文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-01-0057-07
挤压态AZ31镁合金温热拉伸性能的各向异性
吴国华1,肖 寒1,周慧子1,王瑞雪2,程 明2,张士宏2
(1. 昆明理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,昆明 650093;
2. 中国科学院 金属研究所,沈阳 110016)
摘 要:采用单向拉伸实验研究温热条件下挤压态AZ31镁合金板材5个不同方向的力学性能、显微组织、断口形貌。结果表明:挤压态镁合金力学性能具有明显的各向异性,170 ℃时,各向异性最明显,随着拉伸方向与挤压方向所呈角度的增大,抗拉强度从217 MPa增大到271 MPa,屈服强度却从174 MPa减小到71 MPa。镁合金在温热条件下变形机制为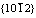 拉伸孪生、
拉伸孪生、 压缩孪生和{0001}基面滑移;沿着不同角度拉伸时,变形机制有所不同。拉伸方向与挤压方向的角度小于45°时,挤压态镁合金表现为微孔聚集型的韧性断裂;且随着角度的增大,表现为韧-脆混合断裂,其中角度为67.5°时,镁合金以解理方式断裂。
压缩孪生和{0001}基面滑移;沿着不同角度拉伸时,变形机制有所不同。拉伸方向与挤压方向的角度小于45°时,挤压态镁合金表现为微孔聚集型的韧性断裂;且随着角度的增大,表现为韧-脆混合断裂,其中角度为67.5°时,镁合金以解理方式断裂。
关键词:镁合金;温热拉伸性能;孪生;断裂机制;各向异性
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
镁合金具有低密度、高强度、电磁屏蔽效果优良及易回收等优点,常被作为轻量化结构材料应用于汽车、交通、电子等行业[1-2]。然而,镁合金为密排六方金属结构,在室温下滑移系较少,塑性较差,导致加工困难。镁合金常见的滑移系有[3]:{0001}< >基面滑移,
>基面滑移, <
< >柱面滑移,
>柱面滑移, <
< >锥面滑移和
>锥面滑移和 <
<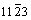 >锥面滑移,除了滑移,孪生是镁合金另一种常见的变形机制。
>锥面滑移,除了滑移,孪生是镁合金另一种常见的变形机制。
目前,对镁合金各向异性的研究日益增多,研究者们深入研究织构对镁合金力学性能的影响[4-7]。CHINO等[8]利用挤压棒材,研究室温和400 ℃时AZ31镁合金的拉伸和压缩非对称性能,表明 拉伸孪生发生于沿垂直c轴压缩时,并受晶粒细化影响;李树梅等[9]在100 ℃下对镁合金轧板进行单向压缩实验,研究了其动态再结晶现象;黄洪涛等[10-11]在150 ℃下沿RD、TD对轧制镁合金板材进行单向压缩试验,研究了不同方向的压缩变形机制;娄超等[12]研究了轧板室温下动态塑性变形,发现镁合金初始变形以
拉伸孪生发生于沿垂直c轴压缩时,并受晶粒细化影响;李树梅等[9]在100 ℃下对镁合金轧板进行单向压缩实验,研究了其动态再结晶现象;黄洪涛等[10-11]在150 ℃下沿RD、TD对轧制镁合金板材进行单向压缩试验,研究了不同方向的压缩变形机制;娄超等[12]研究了轧板室温下动态塑性变形,发现镁合金初始变形以 孪生主导,后期以位错滑移为主导;唐伟琴等[13]研究了镁合金挤压棒材的拉压不对称性,表明 沿{0001}基面方向压缩容易产生
孪生主导,后期以位错滑移为主导;唐伟琴等[13]研究了镁合金挤压棒材的拉压不对称性,表明 沿{0001}基面方向压缩容易产生 孪生;肖寒 等[14]利用EBSD技术研究镁合金型材在弯曲前后织构的演变规律,指出弯曲成形使镁合金线织构削弱,拉伸孪晶减少。
孪生;肖寒 等[14]利用EBSD技术研究镁合金型材在弯曲前后织构的演变规律,指出弯曲成形使镁合金线织构削弱,拉伸孪晶减少。
以往的这些研究主要以轧制态板材为研究对象,主要集中在镁合金单一方向的压缩上,对挤压态板材各向异性的研究鲜有报导,而镁合金具有极强的各向异性,不同的变形机制会产生不同的形变储存能,从而影响再结晶。因此,镁合金挤压板材的不同取样角度会影响拉伸变形行为,目前关于这个问题并未进行深入研究。本文作者在挤压态镁合金板材上切取5个不同方向的试样,研究其在温热条件下的力学性能,并分析取样角度对变形机制的影响。
1 实验
实验材料为商用AZ31镁合金挤压板材,其成分见表1。利用线切割切取与挤压方向成挤压方向0°(Extrusion direction,ED)、22.5°、45°、67.5°、横向90°(Transverse direction,TD)这5组不同角度的试样,然后利用数控机床加工成板料拉伸试样,并打磨其表面,厚度控制在3.2 mm,最终加工成的试样如图1所示。
热拉伸实验在Gleeble-3800型热模拟实验机上进行,以5 ℃/s加热速度加热到设定温度,保温时间3 min,拉伸速度选择1 mm/s,实验温度为25、120、170、210、250 ℃。根据实验结果测定的抗拉强度和屈服强度,分析挤压态镁合金的力学性能。在拉伸断口附近区域取样经过研磨和机械抛光,然后利用光学金相显微镜对拉伸后的显微组织进行观察,利用扫描电镜观察断口形貌特征并分析断裂机理。
表1 实验材料的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of specimens used in experiment (mass fraction, %)

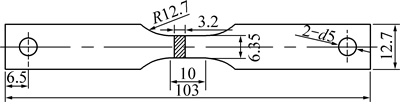
图1 拉伸试样几何尺寸
Fig. 1 Geometry of tensile test specimens (Unit: mm)
2 结果与讨论
2.1 温热条件下挤压态镁合金的力学性能
图2所示为挤压态AZ31镁合金板材在室温和170 ℃时不同取样角度试样的真实应力-应变曲线。由图2 (a)可以看出,在室温(Room temperature,RT)下断裂应变值随取样角度的增加而增大,从ED试样的0.12增大到TD试样的0.42,增大3.5倍;抗拉强度随取样角度增加从300 MPa增加到317 MPa,增大5.7%;屈服强度却随取样角度增加而下降,从ED试样的176 MPa下降到TD试样的73 MPa,降幅超过58%。图2(b)所示为170 ℃时应力应变随取样角度的变化规律:随着取样角度增大,应变和抗拉强度均匀地增加,应变从ED试样的0.16增加到TD试样的0.48;抗拉强度从ED试样的217 MPa增加到TD试样的271 MPa;但屈服强度却从ED试样的174 MPa下降到TD试样的71 MPa,降幅超过59%。

图2 不同温度下挤压态AZ31镁合金板材不同取样角的拉伸应力-应变曲线
Fig. 2 Tensile stress-strain curves of AZ31 magnesium alloy with different sampling angles extruded at different temperatures
综合图2(a)和(b)可以看出,挤压态AZ31镁合金在中低温下有着明显的各向异性,这是由于挤压态镁合金有着两种织构:一种为c轴与板材法线(Normal direction,ND)平行的基面织构,所占比例较大;另一种为c轴平行于TD方向的柱面织构[15],如原始板材ND和TD的反极图所示(见图3(a)和(c))。而在温度较低时,镁合金可参加变形的滑移系较少[16],塑性变形机制为基面滑移, 拉伸孪生以及
拉伸孪生以及 压缩孪生。对于ED试样,拉伸方向与c轴夹角为90°,基面滑移的Schmid因子为0,难以启动基面滑移,只能依靠
压缩孪生。对于ED试样,拉伸方向与c轴夹角为90°,基面滑移的Schmid因子为0,难以启动基面滑移,只能依靠 <
<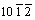 >压缩孪生,但是
>压缩孪生,但是 孪生所需的临界切应力(CRSS)较高,在76~153 MPa[9],因此,ED试样抗拉强度最低,但屈服却最高。对于TD试样,虽然Schmid因子为0,但c轴平行TD取向的晶粒很容易产生
孪生所需的临界切应力(CRSS)较高,在76~153 MPa[9],因此,ED试样抗拉强度最低,但屈服却最高。对于TD试样,虽然Schmid因子为0,但c轴平行TD取向的晶粒很容易产生 拉伸孪晶,而产生此拉伸孪晶的CRSS值很低,只需要2~2.8 MPa[17],并且拉伸孪生可以使晶粒取向发生一定旋转,使晶粒取向利于基面滑移,从而让拉伸孪生和基面滑移交替进行,因此,TD试样的断裂应变值高于ED试样的,屈服强度却最低,除此之外拉伸孪生还可以阻碍位错的移动,使得TD试样的抗拉强度提高。对介于ED和TD之间的某个取样角度,总有一个拉伸方向与晶粒(少量c轴平行于TD)的c轴夹角呈45°,Schmid因子为0.5,易产生基面滑移,而基面滑移的CRSS值为42 MPa[7],因此,屈服强度介于ED和TD试样之间。这与BARNETT等[18]关于c轴与拉伸夹角介于35°和75°之间时,{0001}基面滑移是主要变形机制的论述相吻合。
拉伸孪晶,而产生此拉伸孪晶的CRSS值很低,只需要2~2.8 MPa[17],并且拉伸孪生可以使晶粒取向发生一定旋转,使晶粒取向利于基面滑移,从而让拉伸孪生和基面滑移交替进行,因此,TD试样的断裂应变值高于ED试样的,屈服强度却最低,除此之外拉伸孪生还可以阻碍位错的移动,使得TD试样的抗拉强度提高。对介于ED和TD之间的某个取样角度,总有一个拉伸方向与晶粒(少量c轴平行于TD)的c轴夹角呈45°,Schmid因子为0.5,易产生基面滑移,而基面滑移的CRSS值为42 MPa[7],因此,屈服强度介于ED和TD试样之间。这与BARNETT等[18]关于c轴与拉伸夹角介于35°和75°之间时,{0001}基面滑移是主要变形机制的论述相吻合。

图3 板材法向、挤压方向和横向的反极图
Fig. 3 Inverse pole figures of sheets along ND (a), ED (b) and TD (c)
图4所示为AZ31挤压态镁合金在不同温度下抗拉强度随取样角度变化规律。由图4可以看出,挤压态镁合金的抗拉强度随着取样角度的增大而增大,从室温到120 ℃,镁合金的抗拉强度下降很慢;170 ℃以后,镁合金的抗拉强度下降很快;250 ℃以后,镁合金的抗拉强度降低为室温时的一半,这表明了170 ℃以上是适合镁合金的塑性加工温度,但温度越高,越容易发生氧化,故镁合金的温热加工适合的温度范围是170~250 ℃。120 ℃时,ED和TD试样的抗拉强度差Δσ为25 MPa左右,在170 ℃时,这一差值被迅速提高到54 MPa,随着温度的继续升高,Δσ反而开始降低,250 ℃以上时,各向性能变化微乎其微。这表明了170 ℃时镁合金的各向异性最明显,由于温度升高,再结晶更加容易,将削弱变形机制对各向异性的影响。

图4 板材取样角度对抗拉强度的影响
Fig. 4 Influence of sampling angle on tensile strength of sheet
2.2 显微组织分析
图5(a)所示为挤压AZ31态镁合金板材初始的组织,由粗大的等轴动态再结晶晶粒组成,但晶粒大小分布不均匀。图5(b)~(f)所示为在170 ℃下不同取样角试样的拉伸断口附近金相照片,箭头方向为拉伸方向。由图5可以看出,沿不同方向拉伸均出现了条带状的孪晶,孪晶从晶界处尤其是三叉晶界处开始形核并长大,但各图中孪晶的方向并不一致,这是由于晶粒取向的关系。当晶体在应力的作用下发生变形时,变形部分会沿着一定的晶面(孪生面)和一定的晶向(孪生方向)相对于另一部分做均匀切变,这种切变不会改变点阵结构但会使变形部分的晶粒取向发生改变,从而利于变形的进行。45°试样较其他几个角度的试样,孪晶的比例较小,这表明45°试样塑性变形机制除了少量的孪生,更多的是滑移,这使得45°试样的断后伸长率达到最大(44.5%)。图5(e)和(f)中有着明显的交叉孪晶,多发生在较大的晶粒中,且贯穿整个晶粒,并有多条孪晶带互相平行,这表明了镁合金可以通过孪晶以及交叉孪晶来细化晶粒,导致急剧的加工硬化,提高强度和断裂应变值,因此,ED试样的断裂应变值最低,如图2(b)中67.5°和TD试样应力-应变曲线。孪晶界面的快速迁移和交叉主要发生在变形后期[19],这对镁合金的塑性变形能力有着重要的影响。ED试样和TD试样出现的动态再结晶要明显多于其他几个角度的试样,且优先生长在晶界和孪生交叉处(见图5 (b)和(f)圆圈内所示)。这是由于ED和TD试样拉伸时,易于产生压缩孪晶和拉伸孪晶,其界面更容易旋转,使晶粒更易于向孪晶取向转动,因此,孪生多的晶粒里形变储存能很小,不易达到形核的临界驱动力;而在晶界和孪生交叉处有很大的应力集中区,有着很大的形变储存能,为动态再结晶提供了足够的形核驱动力[20]。因此,动态再结晶的发生在一定程度上提高金属的塑性,使得金属的断裂应变值增加。

图5 170 ℃下挤压镁合金板材不同取样角试样断口金相照片
Fig. 5 Fractures metallographies of magnesium alloy with different sampling angles extruded at temperature of 170 ℃
2.3 断口分析
图6所示为170 ℃下沿不同取样角拉伸断口宏观形貌。由图6可知,1、2、3、5号试样均出现不同程度缩颈,其中3号试样缩颈最大,且缩颈区域周围出现了明显的起皱变形,这是由于晶粒内部变形的不均匀,说明断前发生了剧烈的塑性变形。4号试样断口平齐,无明显缩颈,说明67.5°试样为脆性断裂,断后伸长率只有12.5%,为5组试样中最低的一组。其它几组试样的断后伸长率见表2。虽然67.5°和TD试样的断后伸长率不及45°试样,但其断裂应变值仍大于45°试样(见图2(b)),这说明67.5°和TD试样的变形在标距外也有发生,同时也说明了拉伸孪生促进滑移的产生和加工硬化的形成。
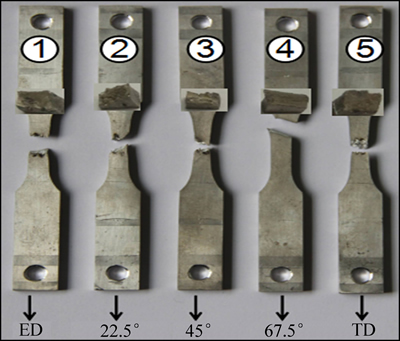
图6 170 ℃下不同取样角度样的拉伸断裂宏观形貌
Fig. 6 Macro-morphologies of tensile fracture of different angle specimens at temperature of 170 ℃
图7(a)~(f)所示分别为ED、22.5°、45°、67.5°、TD试样在170℃下拉伸试验后的断口形貌扫描照片。图7 (a)~(c)出现明显微孔聚合型的等轴韧窝,且韧窝较大,属于典型的韧性断裂;图7 (d)呈现明显的河流花样并伴有撕裂棱,属于典型的解理断裂;图7 (f)的剪切唇与韧窝都被拉长,伴有解理台阶,说明断裂前发生了滑移,属于韧-脆断裂的混合机制。结果表明:挤压态镁合金沿挤压方向45°范围以内拉伸,韧性都较好,尤其是与挤压方向呈45°拉伸时,断口韧窝最大(见图7(c)),塑性最好,这与45°试样的断后伸长率最大相一致;拉伸方向与挤压方向大于45°时伴有解理断裂,在67.5°时呈完全解理断裂。这是由于45°以后,交叉孪晶发生越来越多,会阻碍滑移的进行,造成位错塞积,应力集中,导致脆性断裂;在接近TD方向,由于动态再结晶的增多,缓解了部分应力集中,导致了韧-脆混合断裂机制。
表2 不同取样角试样的断后伸长率
Table 2 Break elongation of different sampling angle specimens after fracture


图7 170 ℃下挤压镁合金板材不同取样角的拉伸断口形貌
Fig. 7 Tensile fracture morphologies of Mg alloy sheet with different sampling angles extruded at 170 ℃
3 结论
1) 挤压态AZ31镁合金力学性能有显著各向异性,170 ℃时各向异性最明显,随着拉伸方向与挤压方向所呈角度的增大,抗拉强度逐渐增大,屈服强度逐渐减小。
2) 挤压态AZ31镁合金在温热条件下拉伸变形,不同取样方向的变形机制不同,导致断裂应变值随着拉伸方向与挤压方向所呈角度的增大而增大。
3) 挤压态AZ31镁合金在温热条件下拉伸方向与挤压方向所呈角度在45°以内时,挤压态镁合金表现为微孔聚集型的韧性断裂,伴随着角度的增大,表现为韧-脆混合断裂,其中67.5°时以解理方式断裂。
REFERENCES
[1] LEE S, CHEN Y H, WANG J Y. Isothermal sheet metal formability of magnesium alloy AZ31 and AZ61[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2002, 124(1/2): 19-24.
[2] 张士宏, 程 明, 王忠堂, 刘劲松. 有色金属板材若干温热加工成形技术的发展[J]. 锻压技术, 2009, 34(4): 1-9.
ZHANG Shi-hong, CHENG Ming, WANG Zhong-tang, LIU Jin-song. Development of warm forming processes for nonferrous alloy sheets[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2009, 34(4): 1-9.
[3] AGNEW S R, DUYGULU O. Plastic anisotropy and the role of non-basal slip in magnesium alloy AZ31B[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2005, 21: 1161-1193.
[4] HUANG Guang-sheng, ZHANG Hua, GAO Xiao-yu, SONG Bo, ZHANG Lei. Forming limit of textured AZ31B magnesium alloy sheet at different temperatures[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(4): 836-843.
[5] STEINER M A, BHATTACHARYYA J J, AGNEW S R. The origin and enhancement of {0001}< > texture during heat treatment of rolled AZ31B magnesium alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 95: 443-455.
> texture during heat treatment of rolled AZ31B magnesium alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 95: 443-455.
[6] BOHLEN J, NURNBERG M R, SENN J W, LETZIG D, AGNEW S R. The texture and anisotropy of magnesium-zinc-rare earth alloy sheets[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55: 2101-2112.
[7] STANFORD N, GENG J, CHUN Y B, DAVIES C H J, NIE J F, BARNETT M R. Effect of plate-shaped particle distributions on the deformation behaviour of magnesium alloy AZ91 in tension and compression[J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60: 218-228.
[8] CHINO Y, KIMURA K, HAKAMADA M, MABUCHI M. Mechanical anisotropy due to twinning in an extruded AZ31 Mg alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 485(1/2): 311-317.
[9] 李树梅, 汪明朴, 张 真, 李 周, 唐 宁. AZ31B镁合金的低温压缩变形机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(7): 1254-1259.
LI Shu-mei, WANG Ming-pu, ZHANG Zhen, LI Zhou, TANG Ning. Compression mechanism of AZ31B Mg alloy at low temperature[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(7): 1254-1259.
[10] 黄洪涛, 刘 伟, GODFREY A, 唐瑞鹤, 刘 庆. AZ31镁合金单轴压缩中孪生行为研究[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(3): 357-362.
HUANG Hong-tao, LIU Wei, GODFREY A, TANG Rui-he, LIU Qing. Study of twin behavior during uniaxial compression of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(3): 357-362.
[11] 黄洪涛, GODFREY A, 刘 伟, 唐瑞鹤, 刘 庆. 样品取向对AZ31镁合金静态再结晶行为的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(8): 915-921.
HUANG Hong-tao, GODFREY A, LIU Wei, TANG Rui-he, LIU Qing. Effect of sample orientation on static recrystallization of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(8): 915-921.
[12] 娄 超, 张喜燕, 任 毅. 动态塑性变形下AZ31镁合金的孪生特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(10): 2642-2648.
LOU Chao, ZHANG Xi-yan, REN Yi. Twinning characteristic of AZ31 magnesium alloy during dynamic plastic deformation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(10): 2642-2648.
[13] 唐伟琴, 张少睿, 范晓慧, 李大永, 彭颖红. AZ31镁合金的织构对其力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(3): 371-376.
TANG Wei-qin, ZHANG Shao-rui, FAN Xiao-hui, LI Da-yong, PENG Ying-hong. Texture and its effect on mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(3): 372-377.
[14] 肖 寒, 宋广胜, 严 操, 张士宏, 阮立群, 张兴国. 温热弯曲成形过程中 AZ31镁合金型材的微观织构演变[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(8): 1815-1819.
XIAO Han, SONG Guang-sheng, YAN Cao, ZHANG Shi-hong, RUAN Li-qun, ZHANG Xing-guo. Microtexture evolution of AZ31 magnesium alloy profile during warm bending process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(8): 1815-1819.
[15] 余 琨, 芮守泰. AZ31镁合金挤压薄板织构及力学各向异性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(12): 2127-2131.
YU Kun, RUI Shou-tai. Texture and mechanical anisotropy of AZ31 extruded sheets[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(12): 2127-2131.
[16] 黄光胜, 黄光杰, 王凌云, 潘复生. 变形镁合金塑性的改善[J]. 材料导报, 2006, 20(1): 39-41.
HUANG Guang-sheng, HUANG Guang-jie, WANG Ling-yun, PAN Fu-sheng. Ductility enhancement of wrought magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(1): 39-41.
[17] 刘 庆. 镁合金塑性变形机理研究进展[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(11): 1458-1472.
LIU Qing. Research progress on plastic deformation mechanism of Mg alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(11): 1458-1472.
[18] BARNETT M R, KESHAVARZ Z, BEER A G, MA X. Schmid behaviour during secondary twinning in a polycrystalline magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56: 5-15.
[19] 杨续跃, 张 雷. 镁合金温变形过程中的孪生及孪晶交叉[J]. 金属学报, 2009, 45(11): 1303-1308.
YANG Xu-yue, ZHANG Lei. Twinning and twin intersection in AZ31 Mg alloy during warm deformation[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45(11): 1303-1308.
[20] 李 萧, 杨 平, 孟 利, 催凤娥. AZ31镁合金中拉伸孪晶静态再结晶的分析[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(2): 147-154.
LI Xiao, YANG Ping, MENG Li, CUI Feng-e. Analysis of the static recrystallization at tension twins in AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(2): 147-154.
Anisotropy of warm-temperature tensile properties of extruded AZ31 magnesium alloy
WU Guo-hua1, XIAO Han1, ZHOU Hui-zi1, WANG Rui-xue2, CHENG Ming2, ZHANG Shi-hong2
(1. Faculty of Materials Science and Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093, China;
2. Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract: The tensile properties, microstructure, appearance of fracture in five different planar directions of extruded AZ31 magnesium alloy sheets at the warm-temperature were investigated by uniaxial compression test. The results indicate that the extruded magnesium alloy sheets show high anisotropy, and the most obvious anisotropic temperature is 170 ℃. With the increase of the angle between tensile direction and extrusion direction, the tensile strength increases from 217 MPa to 271 MPa, and the yield strength decreases from 174 MPa to 71 MPa. There are three deformation mechanisms of magnesium alloys at warm-temperature, which include  extension twinning,
extension twinning,  compression twinning and base slip. The deformation mechanism is different at different stretching angles. When the angle between tensile direction and extrusion direction is less than 45°, the fracture mechanism of magnesium alloy is micropore aggregation fracture. With the increase of angle, it is the mixed fracture of toughness and brittleness, and the cleavage fracture occurs at the angle of 67.5°.
compression twinning and base slip. The deformation mechanism is different at different stretching angles. When the angle between tensile direction and extrusion direction is less than 45°, the fracture mechanism of magnesium alloy is micropore aggregation fracture. With the increase of angle, it is the mixed fracture of toughness and brittleness, and the cleavage fracture occurs at the angle of 67.5°.
Key words: magnesium alloy; warm-temperature tensile property; twinning; fracture mechanism; anisotropy
Foundation item: Project(51305188) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(P2015-12) supported by State Key Laboratory of Materials Processing and Die & Mould Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Received date: 2016-01-04; Accepted date: 2016-05-18
Corresponding author: XIAO Han; Tel: +86-871-65136755; E-mail: kmxh@kmust.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(51305188);华中科技大学材料成形与模具技术国家重点实验室开放课题研究基金(P2015-12)
收稿日期:2016-01-04;修订日期:2016-05-18
通信作者:肖 寒,副教授,博士;电话:0871-65136755;E-mail:kmxh@kmust.edu.cn