文章编号:1004-0609(2014)05-1319-08
基材属性对Ni60A-WC激光熔覆涂层性能的影响
刘发兰,赵树森,高文焱,周春阳,王奕博,林学春
(中国科学院 半导体研究所 全固态光源实验室,北京 100083)
摘 要:在304不锈钢(304SS)和Q235碳钢上分别熔覆Ni60A及Ni60A-WC金属粉末,以及添加Cr和Cr3C2的涂层,利用光学显微镜(OM)、扫描电镜(SEM)、能谱仪(EDS)分析涂层的宏观形貌、微观组织和元素分布,用显微硬度计对涂层的硬度进行测试分析。结果表明:基材中元素成分的不同会导致涂层气孔和裂纹的差异,Ni、Cr元素含量高的304SS上的涂层气孔和裂纹数明显比Q235碳钢上的少;基材的导热性能对涂层的稀释率与性能具有明显影响,导热性能差的304SS稀释率大,WC颗粒分解多,涂层组织粗大;由于Q235导热性能好,冷却速率高,导致涂层硬度高,Ni60A+40%WC涂层平均硬度高达1000HV0.2。此外,Cr和Cr3C2的加入能有效防止涂层气孔的产生。
关键词:WC涂层;激光熔覆;显微组织;显微硬度
中图分类号:TG174.44 文献标志码:A
Effect of substrate on Ni60A-WC laser cladding coatings
LIU Fa-lan, ZHAO Shu-sen, GAO Wen-yan, ZHOU Chun-yang, WANG Yi-bo, LIN Xue-chun
(Laboratory of All-Solid-State Laser Sources, Institude of Semiconductors,
Chinese Academy of Scienses, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: Ni60A and Ni60A-WC laser cladding coatings were prepared on 304 stainless steel and Q235 carbon steel, respectively, as well as adding Cr and Cr3C2 coatings. The macroscopic morphology, microstructure and elemental distribution of the coatings were analyzed by optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). The microhardness of the coatings were tested with microhardness tester. The results show that the element composition on the substrate can cause the differences of pores and cracks. The pores and cracks of the coatings on 304 stainless steel (with high contents of Ni and Cr elements) are significantly less than those of the the coatings on Q235 carbon steel. The thermal conductivity of the substrates have a significant impact on the dilution rate and performance of the coatings. Because of poor thermal conductivity, the coatings on 304 stainless steel have high dilution rate, more WC particles decompose and then coarsen the microstructure. The average hardness of Ni60A +40%WC coating on Q235 substrate up to 1000HV0.2 attributes to its good thermal conductivity and high cooling rate. Furthermore, pore free coatings adding with Cr and Cr3C2 are obtained.
Key words: WC coating; laser cladding; microstructure; microhardness
WC粉末具有极高的硬度,适用于工业领域易磨损部件耐磨涂层的制备[1],其中以Ni基合金-WC颗粒复合涂层应用最为广泛[2-5]。激光熔覆作为一种新兴的表面改性技术,具有高效、高质量、无污染等优点。采用激光熔覆方式制备Ni基合金-WC颗粒复合涂层是近年来激光熔覆修复领域的研究热点。
HUANG等[6-7]采用激光熔覆方法在H13工具钢上获得了WC含量为70%(质量分数)、硬度高达800HV的涂层。WU等[8]用2 kW连续CO2激光器在低碳钢基材上熔覆Ni35+50%(体积分数)WC-Ni (15%Ni,余量WC,质量分数)包WC,获得了无气孔和裂纹的涂层。徐国建等[9]利用侧向送粉激光熔覆的方法得到了Ni基合金粉末和50%WC无裂纹涂层,硬度达到45钢基材的5倍以上。ZHOU等[10]利用激光-感应复合熔覆的方法在A3钢基材上得到了35%WC含量无气孔、无裂纹的涂层,熔覆效率是普通激光熔覆方法的5倍。杨胶溪等[11-12]利用宽带熔覆及梯度熔覆的方法在45钢基材上得到了WC含量为60%无气孔和裂纹的涂层。ZHONG等[13]利用双侧送粉的方式,在低碳钢基体上研究了Stellite6掺入不同含量WC(0~100%,体积分数)的微观组织结构。CHEN等[14]研究了45钢基材上激光熔覆不同粒度WC+Ni60B的涂层性能。
综上所述,已有的研究主要是针对在同种基材上熔覆不同WC含量的工艺探索。然而,Ni基合金-WC复合涂层激光熔覆工艺参数选择及涂层性能与所采用基材密切相关。在不同基材上,工艺相差甚远。因此,有必要针对基体材料对WC涂层熔覆工艺及性能影响机制开展研究。基材属性包括基材的材料属性、几何形态和热处理状态等,这些属性对激光熔覆工艺均具有重要的影响,然而大部分因素可以通过人为方式控制,如基材的表面形貌、粗糙度、热处理状态以及热处理程度;但是基材的物理属性,如化学成分、热传导性能等是材料的固有属性,在实际应用中无法人为干预。本文作者基于上述工艺需求,选取304SS和Q235碳钢两种典型Fe基基体,进行Ni基合金-WC复合粉末激光熔覆工艺研究,重点考察基材成分、导热性能等基材的固有属性对同种涂层在熔覆工艺、涂层性能等方面的影响规律,为Ni基合金-WC复合涂层在不同基材上的工艺移植提供理论指导。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料和方案
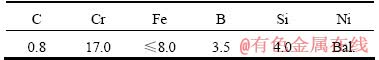
基体材料分别为304SS和Q235碳钢,其尺寸为200 mm×100 mm×10 mm,待熔覆表面粗糙度均为Ra=3.2,预热至200 ℃。熔覆材料为Ni60A(粒度为45~109 μm)和Co基WC(粒度为15~45 μm),其中Ni60A的成分如表1所列。实验中WC含量分别为0和40%(质量分数),具体工艺参数如表2所列。
表1 Ni60A粉末成分
Table 1 Composition of Ni60A powder (mass fraction, %)
1.2 实验方法和设备
采用3KW固体激光器进行激光熔覆实验,光束通过光纤传导与六轴联动的机器人相连,采用焦距为120 mm的聚焦镜聚焦,离焦15 mm,得到直径为5 mm的圆形光斑。粉末以同步送粉的方式送入熔池中,采用氮气送粉,流量为3 L/min,四道搭接熔覆,搭接率为30%。在激光熔覆样件上截取金相试样,经打磨抛光后用王水腐蚀。采用QUANT FEG-450型扫描电镜和9XB-PC型金相显微镜对熔覆层横截面的组织成分进行分析,采用HXD-1000TMS/LCD型显微硬度计进行硬度测试,沿垂直于熔覆层的方向每隔100 μm进行测试,载荷为1.96 N,加载时间15 s。
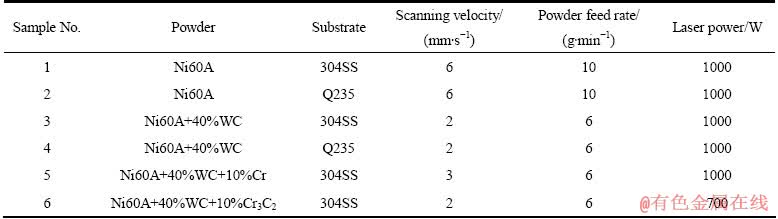
表2 激光熔覆实验方案
Table 2 Experimental technology parameters of laser cladding
2 结果与分析
2.1 涂层宏观形貌分析
图1所示为样品1~4的宏观截面形貌图。从图1(a)可见,304SS上熔覆的Ni60A涂层表面无裂纹和气孔,界面平整光滑;从图1(b)可见,Q235碳钢上熔覆的Ni60A涂层表面有一道大裂纹和少量的气孔,界面有少量的凹坑;从图1(c)可见,304SS上熔覆的Ni60A+40%WC涂层表面没有气孔和裂纹,表面只有少量的WC颗粒,涂层稀释率大(稀释率约为60%);从图1(d)可见,Q235碳钢上熔覆的Ni60A+40%WC涂层表面有大量的气孔,均匀分布了大量的WC颗粒(图中灰白色小颗粒),涂层稀释率约为30%,虽然图中所示的截面没有裂纹,但是从显微镜下观察到激光熔覆后的表面存在裂纹。总之,304SS上的涂层表面没有裂纹和气孔,Q235碳钢板上的涂层表面存在大量的气孔和裂纹;WC含量为40%时,304SS板上的熔覆层稀释率大。
2.2 基材属性对涂层稀释率、气孔和裂纹的影响
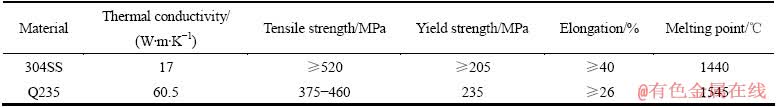
表3所列为304SS和Q235碳钢的物理性能。从表3可以看出,304SS的导热系数为17 W/(m·K),Q235碳钢的导热系数为60.5 W/(m·K),304SS的导热能力较差,在相同的工艺参数条件下导致304SS上熔覆Ni60A+40%WC涂层稀释率大,基材与涂层相互扩散,基材中的元素扩散至涂层,从而影响涂层的性能。
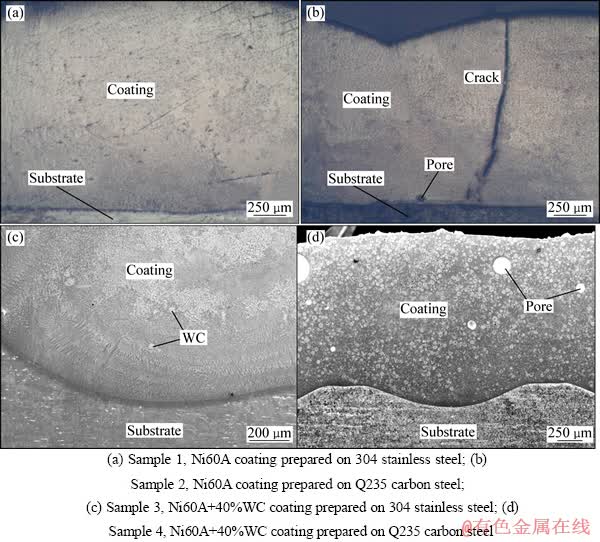
图1 熔覆涂层截面的SEM像
Fig. 1 SEM images of cross-sections of laser cladding coatings
表3 304SS和Q235碳钢的物理性能
Table 3 Physical properties of 304 stainless steel and carbon steel Q235
激光熔覆镍基WC涂层气孔的主要来源是C与O反应生成的CO和CO2气体,其中O的来源可能是熔覆粉末从空气中吸取的水分,也可能是熔池发生剧烈的物理化学变化,周围气流剧烈扰动,保护气体没有始终笼罩熔池周围,使少量空气卷入并接触熔池,O就进入熔池;而C主要来源于Ni基合金中添加的WC在激光高温作用下热分解生成的游离C;游离的C会与O结合生成CO和CO2气体,气体在熔池极快的冷却速度下,来不及逸出便形成了气孔。
涂层中气孔的产生与WC颗粒的熔解密切相关,WC颗粒虽然是一种优良的硬质相,但其在高温下容易氧化脱碳,许多文献证实[15-16]WC的脱碳过程如下:
2WC→W2C+C和W2C→2W+C (1)
生成气体的过程如下[17]:
2C+O2→2CO↑或C+O2→CO2↑或2CO+O2→2CO2↑ (2)
因此,通过减少熔池中C和O含量可以抑制涂层中气孔的产生。
表4所列为304SS和Q235碳钢的成分。从表4可以看到,304SS和Q235碳钢在成分上的最大区别是304SS中含有大量的Cr和Ni元素,由前面的分析可知,304SS上熔覆Ni60A+40%WC涂层稀释率大,基材中的Cr元素扩散至涂层能与涂层中的C结合形成碳化物,降低涂层中的C含量,避免CO和CO2气体的产生,从而减少涂层中的气孔。因此,304SS板上的涂层表面没有气孔,而Q235碳钢板上的涂层存在大量的气孔。
表4 304SS和Q235碳钢的成分
Table 4 Composition of 304 stainless steel and carbon steel Q235 (mass fraction, %)
激光熔覆涂层裂纹的产生主要与应力有关,激光熔覆是一个快速加热和冷却的过程,冷凝时温度梯度导致激光熔覆涂层内产生拉应力,当拉应力大于该温度下材料强度极限时,熔覆层出现裂纹[18]。涂层气孔处应力容易集中,减少和控制气孔数量可以明显减少裂纹的出现。从表4可以看到,304SS中含有大量的Ni元素,一方面,Ni元素扩散至涂层能提高熔覆合金对基体的润湿性、降低熔覆层的热膨胀系数、减少合金的熔化温度区间,从而降低熔覆层的裂纹敏感性;另一方面,304SS上的涂层表面没有气孔进一步降低了涂层的裂纹敏感性,因此,304SS上的涂层表面没有裂纹,而Q235碳钢板上的涂层存在大量的裂纹。
2.3 基材属性对涂层组织和成分的影响
图2所示为样品1和2中局部区域的SEM像。从图2(a)可见,304SS表面Ni基合金的组织是在共晶的基底上分布着黑色块条状颗粒和灰色网状相,组织粗大,其中黑色块条状颗粒较多,尺寸在5~10 μm之间,其体积分数在15%左右。从图2(b)可见,Q235碳钢表面Ni基合金的组织是在共晶的基底上分布着黑色圆形颗粒和灰白色块状相,组织细小。Q235碳钢表面激光熔覆涂层组织较细,原因是激光熔覆涂层的组织主要受成分、加热和冷却速度的影响。304SS与Q235碳钢相比,304SS的导热能力较差,造成熔池内的冷却速度较慢,从而使熔池内的晶核有足够的时间长大,故熔覆层内的组织粗大。而Q235碳钢基体由于导热快,对熔池的冷却速度快,使熔池内的晶核由于快速冷却而来不及长大,因此,获得的涂层组织细小。

图2 熔覆涂层截面的SEM像
Fig. 2 SEM images of cross-sections of laser cladding coatings
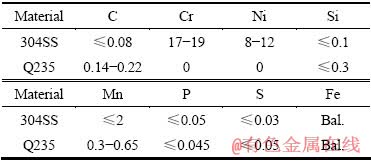
表5所列为图2中304SS和Q235碳钢表面涂层各组织组成物的SEM能谱分析结果,从表5可见,黑色颗粒A、D区域主要元素含量是Cr和B,以及少量的Fe、Ni和C等,说明黑色颗粒是硼铬化合物,样品1中从基材扩散的Cr元素多,因此,涂层中生成的硼铬化合物较样品2的多;图中B、C、E、F区域的主要元素含量是Ni,是γ-Ni的共晶组织,其中固溶了少量的Fe和Cr。
表5 图2中样品1和2不同区域主要元素的含量
Table 5 Chemical compositions of main elements in different areas of samples 1 and 2 shown in Fig. 2

图3所示为样品3和4局部区域的SEM像,从图3(a)可见,在304SS上熔覆的Ni60A+40%WC合金的组织是在褐色H区基底上分布着部分熔解的WC颗粒和大量规则的白色树枝晶,这些白色树枝晶占涂层体积分数的50%左右。从表6的元素分析结果可见,褐色H区的主要元素含量是36.90%Fe和56.43%Ni,白色G区域含有大量的W元素,说明WC分解的W元素与Fe、Ni、Cr形成的碳化物均匀分布在涂层中的γ-(Fe、Ni)固溶体上,且从其所占的体积分数可见,该涂层中WC颗粒分解多。从图3(b)可见,在Q235碳钢上熔覆的Ni60A+40%WC合金的组织是褐色的J基底上分布着部分熔解的WC颗粒和大量花朵状和条状的白色相,其中白色相占整个涂层体积分数的30%左右,明显低于样品3中白色树枝晶所占的体积。从表6的能谱分析结果可见,花朵状和条状白色相中W元素含量高达62.27%(质量分数),Fe、Ni和Cr元素含量明显低于样品3白色区的,说明样品4中WC颗粒的分解较样品3中的少,样品3涂层中由于Cr元素含量高,促进了WC颗粒的分解。样品4涂层中由于Cr含量少,WC颗粒分解产生的C元素得不到有效结合而与空气中的氧气反应产生气体,来不及溢出而形成气孔(见图1(d))。
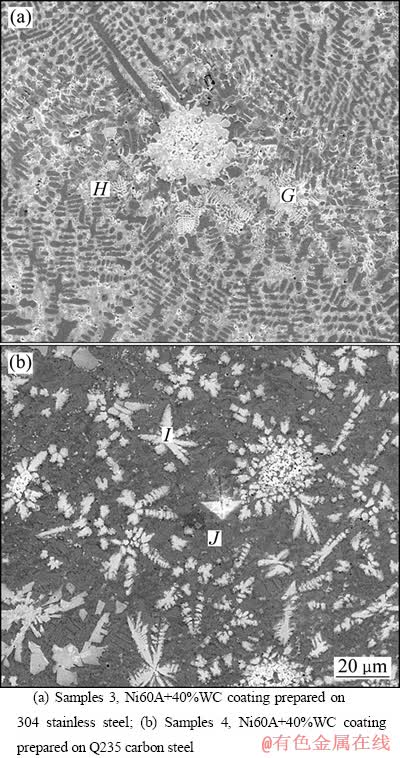
图3 熔覆涂层截面SEM像
Fig. 3 SEM images of cross-sections of laser cladding coatings
表6 图3中样品3和4不同区域的主要元素含量
Table 6 Chemical compositions of main elements in different areas of samples 3 and 4 shown in Fig. 3
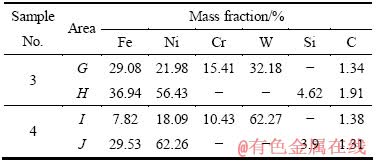

图4 样品5的截面形貌
Fig. 4 SEM images of cross-sections of Sample 5
2.4 Cr和Cr3C2的加入对涂层组织的影响
综上所述发现,基材中Cr元素渗入涂层能有效抑制涂层的气孔,在此,又进一步研究Ni60A+40%WC中分别加入10%的Cr和Cr3C2(见表2中样品5和6),其显微形貌分别如图4和5所示。从图4(a)可见,添加10%Cr的涂层平整光滑无气孔,但涂层表面几乎没有完整的WC颗粒,说明Cr的加入能促进WC的分解、有效地抑制涂层中气孔的产生。图4(b)所示为图4(a)中局部区域放大图,从图中可以看到,涂层中生成了一些灰色团状物K,经能谱分析发现K区的元素含量如图4(c)所示,该区域含有大量的W(60.25%,质量分数),说明Cr的加入促进了WC的分解,分解后产生的W、C元素与Fe、Ni和Cr等聚集形成团状物,从而抑制气孔的生成。从图5(a)可见,Ni60A+40%WC+ 10%Cr3C2(质量分数)涂层中分布了大量的WC颗粒,表面没有气孔,组织细密均匀,从图5(b)的局部放大图可以看到,WC颗粒周围分布大量的深黑色块状物和灰色组织,图5(c)和(d)所示分别为这两个区域的能谱分析图。从图5(c)可见,深黑色块状物所含元素含量为49.13%Cr、21.60%W、13.76Fe、10.27Ni、3.29C和1.95Mn(质量分数),其中含有大量的Cr ,推测是铬的化合物。从图6(d)可见,灰色N区的主要元素是Ni,说明是Ni的固溶体,其中固溶了大量的Fe和少量的Cr、Si。Cr3C2的加入不但可以抑制涂层中气孔的产生,由于其本身就含有C原子因此还可以抑制WC颗粒的分解。
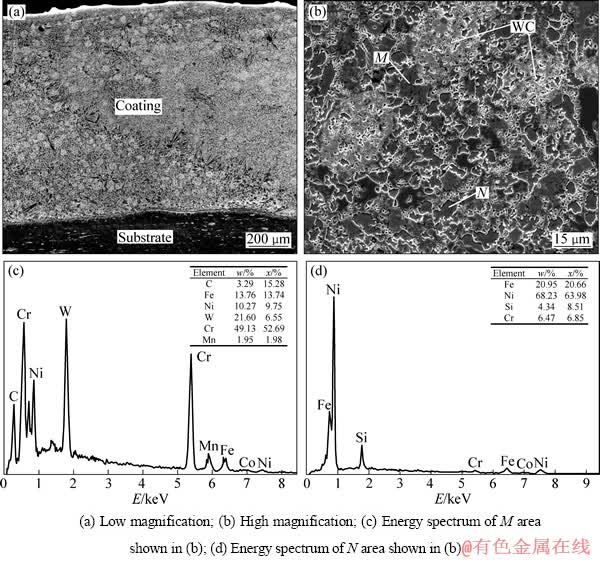
图5 样品6截面形貌
Fig. 5 SEM images of cross-sections of Sample 6
2.5 基材属性对涂层性能影响
图6所示为WC含量为40%时不同基材上涂层截面显微硬度对比曲线。从图6可以看到,基材的平均硬度为200 HV0.2,在Q235基材上涂层的平均硬度高达1000HV0.2,是基材的5倍;304SS基材上涂层的平均硬度为600HV0.2,是基材的3倍,两者硬度相差较大。两者硬度差别大的主要原因是304SS的导热能力较Q235碳钢的差,导致涂层稀释率大,基材中的元素渗入涂层影响涂层的性能,WC颗粒分解多,这从图1(c)和(d)可以明显看到,图1(d)中的WC颗粒明显多于图1(c)中的,而WC是提升熔覆层硬度的主要硬质颗粒,该颗粒的减少会显著降低熔覆层的硬度。
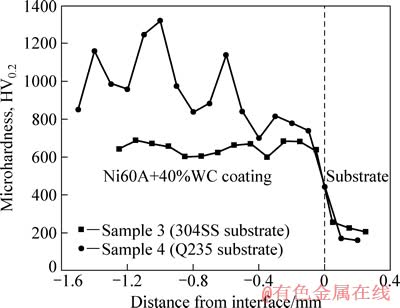
图6 样品3和4的截面显微硬度曲线
Fig. 6 Microhardness comparisonof samples 3 and 4
图7所示分别加入10%的Cr和Cr3C2的样品5和6显微硬度对比曲线。从图7可见,添加10% Cr3C2的样品6的平均硬度高达900HV0.2,与样品4相当。添加10%Cr的样品5的平均硬度为600HV0.2且存在个别硬度较低的点,明显低于样品6的,这主要是由于Cr的加入使涂层中的WC颗粒大部分溶解,因此,加Cr的样品的硬度较低。

图7 样品5和6的截面显微硬度对比
Fig. 7 Microhardness comparison of samples 5 and 6
3 结论
1) 304SS和Q235碳钢元素成分不同导致涂层气孔、裂纹方面存在很大差异。由于Cr元素能够捕捉涂层中的C而形成碳化物,减少了涂层中的气孔;Ni元素能提高熔覆合金对基体的润湿性、降低熔覆层的热膨胀系数、减少合金的熔化温度区间,从而降低熔覆层的裂纹敏感性,因此,Ni和Cr元素含量高的304SS上的涂层气孔和裂纹明显比Q235碳钢上的少;基材的导热性能对涂层的稀释率与性能具有明显影响,导热性能差的304SS的稀释率大,WC颗粒分解较多,涂层组织粗大;由于Q235导热性能较好,使涂层冷却速率高,导致涂层硬度更高,Ni60A+40%WC涂层平均硬度高达1000HV0.2。
2) Cr和Cr3C2的加入能有效防止涂层气孔的产生,Cr元素促使WC分解,涂层硬度较低(平均硬度仅有600HV0.2);添加Cr3C2的涂层中WC颗粒未观察到明显分解,其平均硬度高达900HV0.2。
REFERENCES
[1] 刘建弟, 张述泉, 王华明. 激光熔覆WC 颗粒增强复合涂层的组织及耐磨性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(9): 2600-2607.
LIU Jian-di, ZHANG Shu-quan, WANG Hua-ming. Microstructure and wear resistance of aser cladding WC particles reinforced composite coatings[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(9): 2600-2607.
[2] ST-GEORGES L. Development and characterization of composite Ni-Cr+WC laser cladding[J]. Wear, 2007, 263(1): 562-566.
[3] GUO Chun, ZHOU Jian-song, CHEN Jian-min, ZHAO Jie-rong, YU You-jun, ZHAO Hui-di. High temperature wear resistance of laser cladding NiCrBSi and NiCrBSi/WC-Ni composite coatings[J]. Wear, 2011, 270(7): 492-498.
[4] XU J S, ZHANG X C, XUAN F Z, WANG Z D, TU S T. Microstructure and sliding wear resistance of laser cladded WC/Ni composite coatings with different contents of WC particle[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2012, 21(9): 1904-1911.
[5] NURMINEN J,  J, VUORISTO P. Microstructure and properties of hard and wear resistant MMC coatings deposited by laser cladding[J]. Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2009, 27(2): 472-478.
J, VUORISTO P. Microstructure and properties of hard and wear resistant MMC coatings deposited by laser cladding[J]. Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2009, 27(2): 472-478.
[6] HUANG S W, NOLAN D, BRANDT M. Pre-placed WC/Ni clad layers produced with a pulsed Nd:YAG laser via optical fibres[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 165(1): 26-34.
[7] HUANG S W, SAMANDI M, BRANDT M. Abrasive wear performance and microstructure of laser clad WC/Ni layers[J]. Wear, 2004, 256(11): 1095-1105.
[8] WU P, ZHOU C Z, TANG X N. Microstructural characterization and wear behavior of laser cladded nickel -based and tungsten carbide composite coatings[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 166(1): 84-88.
[9] 徐国建, 黄 雪, 傅新皓, 杭争翔, 于恩洪, 李永波. Ni基合金与WC 混合粉末的激光熔覆层组织[J]. 硬质合金, 2012, 29(5): 297-308.
XU Guo-jian, HUANG Xue, FU Xin-hao, HANG Zheng-xiang, YU En-hong, LI Yong-bo. Microstructure of laser cladding layer prepared by mixed powder of Ni-based alloys and WC[J]. Cemented Carbide, 2012, 29(5): 297-308.
[10] ZHOU Sheng-feng, DAI Xiao-qin. Laser induction hybrid rapid cladding of WC particles reinforced NiCrBSi composite coatings[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 256(14): 4708-4714.
[11] 杨胶溪, 闫 婷, 刘华东, 左铁钏. 激光熔覆WC-Ni基超硬梯度复合涂层的组织与性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2009, 34(11): 5-9.
YANG Jiao-xi, YAN Ting, LIU Hua-dong, ZUO Tie-chuan. Microstructure and properties of laser clad WC-Ni base superhard gradient composite coating[J]. Heat Treatment of Matals, 2009, 34(11): 5-9.
[12] 杨胶溪, 闫 婷, 王喜兵, 郭 江, 左铁钏, 徐文清. 激光宽带熔覆碳化钨/钴基合金的组织与性能[J]. 表面改性技术, 2007(11): 26-29.
YANG Jiao-xi, YAN Ting, WANG Xi-bing, GUO Jiang, ZUO Tie-chuan, XU Wen-qing. Microstructure and properties of laser wide-strip clad WC/Co-base alloy[J]. Surface Modification Technology, 2007, (11): 26-29.
[13] ZHONG Min-lin, LIU Wen-jin, YAO Ke-fu, GOUSSAINB J C, MAYER C, AHIM B. Microstructural evolution in high power laser cladding of stellite 6+WC layers[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2002, 157(2): 128-137.
[14] CHEN Hua-hui, XU Cai-yun, CHEN Jun, ZHAO Hui-you, ZHANG Lei, WANG Zhen-ting. Microstructure and phase transformation of WC/Ni60B laser cladding coatings during dry sliding wear[J]. Wear, 2008, 264(7): 487-493.
[15] 高 南, 孙大千, 曹书云. 镍基碳化钨高温磨损特性的研究[J]. 华中理工大学学报, 1991, 19(6): 83-88.
GAO Nan, SUN Da-qian, CAO Shu-yun. A study of high temperature wearing characteristics of nickel-based self-fluxing alloy with different tungsten carbide contents[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1991, 19(6): 83-88.
[16] 吴新伟, 曾晓雁, 朱蓓蒂, 陶曾毅, 崔 崑. 镍基WC金属陶瓷激光熔覆涂层的熔化烧损规律[J]. 金属学报, 1997, 33(12): 1282-1288.
WU Xin-wei, ZENG Xiao-yan, ZHU Bei-di, TAO Zeng-yi, CUI Kun. Heat damage of laser clad Ni-based WC coating[J]. Acta Metallurggica Sinica, 1997, 33(12): 1282-1288.
[17] 钟文华, 刘贵仲, 葛大梁, 高 原. Cr3C2对镍基碳化钨激光熔覆层组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2012(7): 45-48.
ZHONG Wen-hua, LIU Gui-zhong, GE Da-liang, GAO Yuan. Effect of adding Cr3C2 on microstructure and properties of Ni/WC cladding layer[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2012(7): 45-48.
[18] KADOLKAR P B, WATKINS T R, DE HOSSON J Th M, KOOI B J, DAHOTRE N B. State of residual stress in laser-deposited ceramic composite coatings on aluminum alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(4): 1203-1214.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金青年基金项目(51205380)
收稿日期:2013-04-20;修订日期:2013-11-20
通信作者:林学春,研究员,博士;电话:010-82304165;E-mail:xclin@semi.ac.cn