新型铁炭微电解法降解EDTA有机废水
陈润华,柴立元,王云燕,舒余德,蒋国民
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:开发一种基于铁炭微电解处理有机废水的新方法,处理乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)难降解有机废水。采用活性炭作氧电极载体,铁粉为阳极,在酸性富氧条件下产生的·OH自由基有效降解废水中的EDTA组分,根据微电池原理及Fenton反应导出羟基自由基·OH浓度的热力学关系式,可用于合理解释各种因素对EDTA脱除率的影响。研究pH、通气条件、温度、反应时间及Fe与C的质量比对EDTA脱除效果的影响,得到最佳工艺条件如下:pH为2~4,温度为常温,Fe与C的质量比≥0.01,时间>30 min,有氧气存在,在该条件下使总有机碳(TOC)质量浓度为200 mg/LEDTA的脱除率达到83.8%。
关键词:微电解;有机废水;羟基自由基;乙二胺四乙酸
中图分类号:TP18 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)06-1516-06
Degradation of organic wastewater containing EDTA by Fe-C micro-electrolysis
CHEN Run-hua, CHAI Li-yuan, WANG Yun-yan, SHU Yu-de, JIANG Guo-min
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: A novel technique based on Fe-C micro-electrolysis (FAC) to treat the organic wastewater was proposed, which was used to treat EDTA-containing organic wastewater. In this study, activated carbon and iron were taken as the inert electrode and the cathode, respectively. EDTA in the wastewater could be degradated effectively by ?OH gemerated under the acidic and oxygen-rich conditions. The mechanism and influencing parameters of organic wastewater treatment by FAC were investigated. Thermodynamic relationship was deduced, which could be used to interpret all of the parameters effecting EDTA removal rate reasonably. The results show that the residual TOC is affected by pH of influent, dissolved oxygen DO, temperature, contact time and Fe/C mass ratio, and the conditions are as follows: pH is 2-4, room temperature, Fe/C mass ratio is more than 0.01, contact time is more than 30 min, and oxygen exists. Under the optimal conditions the removal rate of EDTA with 200 mg/L concentration can reach 83.8%.
Key words: micro-electrolysis; organic wastewater; ·OH radicals; EDTA
目前,有机废水的处理技术多为传统的生物法[1-3]处理,对于焦化废水、染料废水、造纸废水、农药和制药废水等富含难降解有机物的典型废水,由于这类废水可生化性生化耗氧量与化学耗氧量比值一般为0.3以下甚至更低[4-6]。对于螯合剂的代表性物质EDTA废水,由于其化学键紧密,能与所有金属离子形成配合物,且配合物稳定性很高,直接采用生物法处理很难达标排放。虽然目前也有一些非生物处理技术的研究,如催化氧化技术(包括湿式催化氧化法、光催化氧化法以及电催化氧化法等),但这些方法都存在一定得局限性[7-8]:湿式催化氧化法的催化剂昂贵,而且反应条件不温和,对反应设备要求很高,运用范围很窄;光催化氧化对能源利用率低[9-13],限制了其应用的范围。微电解法[14-17]是20世纪70年代初随着铁在废水处理中的应用而逐渐发展起来的一种废水处理技术。该技术基于电化学氧化还原反应原理,通过铁屑对絮体的电附集、混凝、吸附、过滤等作用处理废水,具有设备构造简单,易制作操作,处理成本低,易与其他方法联合使用等特点。本文作者基于铁炭微电解的技术原理[18-20],以EDTA废水为研究对象,对难降解有机物EDTA的降解机理及工艺条件的优化进行研究,试图开发一种EDTA难降解有机废水处理新方法,旨在为EDTA难降解废水的高效铁炭微电解降解开辟一条新途径。
1 铁炭微电解降解EDTA原理
1.1 H2O2生成反应及其热力学关联式
铁粉和活性炭混合一起,并有氧存在时,可构成微电池。
阴极反应为:
O2+2H++2e→[H2O2]吸
E(O2/H2O2)=0.682 4 V
式中:E为电位差。
阳极反应为:
Fe-2e→Fe2+
E(Fe2+/Fe)=-0.440 2 V
电池反应为
O2+2H++Fe→Fe2++[H2O2]吸 (1)
平衡常数K1为:
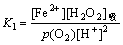 (2)
(2)
取对数得:
 (3)
(3)
由反应物标准摩尔反应吉布斯自由能[26-27]计算得到式(1)自由能变化(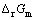 )为:
)为:
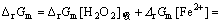
-212.93 kJ/mol (4)
式(4)中标准摩尔反应吉布斯自由能变化很大,表明[H2O2]容易生成。
标准摩尔反应吉布斯自由能变化与平衡常数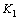 有如下关系:
有如下关系:
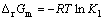 (5)
(5)
将式(4)和(5)及有关常数代入式(3)得:
lg[H2O2]吸=36.68-lg[Fe2+]+lgp(O2)-2pH (6)
式(6)表明:体系中(H2O2)吸生成量的大小由亚铁离子浓度、溶解氧浓度及pH决定。
1.2 羟基自由基?OH生成反应及其热力学关联式
微电池反应所生成的Fe2+与生成的吸附态H2O2发生Fenton反应生成吸附态羟基自由基
[H2O2]吸+Fe2++H+→Fe3++H2O+?OH吸 (7)
标准摩尔反应吉布斯自由能变化为:
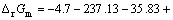
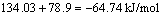 (8)
(8)
式(8)表明体系中羟基自由基?OH容易生成。
式(7)的平衡常数为:
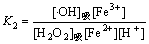 (9)
(9)
取对数得:
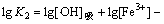
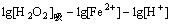 (10)
(10)
将式(5),(8)和(10)合并得:
lg[?OH]=0.0119-lg[Fe3+]+lg[H2O2]+lg[Fe2+]-pH (11)
当反应(1)和反应(7)同时处于平衡状态时,将式(6)代入式(11)得:
lg[?OH]吸=36.69-lg[Fe3+]+lg p(O2)-3pH (12)
式(12)表明:当铁粉与活性炭混合一起,并有氧气存在时,活性炭表面产生了羟基自由基?OH,其生成量取决于体系中3价铁离子浓度、溶解氧浓度及pH。
1.3 降解结果预测
式(1)及式(7)表明:铁粉、活性炭及氧气组成的体系,会产生标准电极电势为2.80 V羟基自由基?OH,攻击吸附于活性炭层状结构的EDTA,EDTA降解受?OH影响,羟基自由基?OH浓度与pH的3次方成反比,平衡转化率随温度升高而降低,?OH的浓度与氧的分压成正比,使得EDTA逐步分解为小分子直至无机物。
2 实验
2.1 实验装置
铁炭微电解反应器为一带隔板的圆柱状反应器,如图1所示。反应器上部内径为10 cm,高度为30 cm,圆柱状结构;内部填充活性炭颗粒并与一定比例的铁粉混合;下部为一椎体结构,可以通过连通的管道均匀曝气;上、下部使用1个隔板隔开,并在侧面设置3个不同高度的取样口。
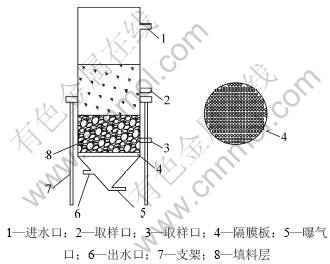
图1 铁炭微电解反应器示意图
Fig.1 Sketch map of micro-electrolysis reactor
反应器外接恒流循环泵实现溶液循环,底部导管为气体入口,外接氧气瓶或氮气瓶。
2.2 实验材料
阳极材料为工业级铁粉,阴极材料为粒径2 360~ 1 000 μm的多孔性活性炭,按照一定比例均匀混合填充于柱体反应器之内。
实验研究用模拟废水由化学纯的EDTA和超纯水配置。称量0.6 g乙二胺四乙酸二钠,用1 L超纯水溶解,使用盐酸调节到适当pH即得到模拟废水。EDTA模拟废水TOC质量浓度为200 mg/L。
2.3 实验过程
2.3.1 活性炭预处理
对活性炭进行除油活化预处理:用稀酸浸泡12 h,用超纯水反复冲洗以去除表面附着的污染物;并用过量TOC质量浓度为200 mg/L的EDTA废水浸泡,直至废水中TOC质量浓度无明显下降趋势为止;之后过滤分离活性炭备用。
2.3.2 实验过程
称取活化并吸附EDTA达到饱和的活性炭40 g与1~5 g工业铁粉混合均匀制作好填料放入反应器填料层,取200 mL TOC质量浓度为200 mg/L的EDTA模拟废水,置于恒温水浴箱中,控制pH为1~10,调节溶解氧量,反应20~120 min后将水取出至烧杯,调节pH至10絮凝沉降、过滤,分析滤液中TOC质量浓度。
表1所示为体系中无氧、有氧及富氧条件。在考察氧气作用试验中,按表1所示控制气氛条件。并控制工业铁粉3 g,调节废水pH为2,控制温度25 ℃,反应时间20 min,分别以表1所示3种条件改变体系中通入气体的条件,考察溶解氧对TOC脱除效果的 影响。
表1 体系中无氧、有氧及富氧条件
Table 1 Aerobic, anaezobic, oxygen-rich states in system

2.3.3 活性炭的再生
采用质量分数为18%的稀盐酸浸泡5 h,用纯水冲洗残余盐酸后,放入微电解反应器中加入3 g铁粉与200 mL超纯水,在常温条件下进行微电解反应 20 min。
2.4 分析方法
废水及出水TOC含量采用日本岛津TOC-VCPH型总有机炭分析仪测定;pH采用上海雷磁PHS-3B型精密pH计测量。
3 结果与讨论
3.1 pH对TOC残余质量浓度的影响
图2所示为pH对TOC残余质量浓度的影响。从图2可见:铁炭微电解反应受到pH影响较大,TOC残余质量浓度随着反应pH的增大而增大;当pH为10时,EDTA几乎不能被矿化为无机组分,pH越低,EDTA脱除效果越好;当pH为2时,TOC质量浓度由200 mg/L降至80 mg/L。pH对EDTA矿化效果的影响可由式(12)进行解释,羟基自由基浓度与pH的3次方成反比。pH越低,越有利于?OH的生成,因此,EDTA脱除效果好;式(12)还表明:增加Fe3+质量浓度对?OH的生成有不利影响,故应将pH控制在使Fe3+刚好水解沉淀的pH范围内。实验表明:最佳的pH为2~4。
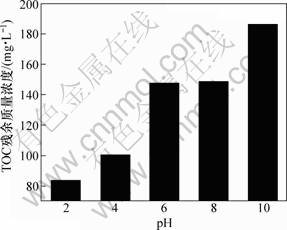
图2 pH对TOC残余质量浓度的影响
Fig.2 Effects of pH on residual mass concentration of TOC
3.2 温度对TOC残余质量浓度的影响
图3所示为温度对TOC残余质量浓度的影响。由图3可看出:温度对TOC脱除效果影响很大,温度升高TOC残余浓度增加;当温度由10 ℃升至60 ℃时,TOC残余质量浓度由20 mg/L提高至120 mg/L。温度升高,TOC脱除率降低的原因分析如下。
式(1)的标准反应焓变为:
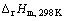 =-176.88 kJ/mol
=-176.88 kJ/mol
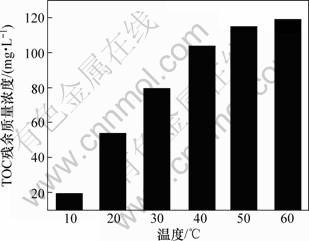
图3 温度对TOC残余质量浓度的影响
Fig.3 Effects of temperature on residual mass concentration of TOC
由vant Hoff方程式
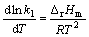 (13)
(13)
得: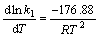 。
。
式(13)表明:温度升高,式(1)中平衡常数k1减小,故[H2O2]吸平衡转化率随着温度升高而降低;结合式(7),由于反应物[H2O2]吸变小,导致羟基自由基?OH的浓度减小。故温度升高,EDTA的矿化效果变差,因而TOC残余质量浓度增加。反应过程取室温为宜。
3.3 通气条件对TOC残余浓度的影响
图4所示为体系不同通气条件下TOC的残余质量浓度。结果表明:在氮气保护条件下TOC残余质量浓度为150 mg/L,脱除率为25%;通空气条件下,TOC残余质量浓度为70 mg/L,脱除率提高到65%;而在纯氧气条件下脱除率进一步提高到85%。式(12)表明:?OH的浓度与氧的分压成正比。增加氧气分压,羟基自由基?OH的浓度增加,故EDTA脱除率提高。
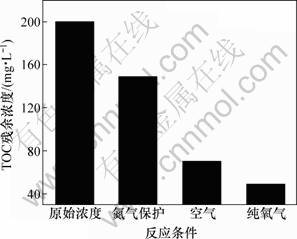
图4 通气条件对TOC残余质量浓度的影响
Fig.4 Effects of ventilation condition on residual mass concentration of TOC
3.4 Fe与C的质量比对TOC残余浓度的影响
铁与碳的质量比对TOC残余质量浓度的影响如图5所示。从图5可见:不加入铁粉时吸附饱和后的活性炭对有机物几乎没有处理效果,在研究的铁粉用量范围内,铁粉加入量对实验数据的影响不大,需要的铁粉量满足Fe与活性炭的质量比≥0.01。实验结果表明:没有铁粉存在时,EDTA不发生矿化反应。
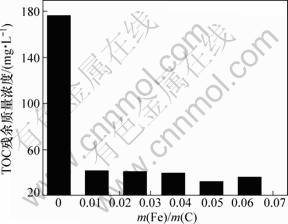
图5 铁与碳的质量比对TOC残余质量浓度的影响
Fig.5 Effects of m(Fe)/m(C) on residual mass concentration of TOC
3.5 反应时间对TOC残余质量浓度的影响
图6所示为不同反应时间对TOC脱除效果的影响。从图6可见:随着反应时间的增加,TOC残余质量浓度不断降低,当反应时间达到30 min时,TOC趋近平衡,表明EDTA的降解反应达到平衡,再继续延长反应时间对TOC脱除效果影响不大。因此,最佳反应时间为30 min。
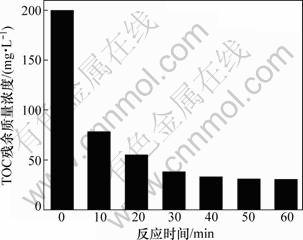
图6 反应时间对TOC残余质量浓度的影响
Fig.6 Effects of reaction time on residual mass Concentration of TOC
3.6 最佳条件实验
取吸附EDTA完全饱和的活性炭40 g,工业级铁粉3 g,pH为2,温度为25 ℃,铁与碳的质量比为3/40,加入200 mL TOC质量浓度为200 mg/L的有机废水置于反应器中,反应时间为30 min,在此最佳条件下,TOC脱除到32.351 mg/L,去除率达到83.8%。
4 结论
(1) 基于铁炭微电解原理设计开发了一套铁炭微电解柱状反应器,并应用于EDTA难降解有机废水的处理。
(2) 铁炭微电解处理EDTA废水最佳工艺条件是:pH为2~4,温度为常温,Fe与C的质量比≥0.01,反应时间>30 min,有氧气存在。在此优化条件下,EDTA的脱除率达到83.8%。
(3) 根据微电池原理及Fenton反应导出了羟基自由基·OH产生量的热力学关系式。活性炭表面羟基自由基·OH生成量取决于体系中铁离子浓度、溶解氧质量浓度及pH,解释了各因素对EDTA脱除率的影响规律。
参考文献:
[1] 张亚平, 韦朝海. 光Fenton氧化降解染料阳离子红GTL[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 39(4): 688-693.
ZHANG Ya-ping, WEI Zhao-hai. Oxidation degradation of cationic red GTL by photo-Fenton[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2008, 39(4): 688-693.
[2] 沈阳化工研究院环保室. 农药废水处理[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2000: 22-26.
Shenyang Chemical Industry Institution Environmental Room. Pesticide wastewater treatment[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2000: 22-26.
[3] 杨书铭, 黄长盾. 纺织印染工业废水治理技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002: 29-32.
YANG Shu-ming, HUANG Chang-dun. Textile printing and dyeing industry wastewater treatment technology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002: 29-32.
[4] 周培国, 傅大放. 微电解工艺研究进展[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2001, 2(4): 18-24.
ZHOU Pei-guo, FU Da-fang. Application and development for microelectrolysis technology[J]. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 2001, 2(4): 18-24.
[5] 李治国, 董里, 史惠祥, 等. Fenton试剂处理2,4-D废水研究[J]. 浙江大学学报: 理学版, 2004, 31(4): 442-445.
LI Zh-guo, DONG Li, SHI Hui-Xiang, et al. Oxidation of 2, 4-Dichlorphenoxyacetic Acid by Fenton reagent[J]. Journal of ZheJiang University: Science Edition, 2004, 31(4): 442-415.
[6] 张波, 何义亮. 铁炭微电解-混凝沉淀预处理化工有机废水[J]. 兰州铁道学院学报, 2001, 20(3): 95-98.
ZHANG Bo, HE Yi-liang. The pretreatment effect of ferric-carbon micro electrolysis and coagulation sedimentation for chemical industrial organic wastewater[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Railway University, 2001, 20(3): 95-98.
[7] Pitter P, Sykora V. Biodegradability of ethylenediamine-based complexing agents and related compounds[J]. Chemosphere, 2001, 44(4): 823-826.
[8] Walsh F, Reade G. Design and performance of electrochemical reactors for efficient synthesis and environmental treatment. Part 2: Typical reactors and their performance[J]. Analyst, 1994, 119(5): 797.
[9] 王有乐, 张庆芳. 内电解法处理工业废水的研究进展[J]. 甘肃工业大学学报, 2003, 29(1): 67-69.
WANG You-le, ZHANG Qing-fang. Development of industrial wastewater treatment with micro-electrolysis[J]. Journal of Gansu University of Technology, 2003, 29(1): 67-69.
[10] 张亚楠, 段舜山, 刘国光, 等. 铁屑法预处理制药废水的研究[J]. 生态科学, 2002, 21(1): 62-64.
ZHANG Ya-nan, DUAN Shun-shan, LIU Guo-guang, et al. Study on pretreatment for pharmacadical wastewater by iron scrap process[J]. Ecologic Science, 2002, 21(1): 62-64.
[11] 马前, 叶少丹, 李义久, 等. 铁屑微电解法处理光致抗蚀剂废水的研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2003, 23(5): 38-40.
MA Qian, YE Shao-dan, LI Yi-jiu, et al. Study on the wastewater treated by the iron chipping micro-electrolysis[J]. Industral Water Treatment, 2003, 23(5): 38-40.
[12] 丁智慧, 刘吉开, 丁靖垲, 等. 拟除虫菊酯的研究进展[J]. 云南化工, 2001, 28(2): 22-24.
DING Zhi-hui, LIU Ji-kai, DING Jing-kai, et al. Progress on the research of pyrethroids[J]. Yunnan Chemical Technology, 2001, 28(2): 22-24.
[13] 常文兴, 曲长宏, 柴德宏. 高浓度农药废水的治理方法介绍[J]. 环境保护科学, 2001, 27(5): 25-26.
CHANG Wen-xing, QU Chang-hong, CHAI De-hong. Introduction on treatment methods of high concentrated pesticide wastewater[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2001, 27(5): 25-26.
[14] 程鸣, 何文英, 彭光明, 等. 农药草甘膦生产废水处理的研究[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2003, 34(1): 30-32.
CHENG Ming,HE Wen-ying, PENG Guang-ming, et al. A test of treatment of wastewater from pesticide glyphosate production[J]. Industrial Water & Wastewater, 2003, 34(1): 30-32.
[15] 刘红, 张林霞, 吴克明. 吸附-氧化法处理焦化废水的研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2003, 5(5): 35-37.
LIU Hong, ZHANG Lin-xia, WU Ke-ming. Study on the treatment of coke plant wastewater by adsorption catalytic oxidation process[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2003, 5(5): 35-37.
[16] 邹定平. 有机化合物结构分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 53.
ZOU Ding-ping. Structure analysis of organic compounds[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 53.
[17] Johnson T L. Knitics of halogenated organic compound degradation by iron metal[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1996, 30: 2634-2640.
[18] 李荻.电化学原理[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2008: 441-450.
LI Di. Electrochemical principle[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press, 2008: 441-450.
[19] 查全性. 电极过程动力学导论(第3版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002: 192-197.
ZHA Quan-xing. Introduction to electrode kinetics (third edition)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002: 192-197.
[20] 曲久辉, 刘会娟. 水处理电化学原理与技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 216-438.
QU Jiu-hui, LIU Hui-juan. Principle and Technology of electrochemical water treatment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 216-438.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2010-06-25;修回日期:2010-09-08
基金项目:国家自然科学基金重点资助项目(50830301);国家科技支撑计划重点项目(2007BAC25B01);教育部科学研究重大项目(308019);湖南省节能减排科技重大专项(2008SK2005)
通信作者:王云燕(1975-),女,山西闻喜人,博士,副教授,从事水处理及电化学研究;电话:0731-88830875;E-mail:wyy@csu.edu.cn