文章编号:1004-0609(2015)-09-2478-06
铜铝液相扩散结合的动力学分析
张建宇1,贲利华2,初 娣2,吴春京2
(1. 河北工程大学 机电工程学院,邯郸 056038;
2. 北京科技大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100083)
摘 要:为了提高铜铝复合材料的冶金结合质量,根据铜铝在共晶温度548 ℃到铝熔点温度660 ℃范围内的液相扩散结合机理,建立相应温度范围内的铜铝等温反应扩散数学模型,并对模型进行求解。计算结果表明:由于铜铝相互扩散,首先在界面形成铜固溶体(α)和铝固溶体(γ),随后铜铝界面发生液化并形成液相扩散层(L)和金属间化合物层(IMC);随着加热时间延长,固液界面IMC/L和γ/L分别向α侧和γ侧迁移,界面迁移距离与加热时间呈抛物线关系,抛物线系数与温度有关,温度越高,系数越大。
关键词:铜/铝;数学模型;动力学;液相扩散结合
中图分类号:TB331 文献标志码:A
Kinetics analysis of liquid phase diffusion bonding between Cu and Al
ZHANG Jian-yu1, BEN Li-hua2, CHU Di2, WU Chun-jing2
(1. School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China)
Abstract: In order to improve the metallurgical bonding in Cu/Al composites, the mathematical model of isothermal reactive diffusion between Cu and Al in the temperature range between eutectic temperature 548 ℃ and aluminum melting point of 660 ℃ was established and solved based on the liquid phase diffusion bonding mechanism. The analytical results show that the copper solid solution (α) and the aluminum solid solution (γ) form firstly owing to the interdiffusion between Cu and Al, then the liquid phase diffusion layer (L) and intermetallic compound (IMC) generate and the bonding boundary liquates. The IMC/L and γ/L solid-liquid interface migrate towards the solid solution phase α and the solid solution phase γ, respectively. Furthermore, there exists the parabolic relationship between the interface migration distance and the annealing time, the parabolic coefficients depend on the temperature, the higher the temperature, the bigger the coefficients.
Key words: copper/aluminum; mathematical model; kinetics; liquid phase diffusion bonding
铜包铝双金属复合材料具有电导率高、耐蚀性好、密度低、性价比高等特点,在信号传输和电力输送等领域获得越来越广泛的应用[1]。铜包铝复合材料的制造方法很多,目前,工业上广泛应用的制备方法主要有静液挤压法、轧制复合法、包覆焊接法等,这些方法本质上属于固相扩散结合,普遍存在界面结合差、表面处理困难、生产流程长等缺点[2-4]。为了克服固相扩散结合的一些缺点,近年来,又发展了液相扩散结合方法,如模铸法[5]和充芯连铸法[6]等。这些方法具有工艺简单,界面为冶金结合等优点。
对于铜铝液相扩散结合,其界面层基本上是由铜铝相互扩散形成的液相扩散层冷却凝固形成,液相扩散层形成机理有两类:1) 在铝的熔点660 ℃以上时,铜是固相,铝是液相,铜铝相互扩散而形成液相扩散层[7];2) 在铝的熔点(660 ℃)以下、共晶温度548 ℃以上时,铜铝都是固相,由于铜铝相互扩散导致固相液化而生成液相扩散层[8]。目前,生产实际中的铜铝液相扩散结合方法都是温度变化过程,反应扩散过程一般是这两种机理的综合作用结果[9-12]。由于铜铝液相扩散结合后形成的较厚的界面层很大程度上影响界面的性能和后续加工[13-14]。因此,弄清楚铜铝反应扩散机理及动力学模型,对于铜铝复合材料加工工艺过程控制具有重要的意义。
TANAKA等[15]研究纯铜铝在700~800 ℃温度范围内的等温反应扩散机理,在此温度范围内,铝是液相而铜是固相,由于铜铝相互扩散,在铜固溶体α和铝液L之间生成β、γ1、ε2等金属间化合物。另外,由于铜在铝液中的扩散系数远大于铝在铜固相中的扩散系数,L/ε2界面向α侧迁移,其迁移距离远大于金属间化合物的厚度,并且与时间的平方根成正比。TANAKA等[16-17]根据实验结果,建立铜铝固液等温反应扩散过程的数学模型并进行了数值计算。对于铜铝在共晶温度到铝熔点温度范围内铜铝反应扩散过程,KAWAKAMI等[8, 18]进行了实验研究并提出反应扩散机理,但关于此温度范围内的铜铝反应动力学模型及计算,目前鲜有报道。基于此作者在总结前人的实验基础上,建立铜铝液相扩散结合的数学模型并进行数学求解,为铜铝液相扩散结合实验研究奠定理论基础。
1 铜铝液相扩散结合的机理
本研究中仅考虑铜铝扩散偶均较厚、加热温度为548~660 ℃且扩散时间较短的情况,根据以前的研究成果,铜铝液相扩散结合的机理如图1所示。在加热过程中,铝铜原子在热激活下相互扩散,铜铝界面出现铜固溶体相(α)和铝固溶体相(γ),由于铜在铝中的扩散系数大于铝在铜中的扩散系数,γ相厚度大于α相厚度(见图1(a));随着扩散反应的进行,当γ相中Cu浓度超过其固溶度极限,开始在γ一侧出现液相扩散层L,同时,在铜铝界面生成铜铝金属间化合物(IMC)层(见图1(b));随着时间的延长,铜向铝侧的扩散,导致金属间化合物发生溶解,IMC/L的界面向α侧迁移,同时,IMC/α界面向α侧迁移并在其界面上生成新的金属间化合物,两者速度的差异导致金属间化合物的长大。同理,铜铝相互扩散导致L/γ界面向铝侧迁移。IMC/L和L/γ界面的反向迁移导致液相扩散层厚度的增加(见图1(c));当温度冷却时,液相扩散层凝固形成界面层(见图1(d))。由于液相的扩散系数远大于固相的,由液相扩散层凝固后形成的固相厚度远远大于反应扩散中生成的金属间化合物的厚度,因此,铜铝液相扩散结合所形成的界面层厚度主要是由反应扩散过程中IMC/L和L/γ固液界面迁移距离决定。
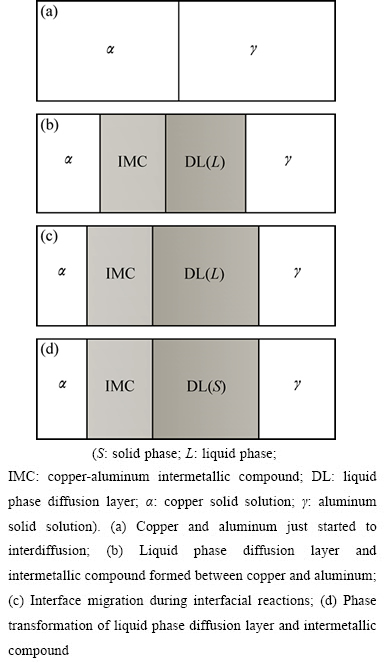
图1 铜铝液相扩散结合示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of liquid phase diffusion bonding between copper and aluminum
2 铜铝液相扩散结合的数学模型
为了建立铜铝反应扩散过程的数学模型,可以根据铜铝液相扩散结合机理作如下假设:1) 扩散过程为等温过程;2) 反应扩散过程中,金属间化合物厚度同液相扩散层厚度相比很小,可忽略不计;3) 固相扩散系数远小于液相扩散系数,可仅考虑液相中的扩散,另外假设液相扩散系数与成分无关;4) 在扩散时间较短情况下,液相扩散层很薄,对流扩散过程可以忽略;5) 各相在界面处局部平衡,界面上每一相的成分可根据Al-Cu二元合金相图求出;6) 忽略液相形成的孕育时间,假设液相瞬间形成;7) 固液界面为平面。根据上述假设,铜铝液相扩散反应模型如图2所示,图中横坐标表示位置x,方向向右为正方向;纵坐标表示铝的摩尔浓度c;γ表示铝固溶体相;α表示铜固溶体相;L表示液相扩散层;图中垂直虚线表示初始时刻t=0时α相和γ相的接触界面位置x=0,zLα、zLγ表示在某个时间t时L/α、L/γ界面从初始位置x=0计算的迁移距离;cα0、cγ0分别表示α相、γ相的初始浓度;cαL、cLα分别表示L/α界面α相和L相的平衡浓度;cLγ、cγL分别表示L/γ界面L相、γ相平衡浓度。由于忽略固相中的扩散,cγ0=cγL、cα0=cαL。
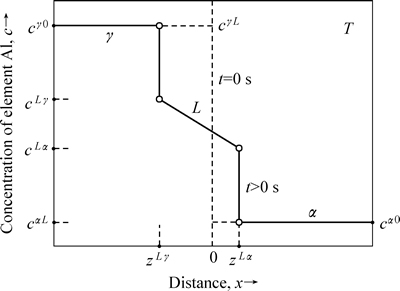
图2 Cu/Al半无限扩散偶中Al在液相中的浓度分布
Fig. 2 Concentration distribution of element Al acrossing L phase along diffusional direction in Cu/Al semi-infinite diffusion couple
由于铜铝扩散偶长度和宽度远大于铜铝扩散层厚度,扩散过程可看成是一维扩散,用菲克第二定律表示:
 (1)
(1)
式中:cL是Al在液相扩散层中的摩尔浓度;DL是液相扩散系数。对于α/γ半无限扩散偶,初始条件可表示为
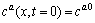 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
当反应扩散开始,液相L在界面瞬间生成,L相与α、γ相在界面局部平衡,边界条件可表示为
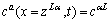 (4)
(4)
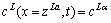 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
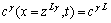 (7)
(7)
在等温反应扩散过程中,由于铜铝相互扩散导致L/α和L/γ界面发生迁移,其迁移速度dzLα/dt和dzLγ/dt分别与L/α和L/γ界面上Al的扩散流量JLα和JLγ有关[19],在忽略固相扩散的情况下,分别可用式(8)和(9)表示:
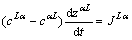 (8)
(8)
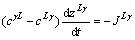 (9)
(9)
式中:扩散流量JLα、JLγ与浓度梯度成正比,根据菲克第一定律,JLα、JLγ可分别表示为
 (10)
(10)
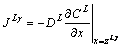 (11)
(11)
假设固液界面的迁移受体扩散控制,L/α、L/γ界面的迁移距离zLα、zLγ可用下式表示
 (12)
(12)
 (13)
(13)
式中:KLα、KLγ为无量纲比例系数;K1、K2称为抛物线系数。
联立式(1)~(13)即可对扩散方程(1)求解[20],即
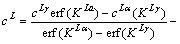

 (14)
(14)
式中:KLα和KLγ可分别由超越方程(15)和(16)求得
 (15)
(15)
 (16)
(16)
从式(15)和(16)可以看出,KLα、KLγ是界面平衡浓度cLγ、cγL、cLα、cαL的函数。
3 计算结果与讨论
在上面的数学模型中,Al的浓度为摩尔浓度c,但在实际应用中,在Al-Cu相图上采用摩尔分数y表示各相组成,两者之间可以通过c=y/Vm互相转化,Vm是铜铝各相的摩尔体积。如果忽略铜铝中各相的摩尔体积差异,式(14)~(16)中的cL、cγL、cLγ、cLα、cαL可分别用摩尔分数yL、yγL、yLγ、yLα、yαL代替,即


 (17)
(17)
式中:KLγ、KLα可分别由超越方程(18)和(19)求得
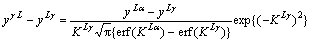 (18)
(18)
 (19)
(19)
扩散偶为纯铜和纯铝,式中yγL=1、yαL=0,yLγ、yLα可根据铜铝二元合金相图[21]求出,与γ相平衡的液相L浓度yLγ与温度近似为直线关系,其计算式如下
 (20)
(20)
式中:θL与θAl分别为相平衡温度和铝的熔点温度,℃;mL为液相线斜率,用摩尔分数表示时为6.55;yLα在数学模型中是与α相平衡的液相浓度,但实际反应扩散中是金属间化合物与液相平衡,在624 ℃以上,液相L与金属间化合物ε2相平衡,其平衡浓度yLα可用表示为[16]
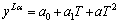 (21)
(21)
式中:a0=1.88,a1=-1.92×10-3,a2=6.00×10-7。
在591~624 ℃范围内,液相与金属间化合物η1相平衡,其平衡浓度yLα与温度的关系可以近似成直线关系;在共晶温度548 ℃到591 ℃,液相L与金属间化合物θ相平衡,其平衡浓度可参考文献[22]。液相扩散系数DL可用阿累尼乌斯定律表示
 (22)
(22)
式中:D0是扩散常数,1.05×10-7 m2/s;Q是扩散激活能,2.38×10-4 J/mol;R是摩尔气体常数;T是绝对温度,K[22]。表1所列为630、600、570 ℃温度下平衡浓度yLγ和yLα、无量纲比例常数KLγ和KLα、液态扩散系数DL的计算值。由表1可看出,KLγ与KLα符号相反,说明L/γ与L/α界面迁移方向相反,另外,KLγ大于KLα,说明液相向铝侧迁移距离大于向铜侧迁移距离。
表1 铜铝液相扩散结合的计算结果
Table 1 Calculated results during liquid phase diffusion bonding between Cu and Al

Al在液相中的浓度曲线cL和界面迁移距离zLα、zLγ随温度和时间的变化如图3所示,图中虚线表示某一时间,如5、10、15 s时,L/γ、L/α界面的迁移距离,点划线表示铜铝界面初始位置;实线表示Al在液相的浓度分布。从图3可以看出,在短时间内,液相L内的浓度分布近似可以看成直线,L/α和L/γ界面随着时间延长分别向α侧和γ侧迁移,迁移距离与时间成抛物线关系。另一方面,等温扩散温度越高,界面迁移距离越大,这是由于温度升高,KLγ、KLα、DL随温度增加而增大。另外,从图3(a)可看出,在5 s内,铜侧溶解厚度为25 μm,与NATSUME等[22]的实验结果较为吻合,证明此模型较为合理。
4 结论
1) 建立了铜铝在548~660 ℃温度范围内等温反应扩散过程的数学模型,计算得出了不同温度和不同时间下Al在液相中的浓度分布和界面迁移距离。
2) 计算结果表明:在铜铝固相间,由于相互扩散瞬间会生成液相,在短时间内,浓度分布近似可以看成是直线关系,另外,固液界面L/α和L/γ会分别向铜侧和铝侧迁移,迁移距离zLα、zLγ与时间t存在抛物线关系,其抛物线系数与扩散系数DL和铜铝固液平衡浓度yγL、yLγ、yLα、yαL等有关,温度越高,抛物线系数越大。
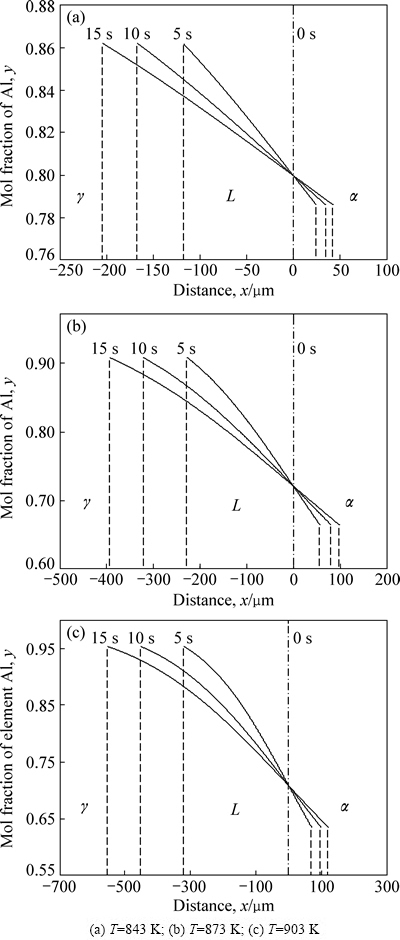
图3 铝在液相中浓度分布曲线
Fig. 3 Calculated concentration profiles of Al in L phase (Thin dashed curves indicate migration distance of solid/liquid interface; dot-dash curves indicate initial position of Cu/Al interface)
3) 此数学模型及计算结果可为铜铝液相结合反应扩散工艺过程提供理论依据。
REFERENCES
[1] 张建宇, 姚金金, 曾祥勇, 韩艳秋, 吴春京. 铜包铝复合材料研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(5): 1275-1284.
ZHANG Jian-yu, YAO Jin-jin, ZENG Xiang-yong, HAN Yan-qiu, WU Chun-jing. Research process of copper cladding aluminum composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(5): 1275-1284.
[2] 李小兵, 祖国胤, 王 平. 退火温度对异步轧制铜/铝复合板界面组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(5): 1202-1207.
LI Xiao-bing, ZU Guo-yin, WANG Pin. Effects of annealing temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu/Al clad sheet fabricated by asymmetrical roll bonding[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(5): 1202-1207.
[3] 王秋娜, 刘新华, 刘雪峰, 谢建新. 退火温度对冷静液挤压铜包铝线材组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2008, 44(6): 675-680.
WANG Qiu-na, LIU Xin-hua, LIU Xue-feng, XIE Jian-xin. Effects of annealing temperature on the microstructures and properties of copper cladding aluminum wire prepared by cold hydrostatic extrusion[J]. Acta Metallurgicga Sinica, 2008, 44(6): 675-680.
[4] LI Xiao-bing, ZU Guo-yin, WANG Ping. Microstructural development and its effects on mechanical properties of Al/Cu laminated composite[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(1): 36-45.
[5] MERENO J, GARRETT J, EMBURY D. A technique rapid characterization of intermetallics and interfaces[J]. Intermetallics, 1999, 7: 1001-1009.
[6] 吴永福, 刘新华, 谢建新, 王连忠, 董晓文. 矩形断面铜包铝复合材料的水平连铸直接复合成形[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(9): 2050-2057.
WU Yong-fu, LIU Xin-hua, XIE Jian-xin, WANG Lian-zhong, DONG Xiao-wen. Copper cladding aluminum composites materials with rectangle section fabricated by horizontal core-filling continuous casting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(9): 2050-2057.
[7] XU B, TONG W P, LIU C Z, ZHANG H, ZUO L, HE J C. Effect of high magnetic field on growth behavior of compound layers during reactive diffusion between solid Cu and liquid Al[J]. J Mater Sci Technol, 2011, 27(9): 856-860.
[8] KAWAKAMI H, SUZUKI J, FUJIWARA M, JUNNA N. Effect of bonding conditions on Al/Cu Dissimilar bonding with liquefaction by reaction diffusion in air[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Japan Welding Society, 2007, 25(1): 24-30.(in Japanese)
[9] 张红安, 陈 刚. 铜/铝复合材料的固-液复合法制备及其界面结合机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(3): 414-419.
ZHANG Hong-an, CHEN Gang. Fabrication of Cu/Al compound material by solid-liquid bonding method and interface bonding mechanism[J]. The Chinese Journal Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 18(3): 414-419.
[10] ZARE G R, DIVANDARI M, ARABI H. Investigation on interface of Al/Cu couples in compound casting[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2013, 29(2): 190-196.
[11] VAHID GOLPAYEGANI AR, DIVABDARI M. Study of Al/Cu rich phases formed in A356 alloy by inserting Cu wire in pattern in LFC process[J]. Materials and Design, 2009, 30: 3279-3285.
[12] 张建宇, 曾祥勇, 韩艳秋, 姚金金, 吴春京. 充芯连铸铜包铝复合材料的界面形成机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(11): 2755-2761.
ZHANG Jian-yu, ZENG Xiang-yu, HAN Yan-qiu, YAO Jin-jin, WU Chun-jing. Formation mechanism of interface in copper cladding aluminum composites fabricated by core-filling continuous casting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(11): 2755-2761.
[13] 吴永福, 刘新华, 谢建新. 连铸直接复合成形矩形断面铜包铝复合材料界面及其在轧制中的变化[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(1): 191-200.
WU Yong-fu, LIU Xin-hua, XIE Jian-xin. Interface of copper cladding aluminum composite materials with rectangle section fabricated by horizontal core-filling continuous casting and its evolvement in rolling process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(1): 191-200.
[14] 吴永福, 刘新华, 谢建新. 退火温度对连铸-轧制成形铜包铝复合扁排组织与性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(1): 188-196.
WU Yong-fu, LIU Xin-hua, XIE Jian-xin. Effect of annealing temperature on texture and properties of copper cladding aluminum flat bar fabricated by continuous casting and subsequent rolling technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(1): 188-196.
[15] TANAKA Y, KAJIHARA M, WATANABE Y. Growth behavior of compound layers during reactive diffusion between solid Cu and liquid Al[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 445/446: 355-363.
[16] TANAKA Y, KAJIHARA M. Numerical Analysis for migration of interface between liquid and solid phases during reactive diffusion in the binary Cu-Al system[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 459: 101-110.
[17] TANAKA Y, KAJIHARA M. Evaluation of interdiffusion in liquid phase during reactive diffusion between Cu and Al[J]. Materials Transactions, 2006, 47: 2480-2488.
[18] KAWAKAMI H, SUZUKI J, NAKAJIMA J. Bonding process of Al/Cu dissimilar bonding with liquefaction in air[J]. Welding International, 2007, 21(12): 836-843.
[19] KAJIHARA M, FURUTO A. Numerical analysis for kinetics of reactive diffusion controlled by boundary and volume diffusion in a hypothetical binary system[J]. Materials Transactions, 2008, 49(2): 294-303.
[20] JOST W. Diffusion in solids, liquid, gases[M]. New York: Academic Press Inc, 1960:74-75.
[21] MURRAY J L. The aluminum-copper system[J]. International Metals Reviews, 1985, 30(5): 211-233
[22] NATSUME Y, OHSASA K, TAYU Y, MOMONO T, NARITA T. Numerical modeling of the transient liquid-phase diffusion bonding process of Al using Cu filler metal[J]. ISIJ International, 2003, 43(12): 1976-1982.
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51274038)
收稿日期:2015-01-12;修订日期:2015-05-28
通信作者:吴春京,教授;电话:010-62332605;E-mail:cjwu @ mater.ustb.edu.cn