Pd掺杂SnO2纳米颗粒的合成、表征和气敏特性
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2011年第7期
论文作者:谭瑞琴 郭艳群 赵俊华 李月 徐铁峰 宋伟杰
文章页码:1568 - 1573
关键词:SnO2纳米颗粒;Pd掺杂;水热合成;气敏性能;X光电子能谱
Key words:SnO2 nano particles; Pd-doping; hydrothermal synthesis; gas sensing property; X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
摘 要:利用非模板水热法合成了Pd掺杂的SnO2纳米颗粒,并利用透射电镜(TEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)和X光电子能谱(XPS)表征了Pd掺杂对晶体结构、表面形貌、微观结构、热稳定性和表面化学状态的影响。研究发现:水热过程中Pd掺杂对形成的SnO2纳米颗粒大小几乎没有影响,在500 ℃以下的煅烧过程中,掺杂的Pd可以有效抑制颗粒的生长,但在700 ℃以上时颗粒生长迅速。XPS结果显示合成样品中Pd的化学状态有三种:Pd0、Pd2+和Pd4+,其中的主化学状态Pd4+有效促进了气敏性能的提高。为了同时提高气敏性能和热稳定性,Pd的最佳掺杂量为2.0%-2.5%(摩尔分数)。
Abstract:
SnO2 nano particles with various Pd-doping concentrations were prepared using a template-free hydrothermal method. The effects of Pd doping on the crystal structure, morphology, microstructure, thermal stability and surface chemistry of these nano particles were characterized by transmission electron microscope, X-ray diffractometer and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope respectively. It was observed that Pd-doping had little effect on the grain sizes of the obtained SnO2 nano particles during the hydrothermal route. During thermal annealing, Pd-doping could restrain the growth of grain sizes below 500 ℃ while the grain growth was promoted when the temperature increased to above 700 ℃. XPS results revealed that Pd existed in three chemical states in the as-synthesized sample as Pd0, Pd2+ and Pd4+, respectively. Pd4+ was the main state which was responsible for improving the gas-sensing property. The optimal Pd-doping concentration for better gas-sensing property and thermal stability was 2.0%-2.5% (mole fraction).

TAN Rui-qin1, GUO Yan-qun2, ZHAO Jun-hua2, LI Yue2, XU Tie-feng1, SONG Wei-jie2
1. Faculty of Information Science and Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China;
2. Ningbo Institute of Material Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo 315201, China
Received 18 October 2010; accepted 23 December 2010
Abstract: SnO2 nano particles with various Pd-doping concentrations were prepared using a template-free hydrothermal method. The effects of Pd doping on the crystal structure, morphology, microstructure, thermal stability and surface chemistry of these nano particles were characterized by transmission electron microscope, X-ray diffractometer and X-ray photoelectron spectroscope respectively. It was observed that Pd-doping had little effect on the grain sizes of the obtained SnO2 nano particles during the hydrothermal route. During thermal annealing, Pd-doping could restrain the growth of grain sizes below 500 °C while the grain growth was promoted when the temperature increased to above 700 °C. XPS results revealed that Pd existed in three chemical states in the as-synthesized sample as Pd0, Pd2+ and Pd4+, respectively. Pd4+ was the main state which was responsible for improving the gas-sensing property. The optimal Pd-doping concentration for better gas-sensing property and thermal stability was 2.0%-2.5% (mole fraction).
Key words: SnO2 nano particles; Pd-doping; hydrothermal synthesis; gas sensing property; X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
1 Introduction
As an n-type wide-gap semiconductor, tin oxide (SnO2) is regarded as an important functional material and is extensively applied in optoelectronic devices and gas sensors for a detection of various toxic or explosive gases in air [1-2]. Studies on novel preparation methods for SnO2 nanostructures and the doping effects on surface properties as well as sensing properties are key steps to obtain gas sensing materials with high performance [3-5]. Now much attention has been focused on the relationship between the nanostructures and the activity [6-7]. It is well known that the availability of oxide and hydroxyl species on the surface is of great importance in gas sensing so-called surface phenomenon. Sensing properties as sensitivity, selectivity, working temperature and thermal stability can be greatly improved by controllable preparation with a small amount doping of transition metals such as Pt, Pd [8-10], Au [11], Ag [12], Ru [13] and Rh [14] by surface modification and systematic coverage. The optimization of morphology, the decrease of grain size and the concentration of free charge carriers promote a remarkable increase of sensor performance. Pd-doping is always considered an effective method to improve the sensitivity and decrease the working temperature. The spill-over mechanism of oxygen atoms or reducing gases from their surface and the direct electron exchange between substrate and additive particle were proposed [15-16]. The surface chemical state analysis has been applied in the reported studies for Pd-doping systems [17-19]. However, the detailed mechanism of additives in semiconductor oxides is still not well understood.
In our previous studies, we reported a mild template-free hydrothermal route for selective synthesis of SnO2 nano-sheets and hollow micro-spheres [20-21]. The possible mechanism responsible for the nanostructure evolution has been discussed on the basis of the structure of the intermediate deposits. The sensing performance was also carried out and the results showed that the sensitivity was lower than that of commercial sintered-type gas sensors. Further work was suggested to be necessary for the application of these SnO2 nanostructures especially by proper doping. In the present work, Pd-doped SnO2 nano particles were successfully prepared using a template-free hydrothermal method. The crystal structure, the morphology and the microstructure were characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The surface chemical states analysis on X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was especially performed to reveal the mechanism of sensitivity enhancement by Pd additive. The gas-sensing property and the thermal stability were also measured using traditional sintered-type sensor structure by employing 10-3 (1000 ppm) of butane gas at the temperature of about 300 °C.
2 Experimental
2.1 Hydrothermal synthesis of Pd-doped SnO2
All the reagents, purchased from Sinopharm chemical Reagent Co., were of analytical grade and used without further purification. Firstly, 12 mmol SnCl2·2H2O and 1.2 mmol PdCl2 were dissolved into 20 mL deionized water, respectively. The dopant of PdCl2 solution was added slowly into the SnCl2 solution according to the designed doping concentration under magnetic stirring for about 20 min. Then 1.0 mol/L NaOH solution was added dropwise into the above suspension until pH=13 and the precursor suspensions were stirred for 2-3 h. The resulted mixture was transferred into a 100 mL Teflon-lined stainless autoclave, sealed and maintained at 180 °C for 12 h, and then cooled down to room temperature. The obtained precipitates were collected and washed several times with deionized water and ethanol, respectively, and finally dried in vacuum at 80 °C for 1 h. The dopant concentrations in mole fraction of Pd were set as 0.5%, 1.0%, 1.5%, 2.0%, 2.5%, 3.0% and 3.5%, respectively. In order to investigate the influence of annealing process on the morphology and the crystal structure of Pd-SnO2, the as-synthesized products were annealed at temperatures of 300, 400, 500, 700 and 900 °C for 3 h, respectively.
2.2 Characterization
XRD analysis for phase identification was performed using a Bruker AXS D8 advance diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation at a power of 1.6 kW. The diffraction pattern was measured in the 2θ angles ranging from 20° to 80° and calibrated using the standard spectrum of corundum. The instrument broadening was subtracted before estimating the grain size using the Scherrer equation. The morphology and microstructure of the SnO2 nanoparticles were characterized by a FEI Tecnai G2 F20 field emission transmission electron microscope.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements were carried out using an AXIS Ultra DLD spectrometer. All spectra were collected using a monochromatic AlKα (1 486.6 eV) X-ray source operated at 150 W, and at a pass energy of 10 eV. The C 1s peak (284.6 eV) from the adventitious carbon was used as the reference for binding energy calibration.
The Pd-doped SnO2 nano-materials were dispersed in ethanol, and then spin-coated on ceramic tubes with designed electrodes to make traditionally sintered bulk gas-sensing devices. The devices were calcined at 450 °C for 2 h. The gas-sensing properties were tested using 10-3 (1000 ppm) butane gas as an example.
3 Results and discussion
Firstly, the crystallization of the Pd-doped SnO2 samples with the concentrations designed above were investigated and shown in the XRD patterns of Fig. 1. All the diffraction peaks were perfectly indexed to the rutile SnO2 structure (JCPDS card, No.41-1445, space group: P42/mnm, a0=4.738 ?, c0=3.187 ?). There was no shift for the diffraction peaks of Pd-doped SnO2 and no impurity phase correlated with Pd was observed. The average grain size of all the samples was calculated according to the Scherrer equation. The results show that the average grain sizes kept as 4-5 nm with increasing the Pd-doping concentration from 0.5% to 3.5%. This indicates that the Pd-doping with the concentrations below 3.5% in this study did not change the crystallization of the SnO2 nano particles and had little effect on the grain sizes.
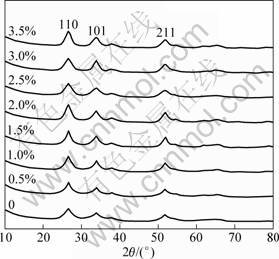
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Pd-doped SnO2 samples with different Pd concentrations
The influence of the Pd-doping on the morphology and microstructure of the SnO2 nanoparticles were carried out using TEM. Figure 2 shows the typical TEM images and SAED patterns of as-synthesized pure SnO2 and 2.5% Pd-doped SnO2. The results indicate that the doped-materials displayed less agglomeration in comparison with pure SnO2. The diameters of the particles were about 5 nm, which indicated that the Pd-doping had little influence on the particle sizes of SnO2. Those two samples were of poly-crystalline structures revealed by the SAED patterns. All the TEM results show that the series doping of 0.5% to 3.5% Pd had little effect on the crystallization and grain sizes of products, which is consistent with the XRD results.
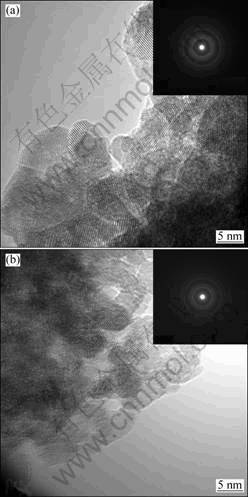
Fig. 2 TEM images with SAED patterns of as-synthesized pure SnO2 (a) and 2.5% Pd-doped SnO2 (b)
This phenomenon is different from the reported work that Pd-doping reduced the crystallite size of SnO2 and was helpful to the formation of distinct spherical nanospheres synthesized by a modified Pechini citrate route. And this total process involves two steps of thermal decomposition at 300 °C and 500 °C for the formation of nanostructured materials. The minimum crystallite size of 11 nm was calculated with the Scherrer equation with 1.5% Pd [22]. On the other hand, the study on crystallite growth kinetics of highly pure nanocrystalline SnO2 and the effect of Pd-doping by co-precipitation method showed that doping with Pd did not result in drag effect on crystallite boundary mobility but led to remarkable increase of crystallite growth rate and activation energy [23]. It is supposed that this difference is originally resulted from the synthesis routes. The hydrothermal synthesis with Pd-doping provides an effective one-step method for the formation of uniform doped-SnO2 crystalline without calcinations. Pd-doping was helpful to reducing the agglomeration but had little change on the grain sizes.
In order to test the sensitivity of as-synthesized Pd-doped SnO2 with different concentrations, the 10-3 butane gas was employed at the working temperature of 300 °C. The sensitivity factor S was defined as the ratio of the resistance in the air (Ra) to the resistance in the butane gas (Rg), which was expressed as S=Ra/Rg. The sensitivity factor of undoped SnO2 was determined to be 3.9±0.2 with a response time of 10 s, as shown in Fig. 3. The sensitivity factor was enhanced to 6.7±0.2 with 0.5% Pd-doping and quickly increased to 12.7±0.2 with increasing the doping concentration to 1.0%. The sensitivity factor almost kept constant when the Pd-doping concentration increased from 1.0% to 3.5%. When the response time was taken as 30 s, the sensitivity factor increased about 1.0 to 2.0 for the Pd-doping (1.0%-3.5%) samples.
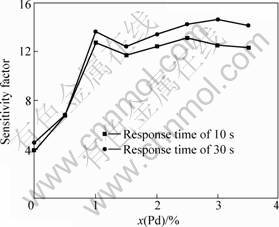
Fig. 3 Sensitivity of Pd-doped SnO2 samples with different concentrations
As the results above, Pd-doping is an effective way to improve the sensitivity. On the other hand, the thermal stability of the Pd-doped SnO2 is crucial to the performance and lifetime of the sensor devices. XRD patterns of the 2.5% Pd-doped samples annealed at different temperatures are shown in Fig. 4(a). As the result above, a rutile SnO2 crystal structure was formed after the sample was hydrothermally synthesized at 180 °C. XRD diffraction peaks change little when the temperature increased from 300 °C to 500 °C. The peaks intensified significantly and became sharp when the sample was annealed at 700 °C and 900 °C. The FWHM of the diffraction peaks decreased, which indicated the rapid increase of grain sizes with increasing the annealing temperature. Figure 4(b) shows the influence of the annealing temperature on the grain sizes of 2.5% Pd-doped SnO2 calculated according to the Scherrer equation and the effect on the sensitivity. We also investigated the influence of the annealing process on the pure SnO2 and doped samples. For the pure SnO2, the grain sizes grew quickly from 13.8 to 37.2 nm when the temperature increased from 500 to 900 °C. When the Pd-doping concentration was 0.5%, the grain sizes obtained at different temperatures were almost the same as un-doped SnO2 (the results were not shown in the figure). When the Pd-doping concentration was 2.5% or above, it was effective to restrain the increase of grain sizes at the annealing temperature below 700 °C. Surprisingly, the grain size increased rapidly to 44-47 nm at the high temperature of 900 °C. The above results indicate that the low doping concentration (0.5%) had little influence on change of grain sizes with the increase of annealing temperature. The high doping concentrations (2.5% and 3.5%) effectively restrained the increase of grain sizes at temperature below 700 °C while accelerated the increase at higher temperature of 900 °C.
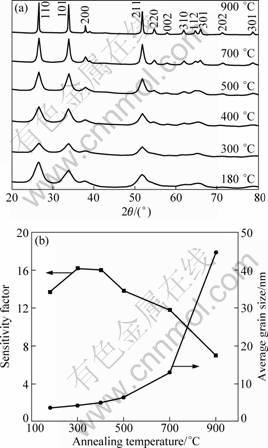
Fig. 4 XRD patterns (a) and grain size and sensitivity (b) of 2.5% Pd-doped SnO2 samples annealed at different temperatures
In order to investigate the thermal stability of the sensing performance, the sensitivity test with 10-3 butane was carried out for the products with 2.5% Pd-doping concentration after annealing process. It was observed that the sensitivity was promoted first to 16.0±0.2 after being annealed at 400 °C. The sensitivity decreased when the temperature increased to 700 and 900 °C. Compared with the samples with other doping concentrations, its performance exhibited more stable, especially below 700 °C. Our sensitivity results also confirmed that the gas-sensing property of the pure SnO2 was weakened with the increase of grain sizes while the Pd-doping optimized the sensitivity. Considering the sensitivity performance and the thermal stability, the optimum Pd-doping concentration was proposed to be 2.5%.
In order to reveal the essential of the influence of Pd-doping on the performance of sample, the surface chemical state analysis was applied with high-resolution XPS. The Sn 3d spectrum shows that the binding energy (BE) of Sn 3d5/2 was 486.4 eV assigned to Sn4+. The BEs and peak shapes did not change after Pd-doping, which indicates that the Pd-doping did not change the chemical states of the base material of SnO2. The chemical states of O 1s also kept the same for the Pd-doped samples. The O 1s spectra could be fitted into two peaks. The main peak at 530.5 eV was attributed to the crystal oxygen in the SnO2 bulk. The small peak at 532.5 eV originated from the absorbed oxygen on the SnO2 surface.
Figure 5 shows the Pd 3d spectra for the as- synthesized 2.5% Pd-doped sample and that annealed at 400 °C. In the as-synthesized sample, the Pd 3d spectrum was reasonably fitted into three peaks (Fig. 5(a)). The peak at 334.6 eV was attributed to Pd0. Another peak at 336.4 eV was assigned to Pd2+ in PdO. And the peak with the highest BE at 337.5 eV was attributed to Pd4+ in PdO2. The atomic constitution was calculated to be 0.37:0.15:0.48 according to the peak areas. This result shows that there existed three chemical states of Pd in the as-prepared hydrothermal products. It is well known that SnCl2 acid solution is a strong reducing agent to reduce many metal ions to low chemical states or even metal state.
It is assumed that the chemical states of the doping element had great effect on the gas-sensing property of Pd-doped SnO2. This was confirmed by the XPS results of the sample annealed at 400 °C in Fig. 5(b). It is observed that the chemical state of Pd0 disappeared after the sample was annealed at 400 °C. The mole ratio between Pd4+ and Pd2+ was approximately 2:1. The above sensitivity testing result shows that the sensitivity increased from 3.9±0.2 to 16.0±0.2 after being annealed at 400 °C. The sensitivity and mole ratio of Pd4+ to Pd2+ decreased with the increase of annealing temperature above 400 °C. It is deduced that Pd4+ is the key factor to promote the sensitivity. Some works have been published that Pd particles on SnO2 were easier to oxidize but more difficult to reduce compared with Pd(111) single crystal. The metal-substrate interaction (MSI) between the Pd additive and the SnO2 substrate is suggested to play an important role in the heating treatment process [24-25]. In our study, the additive of Pd in the hydrothermal synthesized sample was mainly oxidized to Pd4+ which was effective to sustain the performance after thermal treatment. With increasing the annealing temperature, the performance was weakened because of the unpreventable increase of the grain sizes. The detailed mechanism of Pd chemical states affecting the performance of sensor still needs further investigation.
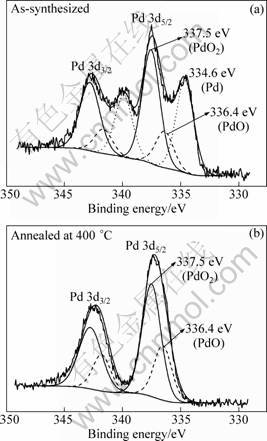
Fig. 5 XPS spectra of Pd 3d for as-synthesized sample (a) and sample annealed at 400 °C with 2.5% Pd-doping (b)
4 Conclusions
1) The Pd-doped SnO2 nano-particles were successfully synthesized through a template-free hydrothermal route at a low temperature. The grain sizes of the obtained SnO2 nano particles changed little with Pd-doping. Studies on the thermal stabilities revealed that Pd-doping could restrain the growth of grain sizes below 500 °C while the grain growth was promoted when the temperature increased above 700 °C.
2) The XPS showed that Pd existed in three chemical states in the as-synthesized sample as Pd0, Pd2+ and Pd4+, respectively. The chemical state analysis for the annealed samples indicated that Pd4+ was the main state responsible for improving the sensitivity. The optimum Pd-doping concentration of 2.5% was recommended for better sensitivity and thermal stability.
References
[1] TOURNIER G, PIJOLAT C. Influence of oxygen concentration in the carrier gas on the response of tin dioxide sensor under hydrogen and methane [J]. Sensors and Actuators B, 1999, 61: 43-50.
[2] ZHAO Qing-rui. Controllable synthesis and catalytic activity of SnO2 nanostructures at room temperature [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19: 1227-1231.
[3] YAMAZAKI T, JIN C J, SHEN Y B, KIKUTA T, NAKATANI N. Microstructure and gas sensing property of porous SnO2 sputtered films [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2007, 539-543: 3508-3513.
[4] WANG Yan, FAN Cai-mei, HUA Bo, LIANG Zhen-hai, SUN Yan-pin. Photoelectrocatalytic activity of two antimony doped SnO2 films for oxidation of phenol pollutants [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19: 778-783.
[5] WANG Y, HERRON N. Nanometer-sized semiconductor clusters: Materials synthesis, quantum size effects and photophysical properties [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1991, 95: 525-532.
[6] JIANG Lu-hua, SUN Gong-quan, ZHOU Zhen-hua, SUN Shi-guo, WANG Qi, YAN Shi-you, LI Huang-qiao, TIAN Juan, GUO Jun-song, ZHOU Bing, XIN Qin. Size-controllable synthesis of monodispersed SnO2 nanoparticles and application in electrocatalysts [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109: 8774-8778.
[7] WANG Wei-wei, ZHU Ying-jie, YANG Li-xia. ZnO-SnO2 hollow spheres and hierarchical nanosheets: Hydrothermal preparation, formation mechanism and photocatalytic properties [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2007, 17: 59-64.
[8] HAHN S H, BARSAN N, WEIMAR U. Investigation of CO/CH4 mixture measured with differently doped SnO2 sensors [J]. Sensors and Actuators B, 2001, 78: 64-68.
[9] JANMANEE R, PIRAKITIKULR P, WETCHAKUN N, LIEWHIRAN C, PHANICHPHANT S. Effect of palladium on photocatalytic activity of SnO2 [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2008, 55-57: 777-780.
[10] KWOKA M, OTTAVIANO L, PASSACANTANDO M, CZEMPIK G, SANTUCCI S, SZUBER J. XPS study of the surface chemistry of Ag-covered L-CVD SnO2 thin films [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254: 8089-8092.
[11] HANYS P, JANECEK P, MATOLIN V, KOROTCENKOV G, NEHASIL V. XPS and TPD study of Rh/SnO2 system-reversible process of substrate oxidation and reduction [J]. Surface Science, 2006, 600: 4233-4238.
[12] WANG Shu-rong, ZHAO Ying-qiang, HUANG Jing, WANG Yan, REN Hong-xia, WU Shi-hua, ZHANG Shou-min, HUANG Wei-ping. Low-temperature CO gas sensors based on Au/SnO2 thick film [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253: 3057-3061.
[13] FENG Yi-si, YAO Ri-sheng, ZHANG Li-de. Synthesis and sensitivity properties of Pd-doped tin oxide nanoparticles dispersed in mesoporous silica [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 89: 311-314.
[14] RAMGIR N S, MULLA I S, VIJAYMOHANAN K P. A room temperature nitric oxide sensor actualized from Ru-doped SnO2 nanowires [J]. Sensors and Actuators B, 2005, 107: 708-715.
[15] KOROTCENKOV G, BRINZARI V, BORIS Y, IVANOV M, SCHWANK J, MARANTE J. Influence of surface Pd doping on gas sensing characteristics of SnO2 thin films deposited by spray pirolysis [J]. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 436: 119-126.
[16] TADEEV A V, DELABOUGLISE G, LABEAU M. Influence of Pd and Pt additives on the microstructural and electrical properties of SnO2-based sensors [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1998, 57: 76-83.
[17] MAILLET T, SOLLEAU C, BARBIER J Jr, DUPREZ D. Oxidation of carbon monoxide, propene, propane and methane over a Pd/A1203 catalyst. Effect of the chemical state of Pd [J]. Applied Catalysis B, 1997, 14: 85-95.
[18] VELTRUSKA K, TSUD N, BRINZARI V, KOROTCHENKOV G, MATOLIN V. CO adsorption on Pd clusters deposited on pyrolytically prepared SnO2 studied by XPS [J]. Vacuum, 2001, 61: 129-134.
[19] ITOH T, MATRUBARA I, KADOSAKI M, SAKAI Y, SHIN W, IZU N, NISHIBORI M. Effects of high-humidity aging on platinum, palladium, and gold loaded tin oxide-volatile organic compound sensors [J]. Sensors, 2010, 10: 6513-6521.
[20] LI Yue, GUO Yan-qun, TAN Rui-qin, CUI Ping, LI Yong, SONG Wei-jie. Selective synthesis of SnO2 hollow microspheres and nano-sheets via a hydrothermal route [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(7): 581-587.
[21] LI Yue, GUO Yan-qun, TAN Rui-qin, CUI Ping, LI Yong, SONG Wei-jie. Synthesis of SnO2 nano-sheets by a template-free hydrothermal method [J]. Materials Letters, 2009, 63: 2085-2088.
[22] VAISHAMPAYAN M V, DESHMUKH R G, MULLA I S. Influence of Pd doping on morphology and LPG response of SnO2 [J]. Sensors and Actuators B, 2008, 131: 665-672.
[23] PAVELKO R G, VASILIEV A A, GISPERT-GUIRADO F, BARRABES N, LLORCA J, LLOBET E, SEVASTYANOV V G. Crystallite growth kinetics of highly pure nanocrystalline tin dioxide: The effect of palladium doping [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 121: 267-273.
[24] YAZAWA Y, YOSHIDA H, TAKAGI N, KOMAI S, SATRUMA A, HATTORI T. Acid strength of support materials as a factor controlling oxidation state of palladium catalyst for propane combustion [J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1999, 187: 15-23.
[25] SKALA T, VELTRUSK K, MOROSEAC M, MATOLINOVA I, CIRERA A, MATOLIN V. Redox process of Pd-SnO2 system [J]. Surface Science, 2004, 566: 1217-1221.
谭瑞琴1,郭艳群2,赵俊华2,李 月2,徐铁峰1,宋伟杰2
1. 宁波大学 信息科学与工程学院,宁波 315211;
2. 中国科学院 宁波材料技术与工程研究所,宁波 315201
摘 要:利用非模板水热法合成了Pd掺杂的SnO2纳米颗粒,并利用透射电镜(TEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)和X光电子能谱(XPS)表征了Pd掺杂对晶体结构、表面形貌、微观结构、热稳定性和表面化学状态的影响。研究发现:水热过程中Pd掺杂对形成的SnO2纳米颗粒大小几乎没有影响,在500 °C以下的煅烧过程中,掺杂的Pd可以有效抑制颗粒的生长,但在700 °C以上时颗粒生长迅速。XPS结果显示合成样品中Pd的化学状态有三种:Pd0、Pd2+和Pd4+,其中的主化学状态Pd4+有效促进了气敏性能的提高。为了同时提高气敏性能和热稳定性,Pd的最佳掺杂量为2.0%-2.5%(摩尔分数)。
关键词:SnO2纳米颗粒;Pd掺杂;水热合成;气敏性能;X光电子能谱
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Foundation item: Projects (60806032, 20975107) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2009R10064) supported by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars of Education Ministry, China; Project (2009R10064) supported by “Qianjiang Talent Program”; Projects (2009A610058, 2009A610030) supported by the Ningbo Natural Science Foundation, China; Project supported by K.C.WONG Magna Fund in Ningbo University, China
Corresponding author: TAN Rui-qin; Tel/Fax: +86-574-87600946; E-mail: tanruiqin@nbu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60898-4

