文章编号:1004-0609(2011)08-1785-09
镁合金等通道转角挤压过程中的晶粒细化机制
何运斌1, 2,潘清林1, 2,刘晓艳1, 2,李文斌1, 2
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用金相显微镜、背散射电子衍射(EBSD)和透射电子显微镜(TEM)分析ZK60镁合金在等通道转角挤压(ECAP)过程中不同部位的显微组织特征。结果表明:ZK60镁合金经240 ℃ ECAP变形1道次后,合金的晶粒得到明显细化,但组织仍不均匀。剪切变形前,合金组织主要为粗大晶粒并伴有大量孪晶,剪切区的组织主要为剪切变形带和少量再结晶组织;剪切变形后,合金的晶粒组织主要为再结晶组织;合金ECAP过程的晶粒细化主要为机械剪切和动态再结晶的综合作用。
关键词: ZK60镁合金;ECAP;动态再结晶
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Grain refinement mechanism of magnesium alloy during equal channel angular pressing process
HE Yun-bin1, 2, PAN Qing-lin1, 2, LIU Xiao-yan1, 2, LI Wen-bin1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Metal Materials Science and Engineering, Ministry of Education,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The microstructure evolution of ZK60 alloy during ECAP process was investigated by optical microscopy, electron backscattered diffractometry (EBSD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results show that, after one pass of equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) process at 240 ℃, the grain size of ZK60 alloy is significantly refined. However, the grain size distribution is not homogeneous. The microstructure prior to shear deformation is consisted of coarse grains and twins. The microstructure in the shear zone is mainly shear bands and dynamic recrystallized grains. After shear deformation, the grain structure is mainly dynamic recrystallized grains. The grain refinement mechanism for ECAP of ZK60 alloy is comprehensive effect of shear deformation and dynamic recrystallization.
Key words: ZK60 magnesium alloy; ECAP; dynamic recrystallization
镁合金由于密度小、比强度和比刚度大、阻尼性能好、易于回收等优点,被誉为21世纪最具发展前途的绿色工程材料[1-3]。鉴于这些优点,镁合金在汽车、航空航天和电子通讯等许多等领域有广阔的应用前景。但是由于其塑性较低,因此,镁合金的塑性加工存在很大的困难。而细化晶粒是提高合金塑性的有效手段,近年来,等通道转角挤压(ECAP)作为制备细晶 材料的加工手段,近年来受到越来越多的关注[4-8]。ECAP方法也在镁合金中得到大量应用,用于制备细晶镁合金[9-15]。由于ECAP变形前后试样的尺寸没有变化,因此,可以对样品进行多道次的ECAP变形而得到较大的应变累积。研究表明[10-11],经过多道次ECAP挤压变形后,镁合金的晶粒可以细化到1 μm以下。经ECAP变形后,合金的塑性明显提高,且在一定温度和应变速率下,还可表现出良好的超塑性[9, 11, 13, 15]。虽然ECAP方法已经广泛应用于各种细晶材料,但对于其晶粒细化机制,却仍然没有一个统一的认识。比较一致的观点认为,细化过程是通过剧烈的剪切变形,使金属内部原本粗大的组织不断破碎,同时剧烈的变形使金属内部位错等各种缺陷密度急剧的增殖,位错的运动与重组导致大角度晶界的形成,最终形成细化的等轴晶粒。IWAHASHI等[16]从实验上研究ECAP变形路径对材料晶粒细化的影响,认为剪切面对材料的晶粒细化有主要影响,但是对具体剪切面如何影响晶粒细化没有做出解释。虽然ZHU和LOWE[17]对其观点进行了补充,认为剪切面与织构以及晶体结构的相互作用是晶粒细化的主要原因,应变的累积是次要因素,但没有考虑变形温度的影响。以上机制基本上是基于Al合金等塑性比较好的FCC合金在低温下变形而建立起来的,但对于镁合金而言,由于其低温塑性较差,一般需要在较高温度下变形,因此,动态再结晶也是一个重要的晶粒细化机制,本文作者通过对ZK60镁合金在240 ℃进行1道次ECAP挤压,分析对比ECAP过程中不同区域的显微组织,探讨镁合金ECAP过程中的晶粒细化机制。
1 实验
本研究的材料为工业ZK60镁合金挤压棒材,其化学成分如表1所列。合金棒材经 465 ℃、10 h固溶处理后,采用电火花切割成d 20 mm×100 mm的ECAP试样。
ECAP挤压采用的模具为圆形通道,通道直径为20 mm,两通道夹角为90°,外弧圆角为20°。为获得剪切区的微观组织,合金在通道内挤下一半长度后取出试样并淬入到水中,然后将试样沿挤压方向切开进行微观组织观察。
微观组织观察取样平行于ECAP挤压方向,分别在剪切区前、剪切区和剪切区后取样,标示为A区、B区和C区,如图1所示。金相组织观察样品经机械抛光后,用金相腐蚀剂1 g草酸+1 g醋酸+1 mL浓硫酸+100 mL蒸馏水进行腐蚀,然后在金相显微镜下观察晶粒大小和形态。EBSD试样经机械抛光后,在5%的高氯酸酒精溶液中进行电解抛光,以消除表面残余应力。EBSD在FEI Sirion200上进行观察,加速电压为25 kV。 TEM观察样品经机械减薄至0.8 μm后冲成3 mm的圆片,最后进行离子减薄。TEM观察在Tecnai G2 20 上进行,加速电压为200 kV。
表1 ZK60 镁合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of ZK60 magnesium alloy (mass fraction, %)
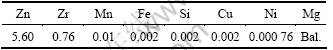
图1 合金微观组织观察取样示意图
Fig.1 Sampling of specimens for microstructure observation
2 结果与分析
2.1 金相组织
图2所示为ZK60合金在240 ℃ ECAP变形1道次过程中合金不同区域的变形组织。图2(a)所示为合金进入剪切区前的组织。从图2(a)可以看出,合金中的组织主要为等轴晶粒,同时由于受到较大挤压力的作用,在进入剪切区前经历了镦粗变形,所以在粗大晶粒中还伴随有孪晶的产生;进入剪切区后,因为通道的转角作用,原始晶粒沿着剪切面发生了明显的拉长和变形,在合金中形成了许多细长的沿挤压方向约呈45°的剪切带,沿着这些剪切带,形成了大量细小的再结晶晶粒,如图2(b)所示。这主要是在剪切变形过程中,剪切变形带内发生剧烈变形,具有很高的储能,为镁合金的再结晶提供了驱动力; 在离开剪切区后,合金的组织仍然在发生变化,除了粗大的变形晶粒外,合金的晶粒组织仍然以细长剪切带和细小的再结晶晶粒为主,但与剪切区的组织相比,细小再结晶晶粒的比例有所提高,如图2(c)所示。总体上来说,经过ECAP变形1道次后,合金的晶粒得到明显的细化,但合金的晶粒大小仍然不均匀。
图3所示为图2(b)中细长剪切带的放大金相组织。从图3可以看出,在这些剪切带内部还存在一些晶界把剪切带分割成几部分,表明在剪切变形带内已经开始发生再结晶,如图3(a)所示。而有些剪切带则已经发生完全再结晶,一些稍宽的剪切带内已经被细小的再结晶晶粒取代,如图3(b)所示。
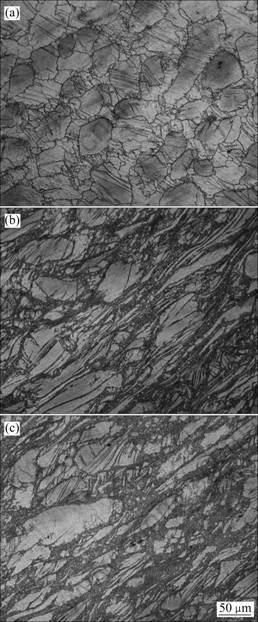
图2 ZK60合金在240 ℃ ECAP变形1道次过程中不同位置的显微组织
Fig.2 Microstructures evolutions of different locations along ECAP die of ZK60 magnesium alloy during one pass ECAP at 240 ℃: (a) Before shearing, position A; (b) Shear zone, position B; (c) After shearing, position C
2.2 TEM显微组织
图4所示为ZK60合金在ECAP过程中典型的TEM显微组织。从图4可以看出,合金的组织主要由晶粒内部位错缠结形成的胞状组织和亚晶组织为主,如图4(a)所示。进一步观察可以发现,在一些局部区域,位错重新排列成了亚晶界。这是因为在变形初期,ECAP的强剪切变形导致了高密度的位错缠结,而相互缠结的位错间存在较大的应力场,根据低能位错结构理论[18],这些位错会相互作用并重新排列,形成如图4(b)中的亚晶结构。
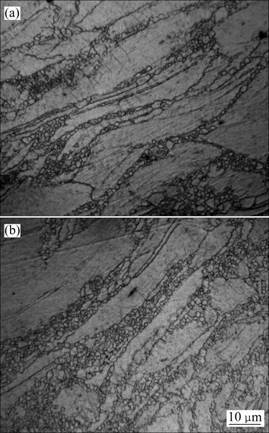
图3 剪切区中的金相组织
Fig.3 Optical microstructures of shear zone: (a) Recrystallized grain along shear bands; (b) Shear bands fully recrystallized
随着变形程度的增加,在亚晶粒内部产生更多的位错,且这些可动位错很容易被亚晶界进一步吸收,演化成大角度晶界,从而形成稳定的再结晶晶粒,如图4(c)和(d)所示。与ECAP变形前的晶粒相比,这些再结晶晶粒要小得多,因此,合金晶粒得到明显细化。
由于受强烈剪切变形,在剪切区中存在大量平行、呈长条状的剪切变形带。在剪切变形带内,位错密度迅速增加,并导致大量的位错缠结,如图5(a)所示。这些缠结的位错在变形剪切带的内部同样形成了如图5(b)所示位错界面。在剪切力的作用下,取向有利的晶粒首先开动易滑移系,部分晶粒由于位错堆积、晶粒发生转动等原因,随后开动其他滑移系,其结果导致先开动的滑移系被后启动的滑移系分割,因此,剪切带内出现大量的位错胞。在离开剪切变形区后,位错缠结形成的胞状组织逐渐形成小角度的亚晶界,如图5(c)所示。并最终转化成大角度晶界,如图5(d)所示。
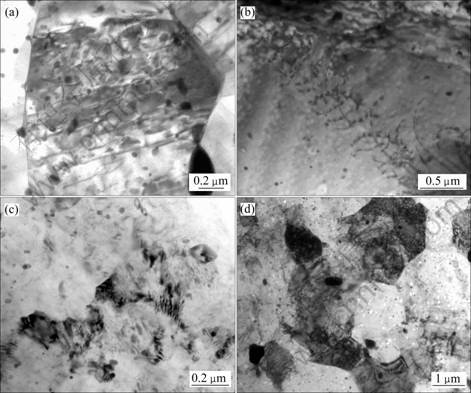
图4 ZK60镁合金ECAP过程中典型的TEM像
Fig.4 Typical TEM images of ZK60 magnesium alloy during ECAP process: (a) Dislocation entanglement; (b) Non-equilibrium grain boundaries; (c) Subgrain structure; (d) Rrecrystallized grains
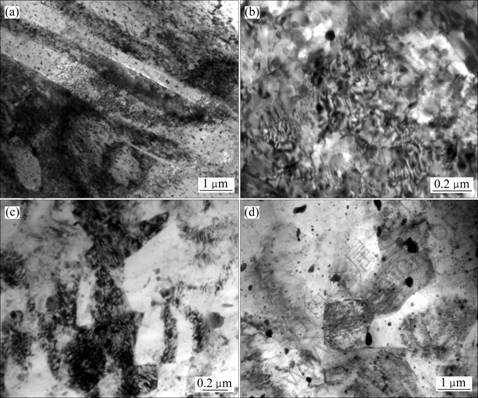
图5 ZK60合金ECAP变形过程中的剪切带组织
Fig.5 Shear band features of ZK60 magnesium alloy during ECAP process: (a) Shear bands; (b) Cell structure in shear bands; (c) Subgrains along shear bands; (d) Recrystallized grains along shear bands
2.3 EBSD分析
图6所示为ZK60合金ECAP前的晶粒取向分布图。图6(a)所示为合金原始挤压态的晶粒取向分布图。可以看出,合金晶粒为典型的混晶组织,其中大晶粒尺寸大于100 μm,而小晶粒尺寸则小于10 μm。在进入剪切变形区前,合金的晶粒组织发生已很大的变化,在一些大晶粒的内部出现大量的剪切带组织,如图6(b)所示。图6(c)显示了剪切变形带之间的取向差,可以看出,各剪切带之间的取向差基本上在40°~70°之间分布。
图7所示为ECAP过程中剪切区和经过剪切区后的晶粒取向分布图。从图7(a)可以看出,合金中的剪切变形带明显减少,大量细小的再结晶晶粒沿着剪切变形带形核长大,在剪切带周围形成了一圈细小的再结晶晶粒,形成了所谓的项链状组织。而离开剪切区后,合金晶粒组织仍然发生变化,合金中的细小再结晶晶粒明显增加。
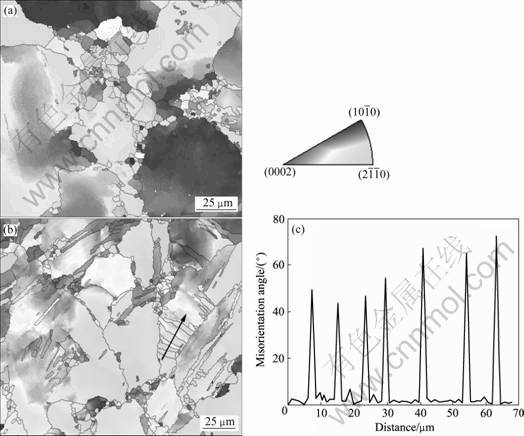
图6 ZK60合金原始挤压态和ECAP变形前的晶粒取向分布图
Fig.6 Orientation imaging microscopy (OIM) mapping of as-extruded and pre-ECAP ZK60 magnesium alloy: (a) As-extruded; (b) Before shearing; (c) Misorientation maps of shear bands in (b)
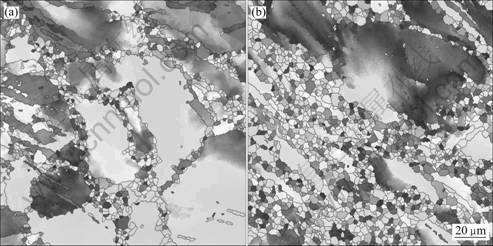
图7 ZK60合金ECAP变形过程中的晶粒取向分布图
Fig.7 OIM mapping of ZK60 magnesium alloy during ECAP process: (a) Shear zone; (b) After shearing
图8所示为采用EBSD分析软件对ECAP过程中不同区域合金的晶粒大小分布的分析结果。在进入剪切变形区前,合金中主要是大于50 μm的大晶粒,其平均晶粒约为45.3 μm;经过剪切变形后,合金的晶粒得到明显细化,合金中粒径小于10 μm的小晶粒分数明显增加,其平均晶粒尺寸约为36.1 μm;而离开剪切区后,合金中的小晶粒分数进一步增加,大部分晶粒尺寸都小于10 μm,平均晶粒尺寸为5.4 μm。
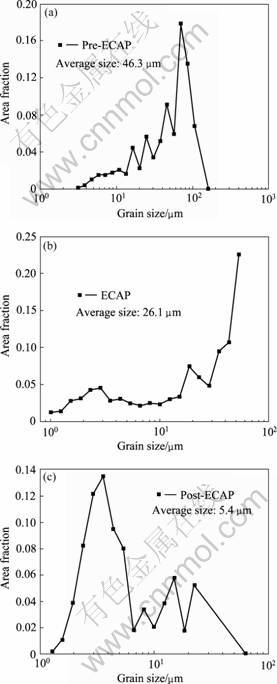
图8 ZK60合金ECAP过程中进入变形剪切区前的晶粒尺寸分布图
Fig.8 Grain size distribution of ZK60 alloy at different locations during ECAP process: (a) Before shearing (position A); (b) Shear zone (position B); (c) After shearing (position C)
为了更好地计算合金中的再结晶分数,近似地把晶粒尺寸小于10 μm的晶粒认为是再结晶形成的晶粒。对合金中尺寸小于10 μm的晶粒进行统计,其再结晶晶粒分布如图9所示,其再结晶分数如表2所列。从图9和表2中可以看出:在进入剪切变形区前,合金中主要是以大晶粒为主,只在晶界处存在少量的细小再结晶晶粒,其再结晶分数较低,只有8.4%;进入剪切变形区时,合金中的再结晶晶粒分数快速增加,其面积分数增至32.8%,而且除了在晶界处外,沿着剪切带形成了大量的细小再结晶晶粒;经过剪切变形后,合金中的再结晶晶粒分数明显增加,与剪切变形前相比,合金中的再结晶分数从8.4%增加至63.6%,说明ECAP过程中的晶粒细化机制主要是靠再结晶实现的。
3 分析与讨论
众所周知,经过多道次ECAP挤压能够使粗晶材料得到明显的晶粒细化,但目前所建立的模型基本上都是依据Al和Cu等塑性好的金属在常温下ECAP变形为依据而建立起来的,认为合金的细化机制为机械剪切和应变累积,而基本上没有考虑温度对晶粒细化过程的影响。因为Al和Cu的剪切变形主要是靠位错的交滑移来实现的,这些位错形成复杂的胞状结构,并组成几何必须晶界(GNB),随着应变的增加,因此,不断的变形可以使合金的晶粒通过这种位错网络的变化而得到明显的变化,相反,加热过程会使位错湮灭,阻碍新晶界的形成。而实际上温度对于位错的回复和再结晶过程都具有非常重要的影响,特别是对于镁合金等容易发生再结晶的材料,单纯用机械剪切模型是无法完全解释其晶粒细化过程的。SU等[19]对AZ31镁合金的ECAP研究也表明镁合金中晶粒细化机制主要为动态再结晶和机械剪切的共同作用,其细化过程可用图10来表示。在ECAP变形初期,由于受到强剪切其层错能较低(约78 kJ/mol),易于发生动态再结晶,因此在进一步的变形过程中,再结晶晶粒很容易在原始晶界或剪切变形带附近形核,如图10(b)所示。另外,镁合金的晶界扩散能较高,变形过程中形成的位错能够迅速被再结晶晶粒吸收,因而加快动态再结晶的过程,使合金组织变成完全再结晶组织而使合金晶粒得到细化,如图10(c)所示。从实验结果看,ZK60镁合金在进入ECAP剪切区前,就已经形成了大量的孪晶和剪切带,而经过剪切变形后,合金中形成了大量细变形,而镁合金中又缺少足够的独立滑移系,因此形成了大量的孪晶和剪切带。图10(a)所示为经过剪切变形后的组织示意图,剪切变形后,合金中存在大量的位错缠结和剪切带,这为动态回复和动态再结晶提供了良好的形核场所和驱动力。对于镁合金而言,由于长的剪切带,这些剪切带的形成把原始晶粒分割成多个细小的亚晶粒,在一定程度上细化了合金的晶粒。另一方面,剪切带为强剪切变形过程中形成的,组织中的变形储能较高,这为后续的动态再结晶过程做好组织和能量上的准备。
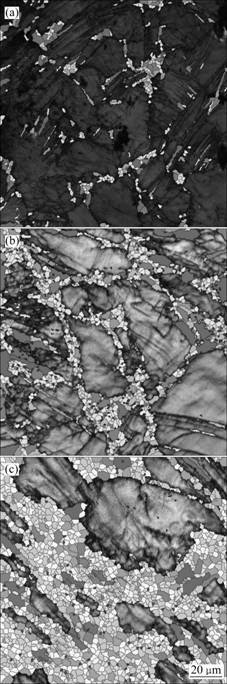
图9 ZK60合金ECAP过程中不同区域的再结晶晶粒分布图
Fig.9 Recrystallization grains distribution of ZK60 alloys at different locations during ECAP process: (a) Before shearing (position A); (b) Shear zone (position B); (c) After shearing (position C)
表2 ZK60合金ECAP过程中不同区域的再结晶晶粒分数
Table 2 Recrystallization grains fraction of ZK60 alloy at different locations during ECAP process

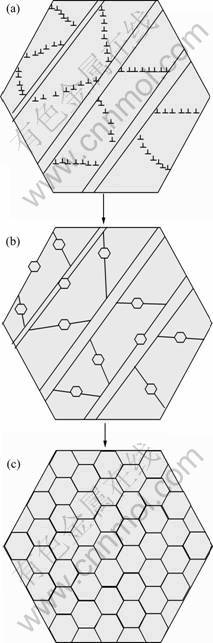
图10 镁合金ECAP过程中晶粒细化过程示意图
Fig.10 Schematic diagrams showing grain refinement mechanism of magnesium alloys during ECAP: (a) Shear bands and dislocation entanglement during shearing; (b) Dynamic recrystallization nucleated at shear bands and dislocations; (c) Dynamic recrystallized grains
从图9中可以看出,在剪切区虽然已经发生再结晶,但大规模的再结晶过程其实是发生在剪切变形后。从实验结果可知,在剪切变形区,再结晶分数只有32.8%,但在剪切变形后,再结晶分数突增到63.6%,可见,剪切变形区是在组织和能量上为后续动态再结晶做好准备,在离开剪切区后,由于ECAP过程中温度较高,合金继续发生再结晶。可以预见,对于粗晶镁合金而言,由于在剪切变形过程中主要是靠位错滑移和剪切变形带或孪晶来协调,因此,剪切变形后的变形储能很高,在后续的动态再结晶过程中,形核率和长大速率都较高。而对于细晶材料而言,除位错滑移外,合金还可以通过晶界滑移和晶粒旋转等方式来协调变形,相对而言,变形储能较小,因此动态再结晶过程也较缓。这也就解释了为什么在镁合金的ECAP过程中,在前几道次的晶粒细化效果较明显,而经过多道次挤压后,由于晶粒得到明显的细化,动态再结晶的速率逐渐减慢,因此晶粒细化效果也逐渐减弱。
4 结论
1) 经过240 ℃ ECAP挤压变形1道次后,ZK60镁合金的晶粒得到明显细化,但是变形后的组织仍不均匀。剪切变形前合金组织主要为粗大晶粒并伴有大量孪晶;剪切区的组织主要为剪切变形带和少量再结晶组织;剪切变形后合金的晶粒组织主要为再结晶组织。
2) ZK60镁合金ECAP过程中晶粒细化为机械剪切和动态再结晶的综合作用。在ECAP变形初期,晶粒细化机制主要是机械剪切;在ECAP变形后期,主要是动态再结晶。
REFERENCES
[1] 余 琨, 黎文献, 王日初, 马正青. 变形镁合金的研究、开发及应用[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2003, 13(2): 277-288.
YU Kun, LI Wen-xian, WANG Ri-chu, MA Zheng-qing. Research, development and application of wrought magnesium alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2003, 13(2): 277-288.
[2] LUO A. Magnesium: Current and potential automotive applications[J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2002, 54(2): 42-48.
[3] MORDIKE B L, EBERT T. Magnesium: Properties—applications—potential[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 302(1): 37-45.
[4] YAMASHITA A, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G. Improving the mechanical properties of magnesium and a magnesium alloy through severe plastic deformation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 300(1/2): 142-147.
[5] SEGAL V M. Equal channel angular extrusion: from macromechanics to structure formation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 271(1/2): 322-333.
[6] JIANG J, WANG Y, DU Z, QU J, SUN Y, LUO S. Enhancing room temperature mechanical properties of Mg-9Al-Zn alloy by multi-pass equal channel angular extrusion[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2010, 210(5): 751-758.
[7] FIGUEIREDO R B, LANGDON T G. Strategies for achieving high strain rate superplasticity in magnesium alloys processed by equal-channel angular pressing[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 61(1): 84-87.
[8] XU C, FURUKAWA M, HORITA Z, LANGDON T G. The evolution of homogeneity and grain refinement during equal-channel angular pressing: A model for grain refinement in ECAP[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 398(1/2): 66-76.
[9] FIGUEIREDO R B, LANGDON T G. Principles of grain refinement and superplastic flow in magnesium alloys processed by ECAP[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 501(1/2): 105-114.
[10] DING S X, LEE W T, CHANG C P, CHANG L W, KAO P W. Improvement of strength of magnesium alloy processed by equal channel angular extrusion[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59(9): 1006-1009.
[11] FIGUEIREDO R B, LANGDON T G. The development of superplastic ductilities and microstructural homogeneity in a magnesium ZK60 alloy processed by ECAP[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 430(1/2): 151-156.
[12] CHUVIL'DEEV V, NIEH T G, GRYAZNOV M Y, KOPYLOV V I, SYSOEV A N. Superplasticity and internal friction in microcrystalline AZ91 and ZK60 magnesium alloys processed by equal-channel angular pressing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 378(1/2): 253-257.
[13] WATANABE H, MUKAI T, ISHIKAWA K, HIGASHI K. Low temperature superplasticity of a fine-grained ZK60 magnesium alloy processed by equal-channel-angular extrusion[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 46(12): 851-856.
[14] HORITA Z, MATSUBARA K, MAKII K, LANGDON T G. A two-step processing route for achieving a superplastic forming capability in dilute magnesium alloys[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 47(4): 255-260.
[15] MABUCHI M, IWASAKI H, YANASE K, HIGASHI K. Low temperature superplasticity in an AZ91 magnesium alloy processed by ECAE[J]. Scripta Materialia, 1997, 36(6): 681-686.
[16] IWAHASHI Y, HORITA Z, NEMOTO M, LANGDON T G. The process of grain refinement in equal-channel angular pressing[J]. Acta Materialia, 1998, 46(9): 3317-3331.
[17] ZHU Y T,LOWE T C. Observations and issues on mechanisms of grain refinement during ECAP process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 291(1/2): 46-53.
[18] GIL SEVILLANO J, AERNOUDT E. Low energy dislocation structures in highly deformed materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1987, 86: 35-51.
[19] SU C W, LU L,LAI M O. A model for the grain refinement mechanism in equal channel angular pressing of Mg alloy from microstructural studies[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 434(1/2): 227-236.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:新西兰奥克兰大学博士生联合培养项目(9071/3607593)
收稿日期:2010-10-26;修订日期:2011-02-15
通信作者:潘清林,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830933;E-mail: pql@mail.csu.edu.cn