DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.08.25
300 kA铝电解槽中氧化铝颗粒的溶解模拟
李 茂,高玉婷,白 晓,李 远,侯文渊,王玉洁
(中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:在铝电解下料过程中,氧化铝颗粒吸热、结块、溶解并受到传热与传质溶解机制的综合作用。基于OpenFOAM计算平台,有效区分主导颗粒溶解的控制机制,考虑气泡作用和下料后的电解质温度响应,开发铝电解槽中氧化铝颗粒传热、传质耦合溶解计算模型;利用Rosin-Rammler分布函数计算下料后电解质中氧化铝颗粒粒径分布,对实际300 kA铝电解槽中氧化铝溶解过程进行数值模拟。结果表明:前18 s氧化铝溶解50%(质量分数),属于快速溶解阶段;一个下料周期144 s结束后,剩余约1.5%(质量分数)的氧化铝未溶解,未溶解颗粒聚集,并在电解槽底部形成沉淀;仅考虑氧化铝溶解吸热的情况下,下料区位置电解质温度在前1 s快速下降,随后,电解质温度快速回升并在60 s之后呈现震荡趋势。
关键词:结块;氧化铝溶解;传热;传质;粒径分布;数值模拟
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-08-1738-10 中图分类号:TF821 文献标志码:A
氧化铝作为铝电解生产中的主要原料,其溶解与扩散的快慢直接决定了电解工艺的稳定性[1]。随着铝电解槽的日益大型化、系列化,对铝电解技术与设备提出了更高的要求,特别是300 kA、500 kA大型铝电解槽的应用,极距区高度逐渐减小,氧化铝的溶解与扩散更为困难,产生的结块不能及时溶解而沉淀到槽底,如何保证氧化铝能够在下料后快速的在电解质中溶解扩散是现在亟待解决的问题。
由于现行工业槽内的高温强腐蚀等不利环境,现场难以直接研究氧化铝在实际电解槽中的溶解过程,主要利用坩埚或透明石英槽对氧化铝的溶解规律进行研究[2-4]。随着计算流体力学地发展,目前国内外一些学者开始从数值模拟的角度来研究实际铝电解槽中氧化铝的溶解扩散过程。詹水清等[5]对整个槽中氧化铝的浓度分布进行数值模拟,研究得出阳极气泡是氧化铝扩散的主要动力,电磁力可促进氧化铝在全槽的扩散。POI等[6]和VERHAEGHE等[7]认为氧化铝溶解的驱动力是氧化铝浓度差,以此提出氧化铝传质控制溶解模型;而LILLEBUEN等[8]和BEREZIN等[9]则认为过热度为驱动氧化铝溶解的主要作用,提出了氧化铝传热控制溶解模型。张家奇[10]在考虑氧化铝物性参数等对氧化铝溶解的影响,通过实验拟合得到了一个氧化铝溶解通用模型。ZHAN等[11-12]提出双颗粒相群体平衡模型(TPPBM),以500 μm作为区分粒径对氧化铝颗粒溶解的传热、传质控制机制进行了数值模拟。张翮辉等[13-14]建立500 kA铝电解槽氧化铝输运过程的多组分多相流模型,讨论分析氧化铝下料过程中电解质流场和氧化铝浓度分布,但研究未考虑氧化铝结块溶解。丁培林等[15]研究下料过程中电解质温度及热平衡的变化趋势,表明氧化铝周期性的下料会破坏电解槽热平衡。TAYLOR等[16]基于实验预测可将400 μm的颗粒粒径作为两种控制机制作用的区分粒径。侯文渊等[17]基于所建立的氧化铝颗粒溶解的传质控制模型和收缩核模型,研究得出氧化铝颗粒溶解速率随粒径的减少而迅速减小。李茂等[18]详细研究分析传热、传质等两种溶解控制机制,并给出了区分主导机制的临界直径,即小于560 μm的氧化铝颗粒溶解受传质机制控制,大于560 μm的氧化铝颗粒溶解受传热机制控制。然而,以上研究或是基于理想电解槽模型进行数值模拟,或认为氧化铝下料后瞬时溶入电解质中,或未对实际槽进行分析验证,或未考虑在不同粒径下氧化铝溶解受到的控制机制不同,因此有待进一步深入研究。
本文作者基于OpenFOAM开源软件平台,分别建立氧化铝颗粒传质溶解模型与传热溶解模型,开发了铝电解槽中氧化铝颗粒传热、传质耦合控制下的溶解求解模块,综合考虑气泡作用和下料后的温度响应效应,对实际300 kA铝电解槽中氧化铝颗粒的溶解过程进行求解,讨论分析一个下料周期144 s内氧化铝质量溶解速率,未溶解颗粒分布以及电解质温度的变化。
1 物理模型
1.1 铝电解槽物理模型
本文作者以300 kA铝电解槽为研究对象,气泡作为分散氧化铝颗粒的主要驱动力,对电解槽中气泡作用下氧化铝的溶解过程进行数值模拟。因铝液对氧化铝在电解质中的溶解影响较小,忽略铝液层的计算,取电解质区域作为计算区域。气泡作用下的电解质流场关于长轴和短轴对称,本文作者选取一个下料点作为研究对象,溶解后的氧化铝主要集中在下料点周围几块阳极区域,不影响计算准确性及为减少计算费用的前提下,选取半槽进行计算,即关于短轴对称的半个铝电解槽。电解槽具体参数如表1所示,半槽尺寸为3840 mm×7400 mm×180 mm,计算区域模型及下料点示意图如图1和2所示。
表1 铝电解槽相关参数
Table 1 Parameters of aluminum electrolytic cell

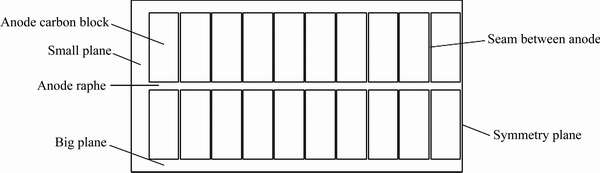
图1 铝电解槽计算区域
Fig. 1 Computation domain of aluminum electrolytic cell
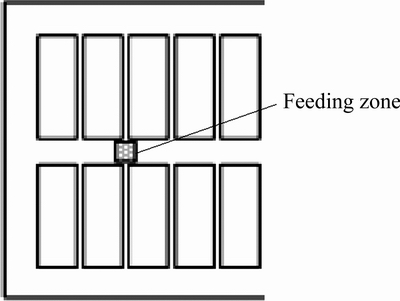
图2 氧化铝下料区示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of alumina feeding zone
1.2 基本假设
实际铝电解过程中,氧化铝颗粒的溶解过程受多方面因素的影响,在进行模拟计算时作出如下假设[19]:
1) 忽略阳极炭块的消耗,阳极底掌水平;
2) 忽略槽帮的影响;
3) 忽略铝液层对电解质运动的影响;
4) 忽略结块的形成过程,即在下料后部分氧化铝迅速形成结块。
5) 忽略电解质中氧化铝的消耗以及电流对电解质的加热,重点关注氧化铝的溶解过程。
2 数学模型
2.1 动量方程
对于气泡作用下电解质的流动过程,其主要受气泡作用力以及氧化铝颗粒与电解质之间动量交换的影响,满足如下动量方程:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
式中:τ为时间,s;u为电解质速度矢量,m/s;ρL为电解质的密度,kg/m3;μ为电解质动力黏度,Pa·s;u、v和w分别代表速度矢量u在x、y和z方向的分量,m/s。S是广义源项,包含体积力、气泡作用力和氧化铝电解质动量交换项Smt等,其中Smt如下所示:
 (4)
(4)
式中:Vcell为单元网格体积,m3;Δτ为时间步长,s;uSe、uSs分别为氧化铝颗粒的初速度和氧化铝颗粒终速度,m/s。通过计算氧化铝颗粒的动量变化可以得出电解质动量变换量,以此对电解质动量方程进行求解。
2.2 颗粒运动与曳力模型
在多数流体—颗粒两相流动过程中,曳力是作用于颗粒的主要作用力,曳力的大小与颗粒大小、颗粒与流体相对运动速度以及曳力系数有关,曳力公式如下所示[20]:
 (5)
(5)
式中:uL、uP分别为电解质流速和氧化铝颗粒流速,m/s ; ,表示氧化铝颗粒横截面积,m2;CD为曳力系数,与氧化铝颗粒雷诺数有关,具体表述如下:
,表示氧化铝颗粒横截面积,m2;CD为曳力系数,与氧化铝颗粒雷诺数有关,具体表述如下:
 (6)
(6)
对于氧化铝颗粒,通过对单个颗粒进行受力分析,运用拉格朗日的方法追踪氧化铝颗粒的运动,运用牛顿第二定律:
 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
通过方程(5)~(8)方程的联立求解,可获得氧化铝颗粒每一时刻的位置以及速度,即氧化铝颗粒的运动轨迹。
2.3 输运方程
氧化铝颗粒溶于电解质后,建立氧化铝浓度输运方程如下:
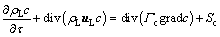 (9)
(9)
式中: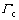 为氧化铝浓度扩散系数,m2/s;Sc与氧化铝颗粒所在位置有关,当前计算网格没有氧化铝颗粒时,Sc为0;存在氧化铝颗粒时,Sc与溶解速率有关,即单元网格内所包含氧化铝颗粒的单位时间溶解量。
为氧化铝浓度扩散系数,m2/s;Sc与氧化铝颗粒所在位置有关,当前计算网格没有氧化铝颗粒时,Sc为0;存在氧化铝颗粒时,Sc与溶解速率有关,即单元网格内所包含氧化铝颗粒的单位时间溶解量。
氧化铝在电解质中的溶解过程是一个吸热过程,造成电解质温度的下降,建立其能量方程如下:
 (10)
(10)
式中:λ为导热系数,W/(m·K);ST同Sc类似,当网格内有氧化铝颗粒时,ST表示单元网格单位时间内所包含所有氧化铝颗粒溶解时吸收的热量。
2.4 初晶温度计算
本研究选取的初始电解质成分如表2所示,经邱竹贤等[21]的经验计算,初始时刻初晶温度为950 ℃。
表2 电解质成分表[22]
Table 2 Composition of electrolyte (mass fraction, %)[22]

2.5 溶解模型
氧化铝的溶解受传热与传质两种溶解机制的控制,研究得出小于560 μm的氧化铝颗粒溶解受传质机制控制,大于560 μm的氧化铝颗粒溶解受传热机制控制,传质与传热溶解控制机制推导过程以及560 μm临界直径的得出详见文献[17-18, 23]。
在传质机制下,氧化铝颗粒收缩核模型表达式如下:
 (11)
(11)
在传热机制下,氧化铝颗粒收缩核模型表达式如下:
 (12)
(12)
式中:k为传质系数,m/s;h为对流换热系数,W/(m2·K);CAl为氧化铝比热容,J/(kg·k);ΔHdiss为氧化铝溶解热,J/kg; 为电解质密度,kg/m3;
为电解质密度,kg/m3;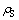 为氧化铝颗粒密度,kg/m3;wsat为电解质中氧化铝饱和浓度,%;w为当地氧化铝浓度,%;TL为电解质当地温度,K;Tliq为电解质初晶温度,K。
为氧化铝颗粒密度,kg/m3;wsat为电解质中氧化铝饱和浓度,%;w为当地氧化铝浓度,%;TL为电解质当地温度,K;Tliq为电解质初晶温度,K。
3 氧化铝颗粒粒径分布
3.1 氧化铝质量累计分布函数
在加入电解质之前,氧化铝颗粒粒径在40~200 μm的范围内,一旦进入电解质,部分氧化铝颗粒被凝固电解质包裹形成结块颗粒,这部分结块颗粒粒径较大,最大约10~15 mm[24]。电解质中实际氧化铝颗粒粒径分布难以测量,但其颗粒粒径一般服从Rosin-Rammler分布(简称R-R分布),分布函数的表达式为[25-27]:
 (13)
(13)
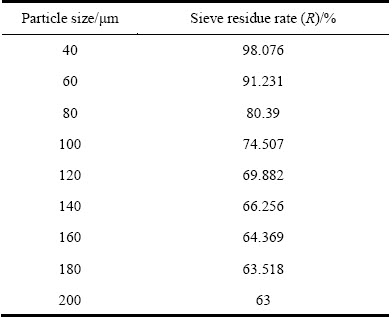
式中:R为累积质量分布,表示大于某一粒径的累积颗粒质量占所有颗粒的质量分数,又称筛余率;β和n分别代表与颗粒粒径分布有关的系数和指数;x表示颗粒粒径。
利用现场测试得到的下料前氧化铝颗粒粒径的分布,通过线性回归的计算方法进行求解,利用最小二乘法原理来评价回归线的好坏[25],以此获得能较为精确描述下料后氧化铝颗粒粒径分布的R-R分布函数。
根据式(14)计算未结块颗粒和结块颗粒的含量[9]:
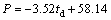 (14)
(14)
式中:P为未结块颗粒所占的含量(质量分数);td为氧化铝完全溶解的时间,一般td为6 min,则P约为37%。初始的氧化铝颗粒的粒径质量分布数据[12]是根据某研究院由粒度测试仪器测试得出,然后根据未结块颗粒质量约占37%,计算外推出下料后分散好的未结块颗粒分布,数据如表3所示。由于实际不能选取所有氧化铝颗粒粒径来计算求得R-R分布函数,本文作者选取如表4中的粒径来进一步计算求解。
经线性回归计算,得出下料后氧化铝颗粒在电解质中的质量累计分布函数为
 (15)
(15)
表3 氧化铝颗粒分布表
Table 3 Distribution of alumina particle
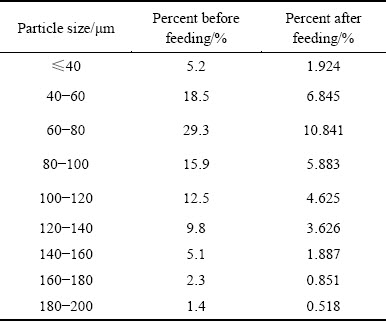
表4 筛余率计算
Table 4 Calculation of sieve residue rate
3.2 下料后初始氧化铝颗粒分布
实际铝电解槽中加入的氧化铝颗粒数以亿计,目前数值模拟还远达不到此计算要求,因此,需要对氧化铝颗粒数进行合理简化,用一个氧化铝计算颗粒代表一定数目的实际氧化铝颗粒,但在计算溶解的时候,通过修正源项的方式将单个颗粒的溶解量乘以其所代表的颗粒数,以此来得到实际氧化铝溶解量,温度场的计算方式相同。本研究中计算下料区大小为16 cm×16 cm×2 cm,共生成128个网格,因此每一时间步长(0.001 s)下料128个颗粒,每个网格每次下料一个颗粒,在0.1 s时长内全部颗粒进入下料区,模拟计算的计算颗粒总数与下料时长以及各计算颗粒所代表的实际颗粒数有关,下料完成后的这些颗粒数将代表实际电解槽中加入的1.8 kg氧化铝颗粒。
由于氧化铝在加入电解质之前绝大多数颗粒粒径集中在100 μm左右,氧化铝颗粒溶解的临界直径为560 μm,实际生产中最大结块颗粒粒径一般在1~1.5 cm之间,计算时选取最大结块粒径为1cm。根据前面已计算得出的R-R分布函数,对下料后的结块和未结块颗粒的质量累计分布进行计算和外推,得到下料后的氧化铝颗粒粒径分布统计表,如表5所示。在模拟实际氧化铝颗粒溶解时,由于不能按照实际的氧化铝颗粒粒径进行模拟,因此,本文作者选取粒径100、200、400、600、1000、2000、4000、6000、10000 μm来实现对实际氧化铝下料进电解质中的溶解模拟。
表5 下料后颗粒粒径分布统计表
Table 5 Distribution of particle size after feeding
4 气泡作用下氧化铝溶解计算结果分析
电解质流动的主要驱动力是气泡作用力和电磁力,而氧化铝颗粒下料后主要集中在铝电解槽中缝,主要受气泡鼓动的作用而分散,因此本文将重点关注300 kA电解槽中氧化铝颗粒在气泡作用下的溶解过程。
4.1 气泡作用下电解质流场分布
提取CFX计算的300 kA铝电解槽内阳极气泡的作用力[23],通过源项添加的方式加入到电解质动量方程中,得到如图3所示的阳极气泡作用下电解质流场分布图。
从图3可以明显看出,阳极气泡作用下电解质最大流速为0.55 m/s,且其出现在间缝对冲区,下料区位于中缝与间缝交接处区域,此处电解质流速较大,两个间缝中流入中缝的电解质形成对冲,使得电解质上下搅拌,有利于氧化铝颗粒的快速分散。
4.2 氧化铝质量溶解分析
利用已得出的1.8 kg氧化铝颗粒粒径分布,模拟在阳极气泡作用下氧化铝的溶解及输运过程,得到氧化铝累积质量分数,模拟结果与文献[28]的对比如图4所示。
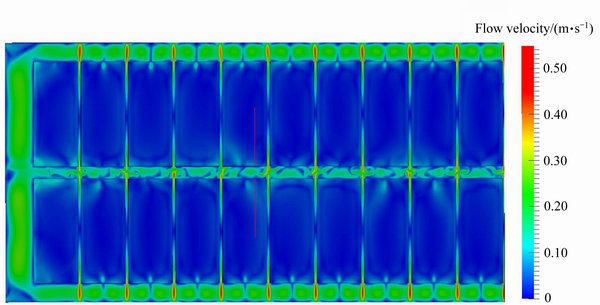
图3 阳极气泡作用下电解质流场分布图
Fig. 3 Electrolyte flow field distribution under effect of anode bubble
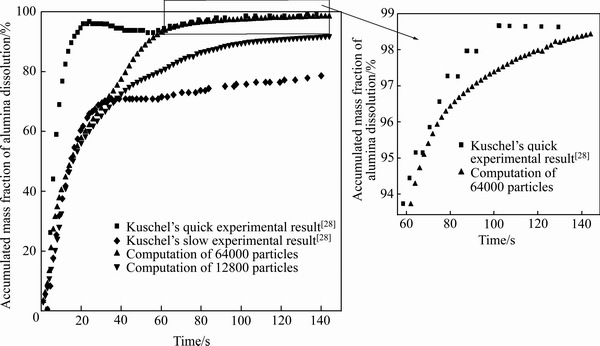
图4 氧化铝累计溶解质量分数
Fig. 4 Accumulated mass fraction of alumina dissolution
图4中KUSCHEL等[28]的实验为在一个固定圆筒容器中加入搅拌器来模拟实际电解质流动,KUSCHEL等[28]将氧化铝溶解实验分为两种情况,第一种是快速溶解实验,将氧化铝快速分散的倒入电解质中,目的是尽可能地避免氧化铝颗粒聚集而形成结块,加快氧化铝溶解;第二种是普通下料无搅拌,考虑了颗粒因聚集而结块的情况,溶解速度较慢。实际电解槽测量氧化铝溶解较为困难,利用与本文计算工况近似的Kuschel实验来进行对比分析:分别选择下料12800个计算颗粒与64000个计算颗粒来代表1.8 kg总的氧化铝颗粒数,研究计算颗粒数对计算结果的影响,选择模拟结果更贴近实际的颗粒数进行分析。
从图4可以看出,前30 s中,12800个计算颗粒、64000个计算颗粒的溶解模拟结果与KUSCHEL等[28]慢速实验结果吻合较好;30~60 s之间,12800个颗粒与64000个颗粒的累计溶解质量曲线高于KUSCHEL等[28]慢速实验结果,逐渐向快速溶解结果曲线靠近, 60 s后,64000个颗粒的溶解曲线与KUSCHEL等[28]快速实验结果基本吻合,而12800颗粒的溶解速度要慢,但也趋近于快速溶解曲线。造成模拟结果与实验结果差别的原因主要有以下几点:KUSCHEL等[28]慢速实验因为无搅拌而反应了颗粒因聚集而结块的情况,模拟的12800个和64000个计算颗粒的溶解同样考虑了氧化铝结块,因此,前30s左右模拟结果与KUSCHEL等[28]慢速实验结果接近。而30~60 s时,由于实验是在直径为10 cm的小槽中做的,浓度差的减小以及过热度降低导致氧化铝溶解速率减小,造成氧化铝溶解缓慢;但实际电解槽尺寸较大,在气泡湍动作用下氧化铝颗粒周边不断有新鲜电解质补充,使总体电解质区域浓度和温度的变化梯度不大,因此模拟计算氧化铝溶解曲线会高于KUSCHEL等[28]慢速实验结果。60 s后,64000个计算颗粒的模拟结果与KUSCHEL等[28]的快速实验吻合,虽然KUSCHEL等[28]的快速实验尽可能地使氧化铝颗粒均匀分散地加入电解质中,但是仍有少部分颗粒会因聚集而形成少量结块,这些结块颗粒溶解缓慢,而在64000个计算颗粒的模拟计算中,小颗粒在前60 s大部分已经溶解,剩余未溶解的颗粒基本为大的结块颗粒,因此,在60 s之后与快速溶解曲线吻合。造成12800个和64000个计算颗粒计算结果差异的原因是模拟颗粒所代表实际颗粒数的不同,模拟颗粒数越多,一个颗粒所代表的实际氧化铝颗粒就越少,越接近于实际生产情况,因此,64000颗粒的模拟更接近于实际,且与实验吻合较好,说明利用传热传质耦合模型计算实际铝电解槽中氧化铝的溶解是可行的。本文作者将选取64000个计算颗粒的模拟结果来研究300 kA铝电解槽中的溶解情况。
KOBBELTVEDT[29]发现氧化铝在15 s左右溶解了50%的质量,且其定义这一时间段为快速溶解阶段。从图4中可以看出,在18 s左右氧化铝溶解了50%的质量,与KOBBELTVEDT[29]的快速溶解时间接近,因此,本研究所计算的300 kA铝电解槽中,下料后前18 s时间段内为氧化铝快速溶解阶段。64000个计算颗粒模拟结果表明,在一个下料周期144 s结束时还有约1.5%左右的氧化铝未溶解,这些未溶解的氧化铝质量绝大部分集中在大的结块颗粒上,这些结块颗粒溶解较慢,最后沉在电解槽底部形成沉淀,通过计算,300 kA铝电解槽的一个下料区在一个下料周期内将会有约0.027 kg的氧化铝形成沉淀,与实际生产符合较好,因此可以利用数值计算的方法为以后的生产下料量及下料周期提供理论指导。
未溶解氧化铝颗粒示意图如图5所示。
图5 未溶解氧化铝颗粒示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of undissolved alumina particle
4.3 下料区电解质温度变化分析
氧化铝从下料区加入到电解质后,因在下料区电解质温度下降最为明显,本文作者选取下料区平均温度作为研究对象,在不考虑电流加热及电解槽周边散热的情况下,研究氧化铝溶解的吸热过程。图6所示为下料区电解质平均温度变化曲线。
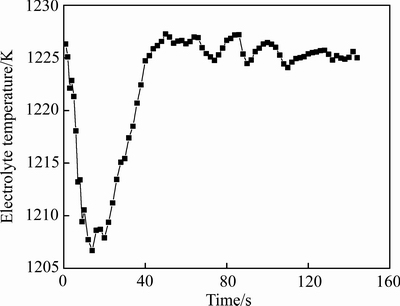
图6 下料区电解质平均温度变化曲线
Fig. 6 Variation of average electrolyte temperature in feeding zone
由图6可知,在下料后的前14 s左右,此时属于氧化铝快速溶解阶段,分散型小颗粒快速溶解而大量吸热,电解质温度由初始的1233 K(960 ℃)迅速下降,温度最多下降达26 ℃,这与相关文献实验得出的电解质在10 s左右降温到最低点,随后温度逐渐上升的结果接近[30-31]。在14 s之后,电解质的流动将下料区温度较低的电解质经对流扩散开,得到周围温度较高的电解质补充使得下料区温度快速升高。此外,在60 s之后温度呈现震荡趋势,这是由于部分氧化铝颗粒还处于下料区未被冲走,以及其余地方温度较低的电解质流过来造成温度震荡。由于本文作者重点研究氧化铝溶解的吸热过程,而要同时耦合铝电解槽热平衡计算则难度较大,因此忽略了极距间电流对电解质的加热,导致最后下料区温度不能上升到初始电解温度1233 K,但总体温度变化规律与实验结果是接近的,比较结果如图7所示。
图7所示为下料区电解质温度下降曲线对比图,图中1~5点的数据为WALKER[30]在91 kA点式下料电解槽上所得到的测试数据,初始电解质温度为985 ℃,1号点位于下料区电解质液面以下1 cm处,2~5点测试位置深度逐个降低1 cm,利用热电偶每隔1 s记录一次数据。由图7可知,1、2点测试的温度下降较快,最高下降了90 ℃,这是由于其测试点位于下料区上层,下料后的氧化铝溶解大量吸热,导致热电偶表面一些氧化铝颗粒和凝固的电解质形成一层凝固层,使其不能与液体电解质直接接触,而氧化铝颗粒的不断吸热造成凝固层温度较低,使得温度测试数据较低而失真。模拟结果与3~5测试点数据比较发现,温度变化规律大体相同,均为先减小后增大,最低下降了26 ℃左右,温度下降最大时所用时间略有差别。在14 s后,模拟下料区温度上升较实验温度上升稍慢,这可能是由于计算值为下料区域均值其变化相对慢,而温度的回升是由电解质流动混合后导致的。
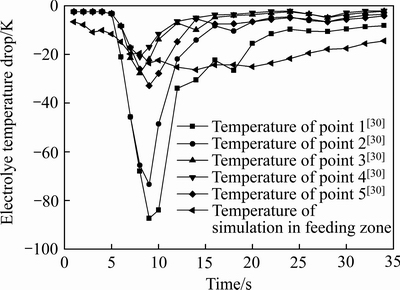
图7 下料区电解质温度变化曲线
Fig. 7 Change curves of electrolyte temperature in feeding zone
5 结论
1) 基于OpenFOAM计算平台,考虑气泡作用和下料后的电解质温度响应及其液相线变化,建立了铝电解槽中电解质以及氧化铝颗粒的欧拉-拉格朗日计算模型,开发了实际300 kA铝电解槽中氧化铝颗粒的传热传质耦合控制下的溶解模型,模拟计算结果与相关实验文献结果吻合较好。
2) 氧化铝颗粒经下料进入电解质后,其粒径服从R-R分布,通过线性回归的计算方法推导出电解质中氧化铝颗粒粒径分布函数为 。
。
3) 氧化铝颗粒下料后主要集中在铝电解槽中缝,主要受气泡鼓动的作用而分散,模拟在阳极气泡作用下氧化铝的溶解过程,在前18 s,氧化铝溶解了50%的质量,分散好的小颗粒快速溶解,属快速溶解阶段;30 s后,溶解速率逐渐减慢;60 s后,绝大部分小颗粒已溶解完全,剩余大的结块颗粒缓慢溶解;一个下料周期144 s结束后,剩余约1.5%的氧化铝未溶解,这些未溶解的颗粒聚集形成沉淀。
4) 仅考虑氧化铝溶解吸热的情况下,下料区位置电解质温度在前14 s快速下降,随后在电解质流动作用下该区域由温度较高的电解质补充,温度快速回升,之后因氧化铝的溶解吸热以及电解质的对流扩散,下料区电解质温度呈震荡变化。
5) 模拟结果与相关文献实验数据吻合较好,验证了模拟的准确性,因此,可以利用数值计算的方法为以后的生产下料量及下料周期提供理论指导。
REFERENCES
[1] YANG You-jian, GAO Bing-liang, WANG Zhao-wen, SHI Zhong-ning, HU Xian-wei. Effect of physiochemical properties and bath chemistry on alumina dissolution rate in cryolite electrolyte[J]. JOM, 2015, 67(5): 973-983.
[2] 徐君莉, 石忠宁, 高炳亮, 邱竹贤. 氧化铝在熔融冰晶石中的溶解[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 24(9): 832-834.
XU Jun-li, SHI Zhong-ning, GAO Bing-liang, QIU Zhu-xian. Dissolution of alumina in molten cryolite[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2003, 24(9): 832-834.
[3] 杨振海, 高炳亮, 徐 宁, 邱竹贤, 刘耀宽. 熔融冰晶石中氧化铝的溶解(摄影研究)[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 1999, 20(4): 398-400.
YANG Zhen-hai, GAO Bing-liang, XU Ning, QIU Zhu-xian, LIU Yao-kuan. Dissolution of alumina in molten cryolite (A video recording study)[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 1999, 20(4): 398-400.
[4] ROLSETH S, HOVLAND R, KOBBELTVEDT O. Alumina agglomeration and dissolution in cryolitic melts[C]// MANNWEILER U. Light Metals1994. San Francisco, CA: TMS, 1994: 351-357.
[5] 詹水清, 李 茂, 周孑民, 周益文, 杨建红. 铝电解槽熔体内氧化铝浓度分布的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014(10): 2658-2667.
ZHAN Shui-qing, LI Mao, ZHOU Jie-min, ZHOU Yi-wen, YANG Jian-hong. Numerical simulation of alumina concentration distribution in melts of aluminum reduction cells[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(10): 2658-2667.
[6] POI N W, HAVERKAMP R G, KUBLER S. Thermal effects associated with alumina feeding in aluminium reduction cells[C]// MANNWEILER U. Light Metals1994. San Francisco, CA: TMS, 1994: 219-225.
[7] VERHAEGHE F, BLANPAIN B, WOLLANTS P. Dissolution of a solid sphere in a multicomponent liquid in a cubic enclosure[J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2008, 16(4): 45007.
[8] LILLEBUEN B O R, BUGGE M, HOIE H. Alumina dissolution and current efficiency in Hall-Heroult cells[C]// BEARNE G. Light Metals2009. San Francisco, CA: TMS, 2009: 389-394.
[9] BEREZIN A I, ISAEVA L A, BELOLIPETSKY V M, POSKAZHOVA T V, SINELNIKOV V V. A model of Dissolution and Heating of Alumina Charged by Point-Feeding System in “Virtual Cell” program[C]// KVANDE H. Light Metals 2005. San Francisco, CA: TMS, 2005: 151-156.
[10] 张家奇. 基于数学模型的铝电解槽动态过程及其预报系统研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2011.
ZHANG Jia-qi. Principal electrolysis processes and corresponding prediction system for aluminum electrolysis cells based on mathematical models[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2011.
[11] ZHAN Shui-qing, LI Mao, ZHOU Jie-min, YANG Jian-hong, ZHOU Yi-wen. CFD simulation of dissolution process of alumina in an aluminum reduction cell with two-particle phase population balance model[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering. 2014, 73(1): 803-816.
[12] ZHAN Shui-qing, LI Mao, ZHOU Jie-min, YANG Jian-hong, ZHOU Yi-wen. Analysis and modeling of alumina dissolution based on heat and mass transfer[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metal Society of China, 2015, 25(5): 1648-1656.
[13] 张翮辉. 铝电解槽内熔体涡运动与氧化铝输运过程的数值模拟研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
ZHANG He-hui. Numerical study of vortex flow of melts and transport process of alumina in aluminum reduction cells[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
[14] 江 南, 邱泽晶, 张翮辉, 张红亮, 杨 帅, 李 劼, 刘庆生. 500 kA级铝电槽内氧化铝浓度场的数值模拟[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(3): 799-805.
JIANG Nan, QIU Ze-jing, ZHANG He-hui, ZHANG Hong-liang, YANG Shuai, LI Jie, LIU Qing-sheng. Numerical simulation of alumina concentration field in 500 kA aluminum reduction cell[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2015, 25(3): 799-805.
[15] 丁培林, 王 恒, 黄 俊, 王紫千, 曹 斌. 铝电解槽下料过程对电解质温度场的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(2): 430-438.
DING Pei-lin, WANG Heng, HUANG Jun, WANG Zi-qian, CAO Bin. Effect of feeding in aluminum reduction cell on electrolyte temperature[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(2): 430-438.
[16] TAYLOR M P, WELCH B J, MCKIBBIN R. Effect of convective heat transfer and phase change on the stability of aluminum smelting cells[J]. AICHE Journal, 1986, 32(9): 1459-1465.
[17] 侯文渊, 李 茂, 李 远, 白 晓. 氧化铝颗粒在传质机制控制下的溶解模拟[J]. 轻金属, 2015(5): 24-28.
HOU Wen-yuan, LI Mao, LI Yuan, BAI Xiao. Simulation of alumina particle dissolution under the control of mass transfer mechanism[J]. Light Metals, 2015(5): 24-28.
[18] 李 茂, 白 晓, 李 远, 侯文渊, 高玉婷. 氧化铝颗粒的溶解控制机制及其临界直径[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(2): 456-462.
LI Mao, BAI Xiao, LI Yuan, HOU Wen-yuan, GAO Yu-ting. Control mechanisms and critical characteristics in dissolution of alumina particles[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(2): 456-462.
[19] 夏小霞. 铝电解槽内电解质流场的数值模拟研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2005.
XIA Xiao-xia. Study on numerical simulation of the flow field in aluminum reduction electrolyte cells[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2005.
[20] 胡道和, 徐德龙, 蔡玉良. 气固过程工程学及其在水泥工业中的应用[M]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学出版社, 2003: 146-148.
HU Dao-he, XU De-long, CAI Yu-liang. Gas-solid process engineering and its application in the cement industry[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 2003: 146-148.
[21] 张明杰, 邱竹贤. 工业铝电解质熔点数学模型的研究[J]. 轻金属, 1981(1): 15-22.
ZHANG Ming-jie, QIU Zhu-xian. Research on mathematical model of industrial aluminum electrolyte melting point[J]. Light Metals. 1981(1): 15-22.
[22] 冯乃祥. 铝电解[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006.
FENG Nai-xiang. Aluminum electrolysis[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006.
[23] 侯文渊. 铝电解槽内氧化铝颗粒溶解过程数值模拟[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2015.
HOU Wen-yuan. Numerical simulation of the dissolution process of alumina particle in aluminum electrolytic cell[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2015.
[24] PETER N. Evolution of alpha phase alumina in agglomerates upon addition to cryolitic melts[D]. Trondheim: Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2002.
[25] 刘 建, 姚海飞, 金龙哲, 欧盛南, 魏传光. 基于罗森-拉姆勒分布函数的粉尘分散度分析[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2010, 32(9): 1101-1106.
LIU Jian, YAO Hai-fei, JIN Long-zhe, OU Sheng-nan, WEI Chuan-guang. Dust dispersion analysis based on the Rosen-Rammler distribution function[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2010, 32(9): 1101-1106.
[26] 郑钢镖, 康天合, 尹志宏, 张驰明, 段 军. 不同冲击形式下煤样产尘粒径分布规律研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2007, 24(1): 96-100.
ZHENG Gang-biao, KANG Tian-he, YIN Zhi-hong, ZHANG Chi-ming, DUAN Jun. Research on dust size distribution of coal impacted with different forms[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2007, 24(1): 96-100.
[27] 戴丽燕. 关于Rosin-Rammler粒径分布函数的研究[J]. 工业安全与防尘, 2000, 26(5): 6-8.
DAI Li-yan. Study on function of Rosin-Rammler particle size distribution[J]. Industrial Safety and Dust Control. 2000, 26(5): 6-8.
[28] KUSCHEL G I, WELCH B J. Further studies of alumina dissolution under conditions similar to cell operation[C]// ELWIN R. Light Metals 1991. New Orleans, Louisiana: TMS, 1991: 112-118.
[29] KOBBELTVEDT O. Dissolution kinetics for alumina in cryolite melts[D]. Trondheim: Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Electrochemistry, 1997.
[30] WALKER D I. Alumina in aluminum smelting and its behaviour after addition to cryolite-based electrolytes[D]. Toronto: University of Toronto, 1993.
[31] WELCH B J, KUSHEL G I. Crust and alumina powder dissolution in aluminum smelting electrolytes[J]. JOM, 2007, 59(5): 50-54.
Simulation of alumina particle dissolution in 300 kA aluminum electrolytic cell
LI Mao, GAO Yu-ting, BAI Xiao, LI Yuan, HOU Wen-yuan, WANG Yu-jie
(School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: During the aluminum electrolytic feeding process, alumina particles will dissolve after absorbing heat, aggregation subject under the control of the mass and heat transfer mechanism. Based on the OpenFOAM computing platform, identifying the dominant mechanism controlling dissolution of alumina, considering the bubble effect and temperature response of electrolyte after feeding, the alumina, dissolution model coupled with heat and mass transfer were proposed. Based on the alumina particle size distribution calculated by Rosin-Rammler function, the actual dissolution process in electrolyte after feeding were simulated in 300 kA aluminum reduction cell. The simulation results show that the first 18 s is the quick stage of dissolution, in which about 50% of the quantity is dissolved. At the end of a feeding cycle 144 s, about 1.5% of the alumina is undissolved, the undissolved particle aggregates and forms sludge at the bottom of the cell. Only considering the alumina endothermic process, the electrolyte temperature in the feeding zone rapidly declines within the first 14 s, then, the temperature quickly is recovered and oscillated after 60 s.
Key words: aggregation; alumina dissolution; heat transfer; mass transfer; particle size distribution; numerical simulation
Foundation item: Project(2010AA065201) supported by the National High Research Development Program of China
Received date: 2016-05-03; Accepted date: 2017-02-21
Corresponding author: LI Mao; Tel: +86-13055169363; E-mail: limao89@163.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2010AA065201)
收稿日期:2016-05-03;修订日期:2017-02-21
通信作者:李 茂,副教授,博士:电话:13055169363;E-mail: limao89@163.com