793-805.
[2] WANG Shao-na, SONG Zi-wei, ZHANG Yan, DU Hao, ZHANG Yi. Solubility data for the NaOH-NaNO3-Na3VO4-Na2CrO4-H2O system at (40 and 80) °C [J]. J Chem Eng Data, 2010, 55(11): 4607-4610.
[3] HAYES E. Chromium and vanadium [J]. Ind Eng Chem, 1961, 53(2): 105-107.
[4] YANG Shao-li, LIU Guo-qin, CHEN Hou-sheng. V and Ti material [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009: 4-5. (in Chinese)
[5] LI Lan-jie, DU Hao, YANG Na, WANG Shao-na, ZHENG Shi-li, ZHANG Yi. Solubility in the quaternary Na2O-V2O5-CaO-H2O system at (40 and 80) oC [J]. J Chem Eng Data, 2011, 56(10): 3920-3924.
[6] QIU Shuang, WEI Chang, LI Ming-ting, ZHOU Xue-jiao, LI Chun-xiong, DENG Zhi-gan. Dissolution kinetics of vanadium trioxide at high pressure in sodium hydroxide-oxygen system [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 105: 350-354.
[7] RAJAB V R. Vanadium market in the world [J]. Steel World, 2007, 13(2): 19-22.
[8] DUAN Lian, TIAN Qing-hua, GUO Xue-yi. Review on production and utilization of vanadium resources in China [J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 22(6): 17-20. (in Chinese)
[9] WANG Jin-chao. Effect of calcium on leaching of vanadium from vanadium slag [J]. Sichuan Nonferrous Metals, 2004(4): 27-29. (in Chinese)
[10] LI Xin-sheng, XIE Bing, WANG Guang-en, LI Xiao-jun. Oxidation process of low-grade vanadium slag in presence of Na2CO3 [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(8): 1860-1867.
[11] BIN Zhi-yong. Study on extraction of V2O5 from vanadium ore by roasting and acid leaching process [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2006, 27(1): 21-26. (in Chinese)
[12] YANG Jing-ling, JIN Xin. A new way of recovering vanadium from iron/vanadium slag [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2007, 34(3): 254-257. (in Chinese)
[13] CAO Lai-zong, LIU Dai-jun, GAO Li-hua, LIU Chang-hong, SHEN Qian. Experimental study on leaching vanadium by sub-molten salt method [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2008, 29(2): 1-4. (in Chinese)
[14] LOZANO L J, GODINEA C. Comparative study of solvent extraction of vanadium from sulphate solutions by Primene 81R and alamine 336 [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003, 16(3): 291-299.
[15] JI Yun-bo, TONG Xiong, YE Guo-hua. Research and progress of vanadium extraction technology [J]. Metallic Ore Dressing Abroad, 2007, 44(1): 10-13. (in Chinese)
[16] XIAO Qing-gui, CHEN Yin, GAO Yi-ying, XU Hong-bin, ZHANG Yi. Leaching of silica from vanadium-bearing steel slag in sodium hydroxide solution [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104: 216-221.
[17] LIU Biao, DU Hao, WANG Shao-na, LI Lan-jie, CHEN Dong-hui, ZHANG Yi, ZHENG Shi-li. A novel method to extract vanadium and chromium from vanadium slag using molten NaOH-NaNO3 binary system [J]. AIChE Journal, DOI: 10.1002/aic.13819.
[18] ZHANG Yi. The green process engineering science [J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2001, 1(1): 10-15. (in Chinese)
[19] ZHENG Shi-li, DU Hao, WANG Shao-na, WANG Xiao-hui, ZHANG Yi, CHEN Dong-hui. A liquid-phase oxidation process of vanadium slag in a molten salt medium: China, 201010034089.5 [P]. 2010-07-20. (in Chinese)
[20] ZHANG Yi, LI Zuo-hu, QI Tao, ZHENG Shi-li, LI Hui-quan, XU Hong-bin. Green manufacturing process of chromium compounds [J]. Environmental Process, 2005, 24(1): 44-50.
[21] XU Hong-bin, ZHENG Shi-li, ZHANG Yi, LI Zuo-hu, WANG Zhi-kuan. Oxidative leaching of a Vietnamese chromite ore in highly concentrated potassium hydroxide aqueous solution at 300 oC and atmosphere pressure [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18: 527-535.
[22] ZHANG Yi, LI Zuo-hu, QI Tao, WANG Zhi-kuan, ZHENG Shi-li. Green chemistry of chromate cleaner production [J]. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 1999, 17(3): 258-266.
[23] ZHANG Yi, LI Zuo-hu, WANG Zhi-kuan, CHEN Jia-yong. Green chemistry and new revolution of chromic salts industry [J]. Progress in Chemistry, 1998, 10(2): 172-178. (in Chinese)
[24] ZHOU Hong-ming, YI Dan-qing, ZHANG Yi, ZHENG Shi-li. The dissolution behavior of Nb2O5, Ta2O5 and their mixture in highly concentrated KOH solution [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2005, 80: 126-131.
[25] ZHENG Shi-li, ZHANG Yi, LI Zuo-hu, QI Tao, LI Hui-quan, XU Hong-bin. Green metallurgical processing of chromite [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2006, 82(3): 157-163.
[26] LIU Hui-bin, LIU Biao, LI Lan-jie, ZHENG Shi-li, DU Hao, WANG Shao-na, CHEN Dong-hui, QI Jian, ZHANG Yi. Novel methods to extract vanadium from vanadium slag by liquid oxidation technology [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 396-398: 1786-1793.
[27] LIU Guang-qi, MA Lian-xiang, LIU Jie. Physical property data handbook of chemistry and chemical Industry (inorganic volume) [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002: 281-303. (in Chinese)
[28] HITCHCOCK L B, MCILHENNY J S. Viscosity and density of pure alkaline solutions and their mixtures [J]. Ind Eng Chem, 1935, 27: 461-466.
[29] ZHANG C Z, FAN F R, BARD A J. Electrochemistry of oxygen in concentrated NaOH solutions: Solubility, diffusion coefficients, and superoxide formation [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(1): 177-181.
[30] GUBBINS K E, THAM M K, WALKER R D. Diffusion of oxygen and hydrogen in aqueous potassium hydroxide solution [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1970, 74(8): 1747-1751.
[31] SUN Zhi, ZHANG Yang, ZHENG Shi-li, ZHANG Yi. A new method of potassium chromate production from chromite and KOH-KNO3-H2O binary sub-molten salt system [J]. AIChE Journal, 2009, 55(10): 2646-2656.
[32] JIN Wei, DU Hao, ZHENG Shi-li, XU Hong-bin, ZHANG Yi. Comparison of the oxygen reduction between NaOH and KOH solutions on a Pt electrode: The electrolyte-dependent effect [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2010, 114(19): 6542-6548.
[33] LIAO Shi-ming, BO Tan-lun. Vanadium metallurgy in foreign countries [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1985: 191-197. (in Chinese)
[34] XIAO Song-wen, LIANG Jing-dong. Advances in the vanadium extraction by roasting in the presence of sodium salts [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 1994, 14(2): 53-55. (in Chinese)
[35] LIU Yu-min, QI Tao, CHU Jing-long, TONG Qi-jie, ZHANG Yi. Decomposition of ilmenite by concentrate KOH solution under atmosphere pressure [J]. Mineral Processing, 2006, 81(2): 79-84.
[36] THROMANS D. Oxygen solubility in inorganic solutions: Concentration, temperature and pressure effects [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1998, 50: 279-296.
[37] ZHANG Yang, ZHENG Shi-li, XU Hong-bin, DU Hao, ZHANG Yi. Decomposition of chromite ore by oxygen in molten NaOH-NaNO3 [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2010, 95: 10-17.
刘挥彬1,2,3,杜 浩1,王大卫4,王少娜1,郑诗礼1,张 懿1
1. 中国科学院 过程工程研究所 湿法冶金清洁生产技术国家工程实验室,北京 100190;
2. 中国科学院大学,北京 100049;
3. 中国恩菲工程技术有限公司,北京 100038;
4. 中国矿业大学(北京) 化学与环境工程学院,北京 100083
摘 要:开发了一种常压下用KOH亚熔盐介质氧化分解钒渣的新工艺,并考察了反应温度、碱矿质量比、粒度、搅拌速率等工艺参数对钒铬浸出的影响。结果表明,反应温度、碱矿比是最重要的影响因素;在反应温度180 °C、碱矿质量比4:1、搅拌速率700 r/min、通氧气流量1 L/min的条件下,反应进行300 min后钒、铬的浸出率分别达到了95%和90%。动力学分析表明,钒渣在KOH亚熔盐介质中的氧化分解遵循缩核模型,并受内扩散控制。钒铬尖晶石分解反应的表观活化能分别为40.54和50.27 kJ/mol。
关键词:钒渣;尖晶石;亚熔盐法;动力学分析;分解;活化能
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Foundation item: Project (2013CB632605) supported by the National Basic Research Development Program of China; Projects (51274178, 51274179) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Hao DU; Tel: +86-10-82544857; E-mail: duhao121@hotmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62621-7

