
Crystallinity and crystallization mechanism of lithium aluminosilicate glass by X-ray diffractometry
GUO Xing-zhong(郭兴忠), YANG hui(杨 辉), CAO Ming(曹 明),
HAN Chen(韩 陈), SONG Fang-fang(宋芳芳)
Center for Nano-Science and Nano-Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
Received 19 July 2005; accepted 5 December 2005
Abstract: The crystallinity of lithium aluminosilicate(LAS) glass after crystallization were studied at different temperatures by X-ray diffractometry and the crystallinity of the standard glass ceramic with known crystal and glass phases was examined. The crystallization mechanism of LAS glass was analyzed by the crystallinity, with a formula relating the crystallinity (X) and temperature (T). The results show that the calculated crystallinity of LAS glass by XRD increases with the crystallization temperature, in the range of 40%-50%, which is close to the calculated ones of standard samples with spodumene quartz ratio of 40%-70%. The activation energy of LAS glass is different within different temperature ranges; nEc is 125.44 kJ/mol at 710-810 ℃ and nEc is 17.42 kJ/mol at 810-980 ℃, which indicates different crystallization mechanisms. It has been proved that the required energy for crystallization of glass in the lower temperature range includes the interfacial energy between glass and crystalline phase and the free energy difference of atoms in structures of glass and crystal, and in the higher temperature ranges only the interfacial energy between glass and crystalline phase is considered.
Key words: glass ceramics; lithium aluminum silicates; crystallinity; crystallization mechanisms; activation energy
1 Introduction
Lithium aluminosilicate(LAS) glass-ceramics has been one of the most intensively studied systems because of its great creep resistance, very low thermal expansion characteristics and excellent thermal shock resistance [1-3]. It has been commercialized to produce stove windows, cookware, cooktop panels and some precision disc substrates[4, 5]. The properties of glass ceramic materials depend on crystalline microstructure and glass phase, thus stimulating many experimental and theoretical studies of the mechanisms of glass crystalliza- tion. The nucleation and crystallization mechanisms of LAS glass had mainly been studied by different measurement methods, such as differential thermal analysis (DTA) [6], differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) [7], transmission electron microscopy (TEM)[8], infrared rays(IR)[9], dilatometry[3], X-ray diffraction (XRD)[10] and viscosity[11,12], therefore different crystallization theories for different systems were established. Johnson-Mehl-Avrami(JMA) [13] equation is one of the main representative theories and becomes the basis of other theories.
In the present study, we attempted to utilize crys- tallinity to reveal the crystallization mechanism of lithium aluminosilicate(LAS) glass by using X-ray diffraction (XRD).
2 Crystallinity theory
Crystallinity of glass is defined as the ratio of crystal mass (volume) to whole glass mass (volume) in the system after crystallization, and it is also known as fraction crystallized. Crystallinity determines the defects, symmetry of microstructure and the properties of glass ceramics, and becomes important parameter to analyze the crystallization mechanism of glass. How to measure the crystallinity of glass has been a key to study crystallization mechanism of glass. We adopt XRD to calculate the crystallinity of LAS glass and study its crystallization mechanism.
XRD has been one of the most widely used methods for materials, especially metal and inorganic materials. The crystalline phases and their relative contents in materials can be quantitatively obtained by the diffraction peak location, diffraction peak number and relative intensity of XRD pattern. The following equation is used to calculate the crystallinity of glass:
 (1)
(1)
where Xc is the crystallized mass fraction (crystallinity), Xa is the non-crystallized mass fraction, Ia is the accumulative intensity of crystalline phase, Ic is the accumulative intensity of non-crystalline phase, and K is a constant related to the measurement condition and glass compositions.
The crystallization of LAS glass can be described by the phenomenological Avrami equation[12, 13] as
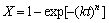 (2)
(2)
where X is the crystallinity after time t, n is the so-called Avrami coefficient, dimensionless parameter related to the reaction mechanism as listed in Table 1, and k is the reaction rate constant (s-1), whose temperature dependence is generally expressed by the Arrhenius equation[14]:
 (3)
(3)
where v is the frequency factor, s-1; Ec is the activation energy for crystallization, J/mol; R is the gas constant, 8.314 J/mol; and T is the absolute temperature, K.
Table 1 Values of parameter n for various crystallization mechanisms[16]

Rearrange Eqns.(2) and (3) and take natural logarithms:
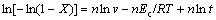 (4)
(4)
According to POULAIN[15], suppose that the temperature point at X in DTA is constant and the crystallization peak temperature (Tp) is related to the heating rate (α), the value n can be described as
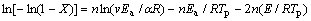 (5)
(5)
The value n and activation energy E can be calculated by Eqns.(1), (4) and (5) to study the crystallization mechanism of LAS glass.
3 Experimental
The composition (mass fraction, %) of the glass raw materials are: Li2O(3.5), Al2O3(19.8), SiO2(67.5), TiO2(4.2), Na2O(2.5), MgO(2.5) and K2O(0.5). TiO2 is introduced as nucleation agent, Na2O and K2O are used to reduce the melting temperature and viscosity of the glass and improve the glass workability. The glass raw materials were melted at 1 600-1 650 ℃ and moulded in a pre-heated die. The glass was annealed at 580 ℃ for 1 h and slowly cooled with the furnace to eliminate internal stress. The crystallization of the annealed glass samples was carried out at different temperatures for 2 h with the heating rate of 20 ℃/min. The samples were fast-cooled, ground, sieved through a 200-mech screen. The standard samples were melted by pure spodumene and pure quartz (chemical reagent) with the stoichiometric ratios of 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80% and 90%.
Phase identification of the samples was performed by X-ray diffraction(XRD) method on a D/max-RA X-ray diffractometer using nickel filtered Cu Ka radiation in the diffraction angle range of 10?-80? at a scanning rate of 2(?)/min, and the crystallinity was calculated by Eqn.(1).
4 Results and discussion
It is well-known that the crystallization temperature of LAS system is in the range of 800-1 100 ℃. We studied the XRD of standard samples and LAS glass ceramics crystallized at different temperatures, as shown in Figs.1 and 2. Note that the main crystalline phase of standard samples is β-spodumene. The LAS glass samples crystallized at and below 710 ℃ still belong to the glass with amorphous diffraction peak; in the samples at 710-810 ℃the hexagonal lithium aluminosilicate (LiAl(SiO3)2) forms, and its crystal structure is similar to β-quartz solid solution; with the increase of temperature (at 870-930 ℃), there is a transformation of hexagonal LiAl(SiO3)2 into tetragonal β-spodumene; at and above 930 ℃ the main crystallization phase basically belongs to tetragonal β-spodumene.
According to the XRD patterns, the crystallinity of LAS glass were calculated by Eqn.(1), where K is indirectly deduced from diffraction peaks intensities of two standard phases, K=0.963, as shown in Table 2, Fig.3 and Fig.4. Note that the calculated crystallinity of standard samples by XRD is close to theoretical crystallinity at ratio of spodumene to quartz of 40% and 50%, and much lower than the theoretical ones at the ratio larger than 50%, which was caused by the superposing of XRD diffraction peaks and unmeasurable peaks at lower diffraction angles. The relationship between calculated crystallinity (y) and theoretical ones (x) is y=27.2+0.34x, which benefits to evaluate the crystallinity of real crystallized glasses.
Table 2 Crystallinity of LAS glass heated at different temperatures and standard samples


Fig.1 XRD patterns of standard samples with different ratios of spodumene to quartz

Fig.2 XRD patterns of sample after crystallized at different temperatures
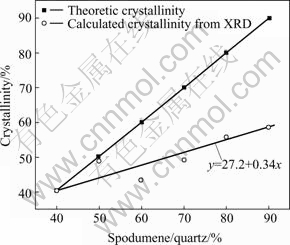
Fig.3 Crystallinity of standard samples

Fig.4 Crystallinity of LAS glass as function of heat-treatment temperatures
The calculated crystallinity of LAS glass increases with the crystallization temperature, and the increasing amplitude of crystallinity at 710-810 ℃ is more than that at 810-980 ℃, thus indicating different crystalli- zation of glass. The calculated crystallinity of LAS glass crystallized at 810-870 ℃ are 40%-50%, which is close to the calculated ones of standard samples with spodumene/quartz of 40%-70%, indicating that the real crystallization of LAS glass after crystallization are 40%-70%.
According to Eqn.(4) and Table 2, the plot of ln[-ln(1-X)] vs 1/T is constructed and shown in Fig.5, and the nEc/R can be estimated from the line slope. By the computer simulation, the slope of line L1 is -2.096, and nEc=17.424 kJ/mol; the slope of line L2 is -15.088, and nEc=125.44 kJ/mol. The line L1 represents the lower temperature range (710-810 ℃) and line L2 represents the higher temperature range (810-980 ℃). The activation energy of LAS glass is different in different temperature ranges, which indicates different crystalliza- tion mechanisms.
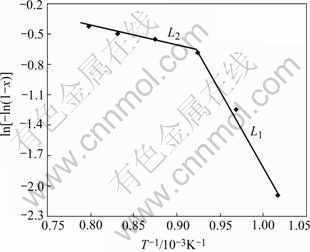
Fig.5 Plot of ln(-ln(1-X)) vs 1/T
According to McMILAN[17], the free energy ?G (whole free energy of crystallization) of atoms in crystal structure is lower than that in glass structure, if an atom wants to go through the interface between glass and crystal, it must overpass an energy barrier, i.e. the activation free energy (?G"), and the whole crystallization of glass (from nucleation to crystal growing) must overpass the energy (?G+?G"), i.e. the whole activation energy E should include interfacial energy between glass and crystalline phase(?G") and free energy difference between glass and crystal(?G). The activation energy of LAS glass from Kissinger equation by DTA is whole activation energy of crystallization during nonisothermal procedure, about 200-300 kJ/mol[16, 17], and is greater than that from crystallinity theory by XRD during isothermal procedure, which indicates new crystallization mechanism of LAS glass.
The crystallization procedure of LAS glass can be described by the change of crystallinity during temperature increasing. In the nucleation stage, enough nuclei form and become saturated for some time at some temperature, as shown in Fig.6. In the crystallization stage, the increase of crystallinity with temperature is not linear, which indicates different crystallization mechanism during temperature increasing. In the lower temperature range (710-810 ℃), the growth of minicrystal must overpass a larger energy barrier, and it includes the energy of atoms diffusing through the interphase of crystal and glass and the free energy difference between atoms in crystal structure and glass structure. The higher activation energy of crystallization in this range restricts the growth of minicrystal and results in a low crystallinity of glass. In higher temperature range (810-980 ℃), the growth of minicrystal only needs the energy of atoms diffusing through the interphase of crystal and glass (here equal to nEc of L2), and the lower activation energy leads to the rapid growth of crystal to obtain a high crystallinity. The activation energy E required for crystal growth is different in different temperature ranges, which shows the different crystallization mechanisms in the crystalli- zation with the increase of temperature. The result is consistent with the conclusions of some researchers[18], i.e. it is not definite that only E value is used to estimate crystallization mechanism of glass system in modifica- tion of JMA equation.

Fig.6 Nucleus number as function of time in nucleation stage at some temperature
5 Conclusions
The crystallinity theory was induced from Avrami and Arrhenius theories: ln[-ln(1-X)]=nlnν-nEc/RT+nlnt, and the crystallinity of crystallized LAS glass and standard glass ceramic were analyzed by XRD patterns. The calculated crystallinity of LAS glass increases with the crystallization temperature, the crystallinity of LAS glass crystallized at 810-870 ℃ is 40%-50%, which was near the calculated ones of standard samples with spodumene/quartz of 40%-70%. The activation energy of LAS glass is different within different temperature ranges; nEc is 125.44 kJ/mol in 710-810 ℃ and nEc is 17.42 kJ/mol in 810-980 ℃, which indicates different crystallization mechanism. The required energy for crystallization of LAS glass is different in different temperature ranges: in the lower temperature range it includes the interfacial energy between glass and crystalline phase and the free energy difference of atoms in structures of glass and crystal, and in the higher temperature range only the interfacial energy between glass and crystalline phase is considered.
References
[1] JAMES P F. Glass ceramic: new compositions and uses [J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 1995, 181: 1-15.
[2] RIELLO P, CANTON P. Nucleation and crystallization behavior of glass-ceramic materials in the Li2O-Al2O3-SiO2 systemt of interest for their transparency properties [J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 2001, 288: 127-139.
[3] KARMAKAR B, KUNDU P. Crystallization kinetics and mechanism of low-expansion lithium aluminosilicate glass-ceramics by dilatometry [J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 2002, 85(10): 2572-2574.
[4] GUO X Z, YANG H, CAO M. Nucleation and crystallization behavior of Li2O-Al2O3-SiO2 system glass-ceramic containing little fluorine and no-fluorine [J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 2005, 351: 2133-2137.
[5] CHENG K G. Determining crystallization kinetic parameters of L2O-Al2O3-SiO2 glass from derivative differential thermal analysis curves [J]. Mater Sci and Eng B, 1999, 60B: 194-199.
[6] WEINBERG M C. Interpretation of DTA experiments used for crystal nucleation rate determination [J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 1991, 74(8): 1905-1909.
[7] REYNOSO V C S, YUKIMITU K, NAGAMI T. Crystallization kinetics in phosphate sodium-based glass studied by DSC technique [J]. J Phys and Chem, 2003, 64: 27-30.
[8] GEBHARDT A, HO?CHE T, CARL1 G. TEM study on the origin of cabbage-shaped mica crystal aggregates in machinable glass-ceramics [J]. Acta Mater, 1999, 47(17): 4427-4434.
[9] NOCUN M, HANDKE M. Structural inhomogeneity in glasses from the system Li2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 revealed by IR spectroscopy [J]. J Mole Struct, 2001, 596: 139-143.
[10] DEMIRKESEN E, MAYTALMAN E. Effect of Al2O3 additions on the crystallization behaviour and bending strength of a Li2O-ZnO-SiO2 glass-ceramic [J]. Ceram International, 2001, 27: 99-104.
[11] SHNEIDMAN V A, UHLMANN D R. Crystallization kinetics in a glass-forming melt with retarded viscosity [J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 1998, 223: 48-52.
[12] KIM K D, LEE S H. Observation of nucleation effect on crystallization in lithium aluminosilicate glass by viscosity measurement [J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 2004, 336: 195-201.
[13] KISSINGER H E. The crystallization kinetics with heating rate in differential thermal analysis [J]. J Res Natl Bur Stand, 1956, 57: 217-221.
[14] SENOL Y, OSMAN T. ?ZKAN. Crystallization kinetics of basalt glass [J]. Ceram International, 1996, 22: 477-481.
[15] POULAIN M. Overview of crystallization in fluoride glasses [J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 1992, 140: 1-9.
[16] PEREZ-MAQUEDA L A, CRIADO J M, MALEK J. Combined kinetic analysis for crystallization kinetics of non- crystalline solids [J]. J Non-Cryst Solids, 2003, 320: 84-91.
[17] MCMILAN P W. Glass Ceramics [M]. Academic Press, 1979.
[18] HU L, JIANG Z H. A new criterion for crystallization of glass [J]. J Chin Ceram Soc, 1990, 18(4): 315-321.
Foundation item: Project(2003C11030) supported by the High Science & Technique Brainstorm of Zhejiang Province, China
Corresponding author: GUO Xing-zhong; Tel/Fax: +86-571-87953313; E-mail: gxzh_zju@163.com
(Edited by LONG Huai-zhong)