文章编号:1004-0609(2011)10-2616-15
高强高韧铝锌镁钪合金板材制备及其组织性能演变
尹志民1,邓 英1,赵 凯1,段佳琦1,唐 蓓1,何振波1, 2,彭勇宜1,姜 锋1,潘清林1
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 东北轻合金有限责任公司,哈尔滨 150060)
摘 要:采用力学性能测试和电子显微分析技术研究了不同加工处理条件下Al-5.4Zn-2.0-Mg-0.25Cu-0.1Sc-0.1Zr合金的显微组织及性能演变。结果表明:在半连续激冷铸造条件下,铸锭存在晶界偏析,形成了富Zn、Mg的非平衡相和富Fe、Si、Mn的杂质相;经470 ℃、12 h均匀化处理后,富Zn、Mg的非平衡相溶入基体,仅剩下少量富Fe、Si、Mn的杂质相;与此同时,铸锭合金固溶体分解析出纳米级的Al3(Sc, Zr)相,470 ℃、12 h是研究合金合适的铸锭均匀化制度;铸锭热变形过程中,随试验温度升高合金强度逐渐降低,伸长率则先增加而后降低,350~400 ℃的温度范围内合金具有较稳定的热变形抗力和塑性,是合宜的热变形温度范围;合金冷轧板材经 470 ℃、1 h固溶处理后,热变形过程中形成的大量非平衡相溶入基体形成过饱和固溶体,时效过程中脱溶顺序为αsss(α过饱和固溶体)?GP区?η′相?η相。合金板材最佳固溶-时效工艺为(470 ℃, 1 h)固溶+(120 ℃, 24 h)时效,在此条件下,试验合金的抗拉强度、屈服强度和伸长率分别可达533 MPa、494 MPa和15%。试验合金的高强度主要来源于η′相析出强化、添加微量Sc和Zr引起的亚晶强化和亚结构强化以及Al3(Sc, Zr)相的弥散强化。
关键词:Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金;板材;铸锭均匀化;热塑性;固溶-时效;组织;力学性能;演变
中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
Preparation of Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy plate and
its microstructure-properties evolution
YIN Zhi-min1, DENG Ying1, ZHAO Kai1, DUAN Jia-qi1, TANG Bei1, HE Zhen-bo1, 2,
PENG Yong-yi1, JIANG Feng1, PAN Qing-lin1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Northeast Light Alloy Co., Ltd., Harbin 150060, China)
Abstract: The evolution of microstructure and properties of Al-5.4Zn-2.0Mg-0.25Cu-0.1Sc-0.1Zr under different processing and heat treatment conditions was studied using mechanical properties measurement and electron microscopy. The results show that, under semi-continuous casting conditions, at grain boundaries there is some segregation which is bearing Zn, Mg non-equilibrium phases and indissoluble impurity phases containing Fe, Si and Mn elements. After the homogenization at 470 ℃ for 12 h the non-equilibrium phases dissolve into matrix completely and only small amounts of indissoluble phases still exist. At the same time, the solid solution matrix precipitates nano-scaled Al3(Sc, Zr) dispersoid particles. The proper homogenization treatment processing of the ingot is at 470 ℃ for 12 h. During the hot deformation of ingot, with the increase of deformation temperatures, the strength decreases, the elongation increases firstly and then decreases. Between 350 ℃ and 400 ℃ the alloy is of a more stable deformation characteristics and this is the suitable deformation temperature range for this alloy. After solutioning at 470 ℃ for 1 h lots of non-equilibrium phases formed during hot rolling dissolve into the matrix. The precipitation sequence of the alloy during aging is described as follows: supersaturated solid solution (α)→GP zones→metastable η′ phase→η phase. The suitable solution-aging treatment processing of the studied alloy is solution-treated at 470 ℃ for 1 h, followed by water quenching and then aged at 120 ℃ for 24 h. Under this condition, the ultimate tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of the studied alloy plate could reach 533 MPa, 494 MPa and 15%, respectively. The strengthening mechanism of the studied alloy is precipitation strengthening of fine η′ phase, subgrain strengthening and dispersion strengthening caused by Al3(Sc, Zr) dispersoid particles.
Key words: Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy; plate; ingot homogenization; thermal plasticity; solution-aging; microstructure; mechanical properties; evolution
Al-Zn-Mg合金具有强度高、塑性好、可焊性好和耐腐蚀性能优良等特点,被广泛用于要求轻质高强的焊接结构件,是航天航空、交通运输工具中重要的轻质结构材料[1-3]。然而,航天航空技术的发展对材料的要求越来越高,需要强度更高及焊接性能优良的铝合金材料。大量研究表明[4-11],在铝合金中复合添加微量Sc、Zr可达到这个目的。YIN等[4]对比研究了复合添加0.35(Sc+Zr)对Al-Zn-Mg合金组织性能的影响,指出添加Sc、Zr后的合金时效后抗拉强度和屈服强度分别提高了93 MPa和104 MPa,其强度的增加主要源自于Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子引起的细晶强化、亚结构强化和沉淀强化;聂波等[9]通过Sc、Zr微合金化研制了中强耐蚀可焊铝镁钪合金板材,其拉伸性能σb≥415 MPa、σ0.2≥302 MPa、δ5≥15%,剥落腐蚀性能达到P级,焊接接头强度系数不小于0.85;DEV等[10]研究指出,在中强Al-Zn-Mg合金焊接料中添加0.65% Sc(质量分数),可显著细化焊接接头凝固组织,从而提高焊接接头强度,降低凝固开裂倾向;OCENASEK和SLAMOVA等[11]研究表明,传统AA5754铝合金的完全再结晶温度为360 ℃,在此合金中复合添加0.25% Sc(质量分数)和0.08% Zr(质量分数)后直到600 ℃时才观察到部分再结晶。俄罗斯全俄轻合金研究院与全俄复合材料研究院合作,在中强可焊Al-Zn-Mg合金基础上,复合添加微量Sc和Zr,开发了牌号为01970、01975和01981的铝锌镁钪合金[5],其中,01975是低Sc含量的合金。这种合金具有较高的强度、较优的耐腐蚀性能、较低的各向异性,成本也较低,是新一代航天轻质高强结构材料。然而,国内外文献对这种低Sc含量的铝锌镁钪合金的研究还鲜见报道。因此,尽快研制出性能指标达到国内航天用户要求的这种合金具有重要意义,本文作者研究了铝锌镁钪合金板材制备过程中铸锭均匀化处理、铸锭均匀化后的热变形以及板材固溶时效处理工艺的优化,在此基础上还研究了合金制备过程中的显微组织结构演变,旨在为这种新型高强高韧铝锌镁钪合金的研究与开发提供理论和实验指导。
1 实验
1.1 材料制备
试验合金名义成分为Al-5.4Zn-2.0Mg-0.25Cu- 0.1Sc-0.1Zr (质量分数,%)。板材制备工艺为半连续铸造成锭?铸锭均匀化处理?铸锭热轧?冷轧成薄板?固溶?时效。
1.2 实验方法
铸锭均匀化处理温度上限通过铸锭DSC结果选定,DSC实验在NETZSCH STA 449C差热分析仪上进行,加热速度为10 ℃/min。均匀化处理样品从铸锭上用线切割截取,尺寸为25 mm×25 mm×6 mm,均匀化处理温度为200、250、300、350、400、450和470 ℃,保温时间为1~24 h。均匀化处理在盐浴中进行,盐浴控温精度为±1 ℃。为了保持均匀化处理状态的组织和性能,均匀化处理后水冷。在D60K数字金属电导率测量仪上进行电导率测试;为了进一步评估均匀化处理对合金性能的影响,铸锭均匀化处理后热轧,然后在室温下对热轧板材进行拉伸性能测试和 比较。
铸锭经过最佳均匀化处理后进行加工热塑性研究,高温瞬时拉伸试验样品尺寸见图1。
高温瞬时试验温度为100、200、300、375、400、425、450和500 ℃,拉伸速度为2 mm/min,每个温度点高温力学性能数值取3个样品的平均值,试验按照GB/T 4338—1995(合金高温拉伸试验方法)的有关规定进行,通过高温性能选定铸锭最佳变形温度范围。高温瞬时拉伸试验在RWS50电子蠕变松弛试验机上进行,为了观察高温瞬时拉伸断口形貌,高温试验后将断口立即置于无水酒精中以避免断口氧化,然后在Quanta MK2-200环境扫描电镜下进行断口分析。
铸锭经过最佳均匀化处理后,在最佳变形温度范围进行热轧,热轧变形程度为90%,热轧后板材厚度为7 mm, 热轧板材经过5道次轧成2 mm的薄板。薄板固溶处理温度为450、460、470、480及490 ℃,固溶时间为0.5~1.5 h,固溶处理也在盐浴炉中进行,固溶处理后水淬,淬火转移时间不长于2 s。时效处理温度为100、110、120及130 ℃,时效时间为10 min~36 h。时效处理在鼓风干燥箱中进行,时效后样品空冷后进行性能测试。最终力学性能、电导率和硬度值均取同一状态下3个样品的算术平均值,误差棒误差采用样本总体的标准偏差。室温拉伸试样按照GB 6397—86(金属拉伸试验试样)的规定加工成标准矩形试样,拉伸试验在CSS-44100电子万能材料实验机上进行,拉伸速度为2 mm/min。
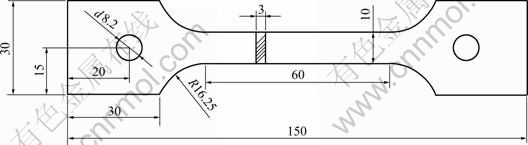
图1 高温瞬时拉伸试样尺寸
Fig.1 Specification of tensile sample at elevated temperatures (Unit: mm)
为了检测不同固溶处理条件下平衡相的溶解程度,在Quanta MK22200 环境扫描电镜下采用背散射扫描电子成像技术对残留相进行观察。薄膜样品经机械预减薄后再双喷电解减薄,电解液为硝酸与甲醇的混合液(体积比为1:3),电解减薄温度低于-20 ℃。透射电子显微组织观察在TECNAI G220 电镜上进 行,高分辨在JEM-3010电镜上完成, 加速电压均为200 kV。
2 实验结果
2.1 均匀化处理对铸态合金组织和性能的影响
2.1.1 铸态合金的显微组织和铸锭加热过烧温度的 测定
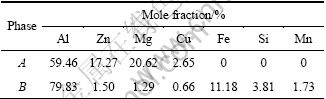
铸态合金扫描电子显微组织如图2所示。由图2可知,铸态合金晶粒尺寸约为50 μm,晶界有明显的偏析,能谱分析结果见表1。其中,白色网络状相A为富Zn、Mg的非平衡相,灰色相B为含Fe、Si、Mn杂质相。可见,为了使合金成分均匀,铸态合金需进行均匀化处理。
试验合金铸锭的DSC结果如图3所示。结果表明,在477.7 ℃可观察到一明显的吸热峰,说明合金铸锭中存在对应于475 ℃开始熔化的非平衡相,该温度应为铸锭的常规过烧温度,因此,均匀化处理的最高温度不能超过470 ℃。

图2 铸态合金的SEM像
Fig.2 SEM images of as-cast alloy: (a) Low magnification; (b) High magnification
表1 图2(b)中第二相化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of the secondary phases shown in Fig.2(b)
2.1.2 均匀化处理对铸态合金硬度与电导率的影响
在不同均匀化处理条件下,Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr合金的布氏硬度和相对电导率的变化如图4所示。
图4(a)和(b)中时间为0时的点分别表示未经均匀化处理的铸态合金的硬度和电导率。结果表明:当均匀化温度低于300 ℃时,合金硬度低于铸态合金硬度,且均匀化温度越低,硬度越低;当均匀化温度达到 350 ℃以上时,合金硬度高于铸态合金硬度,且随均匀化温度的升高,合金硬度先升后降,400 ℃均匀化时合金硬度最高。电导率的变化规律则不同,均匀化处理态合金的电导率均高于铸态合金的,且随均匀化温度的升高,合金电导率单调下降。结果还表明,均匀化时间达到12 h后,延长均匀化时间对电导率和硬度影响不大。

图3 铸态合金DSC曲线
Fig.3 DSC curve of as-cast alloy

图4 均匀化处理对铸态合金硬度与相对电导率的影响
Fig.4 Effect of homogenization treatment on hardness and relative conductivity of cast alloy: (a) HB; (b) Conductivity
2.1.3 均匀化处理对铸态合金显微组织的影响
铸态合金经不同均匀化处理后的扫描电子金相组织及其能谱如图5所示。
合金经470 ℃、12 h均匀化处理后的透射电子显微组织见图6。
对比图2(a)和图5(a)可知,铸态合金经350 ℃、12 h均匀化处理后,大量非平衡相从基体中析出;经 450 ℃、12 h均匀化处理后,大部分平衡相又溶解到基体中;经470 ℃、12 h均匀化处理后,非平衡相基本上溶解到基体中,但是仍然残存少量富Fe、Si、Mn杂质相;合金经470 ℃、24 h均匀化处理后,难溶杂质相并没有减少的迹象。由图6可知,铸态合金经 470 ℃、12 h均匀化后,除晶界和晶内非平衡相全部回溶入铝基体外,晶内还析出了大量蹄印状Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子。
2.1.4 均匀化处理对热轧板材拉伸力学性能的影响
合金铸锭经不同均匀化处理后热轧成板材,板材拉伸力学性能如图7所示。
由图7可以看出,随着均匀化温度的升高,热轧板强度略有升高而后又稍有下降,其中,经450 ℃、12 h均匀化处理热轧板的强度较高;伸长率则单调上升,其中,经470 ℃、12 h均匀化处理热轧板的伸长率最高。综合强度和伸长率结果可见,470 ℃、12 h是合金较合适的铸锭均匀化工艺。
2.2 均匀化处理后铸锭的热塑性
2.2.1 高温瞬时拉伸力学性能
经470 ℃、12 h均匀化处理后铸锭在不同试验温度下的高温拉伸力学性能如图8所示。结果表明,随试验温度升高,强度单调下降,伸长率先升后降,350~400 ℃范围内,强度和塑性随试验温度的变化比较缓慢,即在该温度范围内,合金具有较稳定的热变形抗力和塑性。
2.2.2 瞬时拉伸后试样的断口形貌
不同试验温度下瞬时拉伸后合金的断口特征如图9所示。可以看出,在不同试验温度下,合金的断口特征明显不同。较低温度下,断口主要呈现穿晶断裂特征,升高温度,断口逐渐呈现沿晶断口特征(见图9(d)),表明高温下晶界发生了弱化。综合不同试验温度下的高温拉伸力学性能和断口特征可知,400 ℃左右为该合金适宜的变形温度。

图5 均匀化处理对铸态合金微观组织的影响
Fig.5 Effect of homogenization treatment on microstructure of as-cast alloy: (a) 350 ℃, 12 h; (b) 450 ℃, 12 h; (c) 470 ℃, 12 h; (d) 470 ℃, 24 h; (e) Magnified image of figure (c); (f) EDS result of point A in (e)
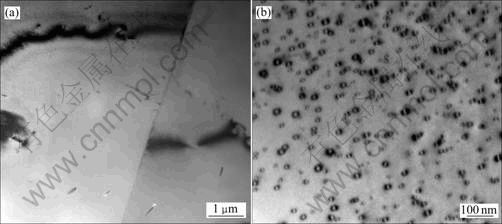
图6 合金经470 ℃、12 h均匀化处理后的TEM像
Fig.6 TEM images of cast alloy homogenized at 470 ℃ for 12 h: (a) Non-equilibrium phases dissolved into Al matrix; (b) Al3(Sc, Zr) particles within grain
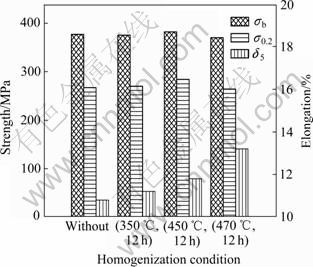
图7 均匀化处理对热轧板拉伸力学性能的影响
Fig.7 Effect of homogenization treatment on mechanical properties of hot rolling plates

图8 均匀化处理后的铸锭在不同试验温度下的高温瞬时拉伸性能
Fig.8 High temperature instantaneous tensile properties of as-homogenized ingot at different test temperatures
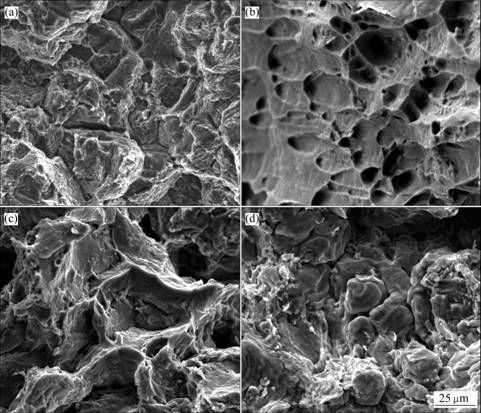
图9 不同试验温度下瞬时拉伸后试样的断口形貌
Fig.9 Fractographs of as-homogenized ingot after instantaneous tensile test at different test temperatures: (a) 28 ℃; (b) 300 ℃; (c) 400 ℃; (d) 500 ℃
2.2.3 瞬时拉伸后试样的透射电子显微分析
不同试验温度下瞬时拉伸后试样的透射电子显微分析如图10所示。
图10结果表明,常温下变形组织主要为位错亚结构,由于位错应变场的干扰,原来与基体共格的Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子的蹄印状特征消失,粒子变为球形(见图10(b));在300 ℃和400 ℃试验温度下,位错亚结构仍然存在;在500 ℃试验温度下,晶界附近可以见到明显的强滑移线(如图10(e)中箭头所指),显示出高温下晶界滑动的特征,由于变形只集中在晶界附近,导致晶界弱化,表现出如图9(d)所示的沿晶断口特征。与此同时,晶内大部分位错亚结构消失,位错应变场也随之消失,显示出与基体共格的Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子的蹄印状特征(见图10(f))。
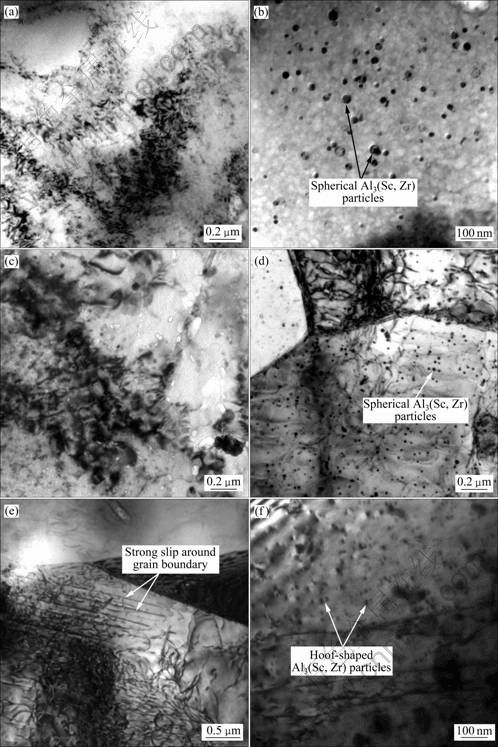
图10 不同试验温度下瞬时拉伸后试样的TEM像
Fig.10 TEM images of instantaneous tensile sample at different test temperatures: (a), (b) 25 ℃; (c) 300 ℃; (d) 400 ℃; (e), (f) 500 ℃
2.3 固溶-时效处理对合金板材组织与性能的影响
2.3.1 对板材拉伸性能的影响
不同固溶处理后经120 ℃、24 h时效处理的板材拉伸力学性能如图11所示。图11(a)结果表明,随固溶温度的升高,合金板材强度和伸长率先升后降,经470 ℃固溶后时效板材的综合性能最佳,抗拉强度、屈服强度和伸长率分别为533 MPa、494 MPa和15%。由图11(b)可知,随固溶时间的延长,合金抗拉强度和伸长率先升后降,屈服强度先降后升,综合比较,合金板材最佳固溶处理工艺为470 ℃、1 h。

图11 固溶处理对板材拉伸性能的影响
Fig.11 Effect of solution treatment processing on tensile properties of as-aged alloy: (a) Effect of solution temperatures; (b) Effect of solution time
经470 ℃、1 h固溶处理后,合金板材在不同时效温度下时效24 h后的力学性能如图12(a)所示。结果表明,随时效温度的升高,合金强度先升后降,伸长率则先降而后略有上升,当时效温度为120 ℃时,合金的综合力学性能较优。在120 ℃时效条件下,合金板材硬度、电导率及拉伸性能随时效时间的变化如图12(b)和(c)所示。可以看出,时效初期合金的硬度、电导率及强度急剧上升,而伸长率急剧下降;时效12 h后,合金的硬度和强度缓慢上升,伸长率缓慢下降,时效24 h后硬度及强度达到峰值,继续时效合金硬度及强度随之下降,合金电导率则单调上升。可以看出,合金板材较合适的时效时间为24 h。
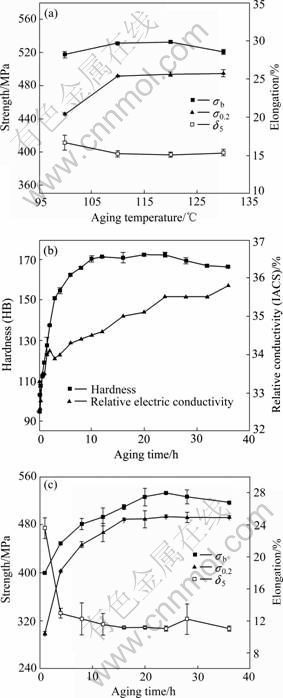
图12 时效处理对板材性能的影响
Fig.12 Effect of aging processing parameters on properties of test alloy plate: (a) Effect of aging temperatures on tensile properties; (b) Effect of aging time on hardness (HB) and relative electric conductivity; (c) Effect of aging time on tensile properties
2.3.2 对冷轧板材组织影响
冷轧板材经470 ℃、1 h固溶前、后的SEM像如图13所示。由图13(a)可知,冷轧板材中存在两种类型的物相,能谱分析表明(表3),一种是富Zn和Mg的铝化物,另外一种是沿轧向排列的富Fe和Si的杂质相。经470 ℃、1 h固溶后,非平衡富Zn和Mg的铝化物相已经溶入基体,只剩下少量难溶的Fe和Si杂质相。

图13 冷轧板材经470 ℃、1 h固溶前后的SEM像
Fig.13 SEM images of cold-rolled alloy plate before(a) and after(b) solution treated at 470 ℃ for 1 h
表3 图13中第二相化学成分
Table 3 Chemical compositions of the secondary phases shown in Fig.13

固溶态合金板材的TEM像如图14所示。由图14(a)可知,经470 ℃、1 h固溶后,合金为未再结晶的纤维状组织,纤维状晶粒由亚晶组成(箭头所示)。经放大观察可以看出(见图14(b)),亚晶内及亚晶界存在大量细小弥散的纳米级Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子。固溶态合金沿铝基体的[011]入射方向的选区电子衍射花样(SAED)如图14(c)所示。通过标定并根据参考文献[12-14]可知,铝基体中超点阵斑点来自L12结构Al3(Sc, Zr),其斑点出现在1/2(200)和1/2(220)的位置。
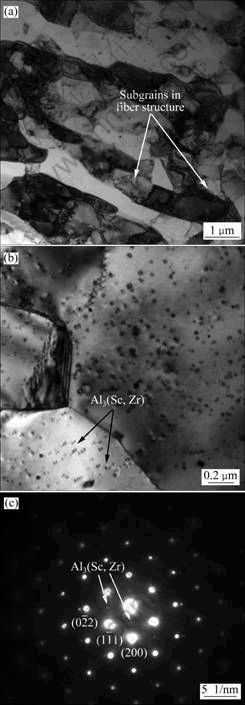
图14 470 ℃/1 h固溶态合金板材的TEM像
Fig.14 TEM images of alloy plate solution treated at 470 ℃ for 1 h: (a) Fiber structure with subgrains; (b) Al3(Sc, Zr) within grains; (c) SAED, B=[011]
经470 ℃、1 h固溶后,再进行120 ℃时效,合金板材的TEM像图15所示。由图15(a)和(b)可以看出,经120 ℃、1 h时效,晶内有细小的弥散质点析出,经高分辨分析可知,这种弥散质点为GP区;随时效时间的延长,GP区逐渐转变为短棒状析出相,晶界上可观察到断续分布的平衡相(见图15(c));在120 ℃、24 h峰值时效条件下,合金晶粒组织仍为纤维状亚晶组织(如图15(d)箭头所示),晶内弥散分布着大量纳米级短棒状析出相,选区电子衍射花样表明,除在1/2(220)位置上观察到较强的Al3(Sc, Zr)斑点外,在1/3(220)和2/3(220)位置上可观察到微弱的衍射斑点,根据参考文献[15-20]可知,这种析出相为η′相(见图15(d)~(g))。

图15 经(470 ℃, 1 h)固溶+120 ℃时效后合金板材的TEM像
Fig.15 TEM images of alloy plate treated by 470 ℃ for 1 h solution and 120 ℃ aging: (a) 120 ℃, 1 h; (b) 120 ℃, 1 h, HREM, B=[110]; (c) 120 ℃, 12 h; (d)-(f) 120 ℃, 24 h; (g) SAED, 120 ℃, 24 h, B=
3 分析与讨论
3.1 均匀化处理过程中铸锭组织性能演变
在半连续激冷铸造条件下,铝合金熔体冷却速度快,凝固过程为非平衡结晶过程,铸锭外部相当于熔体淬火,基体近似为饱和固溶体[21-23];但是由于铸锭尺寸较大,铸锭中心温度较高,冷却速度较慢,凝固过程中,熔体中先结晶出来的高熔点化合物以及低熔点共晶化合物被推移到最后凝固的晶界区域,由此形成富Zn、Mg的低熔点非平衡相和富Fe、Si、Mn的难溶杂质相;在铸锭均匀化过程中, 铸锭组织会发生如下3个方面的变化:1) 晶界区域富Zn、Mg的低熔点非平衡相会逐步溶入基体中;2) 过饱和固溶体会 分解析出非平衡相,由于析出温度高,析出相粗大;3)从过饱和固溶体中分解析出纳米级的二次Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子。另一方面,随均匀化温度的升高,过饱和固溶体先分解析出的粗大非平衡相又重新溶入基体中, 基体的固溶度出现先降后升的现象,固溶强化效果也先弱后强(析出相过于粗大没有析出强化作用),因此,铸态合金硬度先降而后升(见图4(a))。另一方面,基体固溶度的先降后升导致溶质原子对电子散射几率先降后升,这就使得铸态合金电导率呈现先升后降的现象(见图4(b))。在470 ℃、12 h条件下均匀化处理后,非平衡相已基本回溶完全,只剩下少量的Fe、Si、Mn难溶杂质相。
随均匀化温度的升高,铸锭中非平衡相逐渐溶解,固溶体溶质浓度逐渐增加,固溶强化效果逐渐增强,因此,均匀化温度越高,热轧后板材强度越高,当均匀化温度继续升高时,合金晶粒粗化,热轧板材强度降低。此外,均匀化温度的升高致使合金内成分均匀及铸造过程形成的内应力消除,从而使热轧板材伸长率单调上升,经470 ℃、12 h均匀化处理后热轧板材的伸长率达到最大值(见图7)。
文献和作者先前的研究指出[24-26],含过渡族元素Sc、Zr的铝合金均匀化处理的目的如下:1) 消除组织与成分的不均匀性;2) 消除非平衡凝固过程中产生的残余应力;3) 从过饱和固溶体中分解析出纳米级的二次Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子。本研究的实验结果再次说明了这一点。综上所述,470 ℃、12 h均匀化处理已达到均匀化目的,是合适的铸锭均匀化制度。
3.2 铸锭热变形过程中的组织性能演变
铸锭热轧工艺研究最重要的是铸锭加热温度的确定,过高的加热温度可能引起热脆、过烧或导致热轧粘辊,热轧塑性下降。温度过低,变形抗力增大,还可能引起不均匀变形,铸锭开裂,热轧过程难以进行。通常热轧温度是根据已有相图、塑性图、变形抗力图和第二类结晶图来确定的。对于新型合金的热加工特性,可以通过高温瞬时拉伸试验(或热模拟试验)和生产现场验证试验来确定。MENG等[27]及HUANG等[28]指出,铝合金热变形过程中的流变应力与变形体内的位错组态密切相关。在较低温度下变形,需要较高的能量来启动位错,随着变形程度的加大,易于形成位错缠结,而这种位错缠结有效阻碍金属变形,因此,合金变形抗力较大。升高变形温度,位错由于热激活程度的不同而发生动态回复或再结晶,合金变形抗力减小。变形温度越高,变形抗力越小。在350~400 ℃试验温度范围内,强度随温度升高而降低的趋势趋缓,合金的塑性随试验温度的变化也相对缓慢,在此温度范围内,合金具有较稳定的热变形抗力和塑性。试验温度进一步增加,晶界弱化,变形只集中在晶界附近,试样由穿晶断裂转变为沿晶断裂。生产现场试验也表明,铸锭在380~400 ℃热轧,热轧效果较好。继续升高热加工温度,热轧板坯就会出现边裂。因此,350~400 ℃是试验合金锭坯合宜的热加工温度范围。
3.3 固溶-时效过程中板材组织性能演变
合金热轧后经过冷轧成薄板,冷轧态合金中晶内有密度很高的位错缠结,还有粗大的平衡相(见图13)和球形Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子。高密度位错是冷轧变形的结果,平衡相是热轧后冷却过程中形成的,Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子则是铸锭均匀化过程中析出的。冷轧板材固溶处理的主要目的是使冷轧板材中粗大的第二相尽可能地溶入基体,提高溶质原子在基体中的固溶度,进而增加时效过程中的相变驱动力,以便时效过程中析出尽可能多的第二相[29-30]。与此同时,还必须控制固溶过程中的晶粒长大。固溶处理过程中,位错受热激活发生滑移和攀移,形成了沿轧制方向排列的竹节状亚晶结构(见图14(a)),由于位错应力场的消失,球形Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子的蹄印状共格特性又显示出来(见图14(b)),同时,粗大的平衡相η(MgZn2)溶入基体。实验结果表明,当合金的固溶温度较低(450 ℃、1 h)或固溶时间过短(470 ℃、20 min)时,合金中残留的第二相较多,说明固溶不彻底,固溶强化效果没有充分发挥,故合金的强度较低。提高固溶温度,残留的第二相减少,固溶后基体的过饱和度增大,时效后第二相析出增多,合金的强度提高。继续升高固溶温度,合金体内的变形组织消失、晶粒粗化,合金强度随之下降(见图11)。大量研究表明[32-34],时效过程中Al-Zn-Mg合金过饱和固溶体脱溶顺序为:αsss(α过饱和固溶体)?GP区? η′相?η相。对于本研究合金,是在Al-Zn-Mg合金基础上添加少量Cu和微量Sc和Zr的合金。少量Cu主要固溶在基体中,微量Sc和Zr与Al主要形成Al3(Sc, Zr)化合物,时效过程中的析出结果表明(见图15),微量Sc和Zr的存在并未明显改变Al-Zn-Mg合金的时效析出特征。
3.4 时效态试验合金的强化机制
以上显微组织结构观察和分析表明,时效态试验合金的晶粒组织为未再结晶的纤维状组织,纤维状晶粒由位错亚结构和细小的亚晶组成,相组织结构为铝基固溶体、η′相、η相和Al3(Sc, Zr)化合物粒子。因此,时效态试验合金的强化机制应包括固溶强化、亚结构和亚晶强化、主要析出相η′的强化和Al3(Sc, Zr)化合物粒子的弥散强化。
3.4.1 固溶强化
由Al-Zn-Mg三元相图富铝角[35]可以看出,在Al-5.4Zn-2.0Mg成分范围内,合金处在α(Al)+ η(MgZn2)相区内,说明Zn和Mg大部分形成了η(MgZn2)化合物,但是仍有小部分固溶在铝基体中。图15的物相和结构分析表明,时效态Al-5.4Zn-2.0Mg- 0.25Cu-0.1Sc-0.1Zr试验合金只有铝基固溶体α(Al)、η′相、η相和Al3(Sc, Zr)化合物粒子,没有观察到含Cu相的存在,说明微量 Sc和Zr主要以Al3(Sc, Zr)化合物粒子的形式存在,而Cu主要固溶在铝基体中,起固溶强化作用并能改善合金的耐蚀性[5]。
3.4.2 微量 Sc和Zr引起的亚结构强化、亚晶强化和弥散强化
文献[2, 4, 6 ]的结果表明:当0.25Sc和0.12Zr(质量分数,%)添加到Al-Mg合金和Al-Zn-Mg合金中,微量 Sc和Zr与Al会形成两种不同性质的Al3(Sc, Zr)化合物,一种是合金凝固过程中析出的初生Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子,这种粒子为面心立方结构,与基体α(Al)相同,点阵常数与基体也极为相近,这种粒子在合金凝固时优先析出,是理想的非均质晶核,能显著细化合金的铸态晶粒组织,造成细晶强化。另一种为合金均匀化处理过程中大量析出的次生Al3(Sc,Zr)粒子,细小弥散、呈蹄印状且与基体共格。这种粒子强烈钉扎位错和亚晶界,阻碍位错的运动和晶界迁移,有弥散强化和抑制合金变形后再结晶的作用。在本实验条件下,添加的Sc和Zr含量(质量分数,%)分别均仅为0.1,远低于Al-Sc-Zr三元相图出现初生Al3(Sc, Zr)相的临界成分0.25和0.12,因此,铸态合金没有晶粒细化的效果,但是,次生的弥散细小Al3(Sc, Zr)粒子仍然存在,这种粒子强烈钉扎位错和亚晶界,阻碍位错的运动和晶界迁移,减缓回复和再结晶过程,合金固溶后仍保持小角度亚晶组织(见图14(a)),使合金产生显著的亚结构强化和亚晶强化。此外,大量细小弥散与基体共格的Al3(Sc, Zr)化合物粒子在铝基体中的存在,也会产生显著的共格强化和弥散强化。
3.4.3 主要析出相η′的强化
有关Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金的强化机制至今还没有统一的结论,一些学者认为[36],Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金主要的强化相是GP区,即基体组织中刚刚出现η′相时合金的强度最高;有一些学者认为[37],主要强化相是η′相,而不是GP区;还有一些学者认为[38],η′和η相的沉淀析出使硬度达到峰值。本实验条件下,经120 ℃、1 h时效处理后合金基体内观察到GP区的析出(见图15(b))、120 ℃时效12 h合金中就可以观察到粒状的η′相,而120 ℃时效24 h后合金强度达到峰值,所以,时效态试验合金主要析出相的强化机制应当以η′相强化为主。η′相为六方结构,与基体保持半共格,变形过程中,位错与粒子的交互作用以切割为主,其强化效应随质点体积分数和尺寸的增大而增大;随时效时间的延长,晶内析出相η′逐渐粗化,η′相与基体的半共格关系逐渐丧失,位错与粒子的交互作用转变为绕过机制,对位错运动的阻碍作用逐渐降低。与此同时,晶界一部分η′相转化为较为粗大的η相,晶界出现无沉淀析出带并逐渐宽化,因此,合金强度下降出现过时效(见图12(c))。
综上所述,时效态Al-5.4Zn-2.0-Mg-0.25Cu-0.1Sc- 0.1Zr试验合金的高强度除小量固溶强化外,主要来源于η'相析出强化、添加微量Sc和Zr引起的亚晶强化和亚结构强化以及Al3(Sc, Zr)相的弥散相强化。
4 结论
1) 在半连续铸造条件下,熔体冷却速度较快,基体近似为过饱和固溶体,晶界处存在富Zn、Mg的低熔点非平衡相及富Fe、Si、Mn难溶杂质相,铸锭需要进行均匀化处理。
2) 在均匀化处理过程中,一方面晶界区域富Zn、Mg的低熔点非平衡相逐步溶入基体中,另一方面过饱和固溶体分解析出非平衡相,随均匀化温度升高,析出的非平衡相又会重新回溶入基体中,与此同时,固溶体分解析出弥散的纳米级Al3 (Sc, Zr)粒子,470 ℃、12 h是研究合金合适的铸锭均匀化制度。
3) 在铸锭热变形过程中,随试验温度的升高,合金强度单调下降,伸长率先升后降,350~400 ℃的范围内,合金具有较稳定的热变形抗力和塑性,是试验合金锭坯合宜的热加工温度范围。
4) 铝锌镁钪锆合金板材合适固溶时效处理为470 ℃、1 h固溶水淬,随后120 ℃、24 h时效,在此条件下,合金的抗拉强度、屈服强度和伸长率分别达到533 MPa、494 MPa和15%。
5) 铝锌镁钪锆合金的强化机制主要为η′相引起的析出强化、添加微量Sc和Zr引起的亚晶强化和亚结构强化以及Al3(Sc, Zr)相的弥散相强化。
REFERENCES
[1] WU L M, WANG W H, HSU Y F, TRONG S. Effects of homogenization treatment on recrystallization behavior and dispersoid distribution in an Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 456(1/2): 163-169.
[2] XIAO Jing, YIN Zhi-min, LEI Xue-feng, JIANG Feng, NIE Bo, HE Zhen-bo. Effects of minor Sc on microstructure and mechanical properties of A1-Zn-Mg-Zr alloy welded joint[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(1): 244-248.
[3] WU L M, SEYRING M, RETTENMAYR M, WANG W H. Characterization of precipitate evolution in an artificially aged Al-Zn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(1/2): 1068-1073.
[4] YIN Zhi-min, YANG Lei, PAN Qing-lin, JIANG Feng. Effects of minor Sc and Zr on microstructures and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg based alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2001, 11(6): 822-825.
[5] DAVYDOV V G, ELAGIN V I, ZAKHAROV V V, ROSTOVA T D. Alloying aluminum alloys with scandium and zirconium additives[J]. Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 1996, 38(7): 347-352.
[6] 尹志民, 潘清林, 姜 锋, 李广汉. 钪和含钪合金[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2007: 363-513.
YIN Zhi-min, PAN Qing-lin, JIANG Feng, LI Guang-han. Scandium and its alloys[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2007: 363-513.
[7] HE Yong-dong, ZHANG Xin-ming, YOU Jiang-hai. Effect of minor Sc and Zr on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16: 1228-1235.
[8] 郭加林, 尹志民, 王华, 何振波, 商宝川. 微量Sc和Zr对2524SZ合金薄板疲劳裂纹扩展特性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(5): 827-832.
GUO Jia-lin, YIN Zhi-min, WANG Hua, HE Zhen-bo, SHANG Bao-chuan. Effects of minor Sc and Zr on fatigue crack development characteristics of 2524SZ alloy sheet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(5): 827-832.
[9] 聂 波. 中强可焊铝镁钪合金制备及其相关基础研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2007: 46-97.
NIE Bo. Preparation and relative basic research on Al-Mg-Sc alloy with middle strength and weldability[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007: 46-97.
[10] DEV S, STUART A A, RAVI DEV KUMAAR R C, MURTY B S, RAO K P. Effect of scandium additions on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg alloy welds[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 467(1/2): 132-138.
[11] OCENASEK V, SLAMOVA M. Resistance to recrystallization due to Sc and Zr addition to Al-Mg alloys[J]. Materials Characterization, 2001, 47(1/2): 157-162
[12] KENDIG K L, MIRACLE D B. Strengthening mechanisms of an Al-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(1/2): 4165-4175.
[13] KNIPLING K E, KARNESKY R A, LEE C P, DUNAND D C, SEIDMAN D N. Precipitation evolution in Al-0.1Sc, Al-0.1Zr and Al-0.1Sc-0.1Zr (at.%) alloys during isochronal aging[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(1/2): 5184-5195
[14] KNIPLING K E, DUNAND D C, SEIDMAN D N. Precipitation evolution in Al-Zr and Al-Zr-Ti alloys during aging at 450-600 ℃[J]. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(1/2): 1182-1195.
[15] LI Zhi-hui, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHANG Yong-an, ZHU Bao-hong, WANG Feng, LIU Hong-wei. Investigation of microstructural evolution and mechanical properties during two-step ageing treatment at 115 ℃ and 160 ℃ in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy pre-stretched thick plate[J]. Materials Characterization, 2008, 59(1/2): 278-282.
[16] LI X Z, HANGSEN V, GJ?NNES J, WALLENBERG L R. Hrem study and structure modeling of the η' phase, the hardening precipitates in commercial Al-Zn-Mg alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(9): 2651-2659.
[17] DU Z W, SUN Z M, SHAO B L, ZHOU T T, CHEN C Q. Quantitative evaluation of precipitates in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy after isothermal aging[J]. Materials Characterization, 2006, 56(1/2): 121-128.
[18] WEI Fang, LI Jin-shan, HU Rui, KOU Hong-chao. Influence of 1.0 wt% Li on precipitates on Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2008, 21(1/2): 565-570.
[19] BAI P C, ZHOU T T, LIU P Y, ZHANG Y G, CHEN C Q. Effects of lithium addition on precipitation in Li-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58(1/2): 3084-3087.
[20] 樊喜刚, 蒋大鸣, 孟庆昌, 李念奎, 孙兆霞. 时效制度对7150 铝合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2006, 35(16): 22-25.
FAN Xi-gang, JIANG Da-ming, MENG Qing-chang, LI Nian-kui, SUN Zhao-xia. Effect of aging on microstructure and properties of 7150 aluminum alloy[J]. Material and Heat Treatment, 2006, 35(16): 22-25.
[21] WANG Guo-jun, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHANG Yong-an, LI Zhi-hui, LI Pei-yue. Microstructural characterization of as-cast and homogenized 2D70 aluminum alloy[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2009, 16(4): 427-431.
[22] 万 里, 邓运来, 张云崖, 张新明. Al-(7.8~9.0)Zn-1.6Mg- (1.0~2.2)Cu合金铸态及其均匀化组织[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(9): 1698-1704.
WAN Li, DENG Yun-1ai, ZHANG Yun-ya, ZHANG Yin-ming. Microstructures of as-cast and homogenized Al-(7.8-9.0)Zn- 1.6Mg-(1.0-2.2)Cu aluminum alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(9): 1698-1704.
[23] 高凤华, 田 妮, 孙兆霞, 赵 刚. Al-6.5Zn-2.4Mg-2.3Cu铝合金半连续铸锭的均匀化处理[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 29(8): 1118-1121.
GAO Feng-hua, TIAN Ni, SUN Zhao-xia, ZHAO Gang. Homogenization treatment of semi continuous casting ingot of Al-6.5Zn-2.4Mg-2.3Cu aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2008, 29(8): 1118-1121.
[24] 李松瑞, 周善初. 金属热处理[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2005: 9-22.
LI Song-rui, ZHOU Shan-chu. Metal heat treatment[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2005: 9-22.
[25] JIA Z H, HU G Q, FORBORS B, SOLBERG J K. Effect of homogenization and alloying elements on recrystallization resistance of Al-Zr-Mn alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 444(1/2): 284-290.
[26] TOTIK Y, SADELER R, KAYMAZ I, GAVGALI M. The effect of homogenisation treatment on cold deformations of AA 2014 and AA 6063 alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 147(1/2): 60-64.
[27] MENG G., LI B L, LI H M, HUANG H, NIE Z R. Hot deformation behavior of an Al-5.7wt.% Mg alloy with erbium[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 516(1/2): 131-137.
[28] HUANG X D, ZHANG H, HAN Y, WU W X, CHEN J H. Hot deformation behavior of 2026 aluminum alloy during compression at elevated temperature[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(1/2): 485-490.
[29] TODA H, NISHIMURA T, UESUGI K, SUZUKI Y, KOBAYASHI M. Influence of high-temperature solution treatments on mechanical properties of an Al-Si-Cu aluminum alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(1/2): 2014-2025.
[30] HAN N M, ZHANG X M, Liu S D, HE D G, ZHANG R. Effect of solution treatment on the strength and fracture toughness of aluminum alloy 7050[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(1/2): 4138-4145.
[31] 张新明, 黄振宝, 刘胜胆, 刘文辉, 张 翀, 杜 予. 双级固溶处理对7A55铝合金组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(9): 1527-1533.
ZHANG Xin-ming, HUANG Zhen-bao, LIU Sheng-dan, LIU Wen-hui, ZHANG Chong, DU Yu. Effects of two-stage solution on microstructures and mechanical properties of 7A55 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(9): 1527-1533.
[32] STILLER K, WARREN P J, HANSEN V, ANGENETE J, GJ?NNES J. Investigation of precipitation in an Al-Zn-Mg alloy after two-step ageing treatment at 100 °C and 150 °C[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 270(1/2): 55-63.
[33] 韩小磊, 熊柏青, 张永安, 李志辉, 朱宝宏, 王 锋. 双级时效制度对7150铝合金微观组织和性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属, 2010, 34(2): 302-306
HAN Xiao-lei, XIONG Bai-qing, ZHANG Yon-gan, LI Zhi-hui, ZHU Bao-hong, WANG Feng. Effect of two-step aging on microstructure and properties of 7150 aluminum alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2010, 34(2): 302-306.
[34] BERG L K, GJ?NNES J, HANSEN V, LI X Z, KNUTSON-WEDEL M, WATERLOO G, SCHRYVERS D, WALLENBERG L R. GP-zones in Al-Zn-Mg alloys and their role in artificial aging[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(1/2): 3443-3451.
[35] 王祝堂, 田荣璋. 铝合金及其加工手册[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2005: 117.
WANG Zhu-tang, TIAN Rong-zhang. Aluminum and its processing manual[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2005: 117.
[36] WU Y L, FROESA F H, ALVAREZ A. Microstructure and properties of a new super-high-strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy C912[J]. Materials and Design, 1997, 18(4): 211-215.
[37] 华明建, 李春志, 王鸿渐. 微观组织对7075铝合金的屈服强度和抗应力腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 1988, 24(1): 41.
HUA Ming-jian, LI Chun-zhi, WANG Hong-jian. Effect of microstructures on the yield strength and scr of 7075 aluminum alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1988, 24(1): 41.
[38] 谷亦杰, 李永霞, 张永刚, 黄 正, 陈昌麒. 7050合金RRA沉淀析出的TEM研究[J]. 航空材料学报, 2000, 20(4): 1-7.
GU Yi-jie, LI Yong-xia, ZHANG Yong-gang, HUANG Zheng, CHEN Chang-qi. TEM observation of precipitates in a 7050 alloy after RRA treatment[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2000, 20(4): 1-7.
(编辑 陈卫萍)
基金项目:总装预研项目(51312010402);民口配套项目(JPPT-115-2-948)
收稿日期:2010-04-20;修订日期:2011-07-20
通信作者:尹志民,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830262;E-mail: zmyin@163.com
尹志民教授简介
尹志民,1946年1月出生,1987年Toronto大学留学回国人员,博士,博士生导师,中南大学“材料物理与化学”国家重点学科首席教授,享受政府特殊津贴。主要从事高性能铝合金和高强高导铜合金研制与开发。先后主持完成国家自然科学基金3项、国家“973”项目子课题2项、总装预研1项、国家“863”高技术1项、民口配套2项、科技部创新基金和国家重点新产品各1项、省部级科研项目6项。作为课题第二负责人配合产业单位承担“九五”和“十五”攻关项目各1项、民口配套材料研究项目9项。成功研制了2种用钪和锆微合金化的Al-Mg基和Al-Zn-Mg基合金,产品应用于航天部门;研制开发了用于高速、地铁和轻轨列车大功率调频调速异步牵引电动机的铜合金转子部件,产品被认定为国家重点新产品。获国家科技进步二等奖1项、中国有色金属工业科技进步一等奖1项、二等奖4项、湖南省科技进步二等奖3项,发明专利5项,发表论文236篇、专著2部,指导博士后5人,博士研究生20人,硕士研究生52人。