文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-11-2403-09
空间结构对硫化矿物表面能带结构和电子性质的影响
陈 晔1, 2,陈建华1, 2,李玉琼1, 2,赵翠华3
(1. 广西大学 资源与冶金学院,南宁 530004;
2. 广西大学 广西高校矿物工程重点实验室,南宁 530004;
3. 广西大学 材料科学与工程学院,南宁 530004)
摘 要:采用密度泛函理论,计算方铅矿、黄铁矿和闪锌矿的体相及表面电子性质,研究表面空间结构对这3种典型硫化矿物能带结构和电子性质的影响。结果表明:表面结构弛豫导致方铅矿(100)表面带隙变大,表面电子比体相更加活跃;而黄铁矿(100)表面带隙变窄,表面显示出一定的金属性。对3种硫化矿表面原子Mulliken电荷的分析表明,闪锌矿(110)表面和方铅矿(100)表面的电子从体相向表面层转移;而黄铁矿(100)表面的电子则从表面向体相转移。对黄铁矿体相和(100)、(210)和(110)表面具有不同配位数的铁原子的态密度分析表明,铁原子配位数的减少,导致Fe 3d电子能级升高,表面态能级变大。
关键词:硫化矿;空间结构;密度泛函理论;电子性质;能带结构
中图分类号:TD923.13 文献标志码:A
矿物表面由于键的断裂,表面原子受力处于不平衡状态,表层原子之间的距离需要重新调整,以达到新的平衡,这种现象称为表面弛豫。由于表面原子配位数的变化,以及原子间距离的调整,电子分布也会出现相应调整;另外,由于表面原子不再处于周期性势场的作用,其电子能级也会发生变化,表面电子会产生不同于体相电子的性质。如晶体存在自由表面时在能隙中产生的电子Tamm表面态[1]和共价晶体表面的悬挂键在能隙中产生的Schockley表面态[2]。
硫化矿物的浮选是一个电化学过程,研究表明窄禁带硫化矿物具有显著的表面邻近效应(Surface proximity effect)[3],矿物表面结构影响表面反应原子的电子性质,从而影响硫化矿物的浮选电化学行为;另外,矿物表面原子是浮选药剂分子发生吸附作用的地方,矿物表面结构和浮选药剂分子需要在结构和性质上相互匹配,浮选药剂才能在矿物表面上发生有效作用[4-5]。因此,研究矿物表面空间结构对硫化矿物的能带结构和电子性质的影响具有重要的理论意义和实践价值。
目前,很多学者采用X射线光电子能谱(XPS)[6-13]、扫描隧道电镜(STM)[14-17]、紫外光电子能谱(UPS)[18-20]、低能电子衍射(LEED)[21-23]和程序升温脱附法(TPD)[24-25]等测试方法研究方铅矿、黄铁矿和闪锌矿的表面性质。另外,也有研究者采用Hartree-Fock[26-29]及密度泛函理论[30-38]对这3种硫化矿物的簇模型或周期性模型进行研究计算。虽然对硫化矿物表面性质的实验研究和模拟研究已经有很多,但是从表面空间结构方面来讨论硫化矿物表面电子性质的研究还未见到报道。
本文作者采用密度泛函理论,构建了方铅矿、黄铁矿和闪锌矿的体相与表面模型,研究了这3种典型硫化矿物表面空间结构对能带结构和电子性质的影响,讨论了表面原子配位与化学活性的关系。研究结果对硫化矿物浮选电化学机理研究和药剂分子设计具有参考价值。
1 计算方法与模型
本研究的计算采用基于密度泛函理论的Materials Studio 计算软件中的CASTEP模块完成[39]。方铅矿和黄铁矿计算中交换关联函数采用GGA-PW91,闪锌矿的计算采用GGA-PBE [40-41],采用超软赝势(Ultrosoft)描述离子实和价电子的相互作用[42]。各原子的赝势计算选取的价电子分别为Pb 5d106s26p2,Fe 3d64s2,Zn 3d104s2和S 3s23p4,在优化含铁原子体系的几何构型中考虑了自旋极化。根据平面波截断能的测试结果,方铅矿、黄铁矿和闪锌矿表面计算所采用的截断能分别为270 eV,280 eV 和310 eV, Brillouin区的积分计算采用Monkhorst-Pack方案[43]来选择k网格点分别为1×2×1,2×2×1和2×3×1,以保证体系能量和构型在准完备平面波基水平上的收敛。在自洽场运算中,采用了Pulay密度混合法,自洽场收敛精度设为2.0×10-6 eV/atom。在对模型的结构优化中采用BFGS算法,优化参数包括原子间相互作用力的收敛标准设为0.05 eV/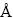 ,晶体内应力的收敛标准设为0.1 GPa,原子最大位移收敛标准设为2×10-3
,晶体内应力的收敛标准设为0.1 GPa,原子最大位移收敛标准设为2×10-3 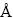 。对这3个参数同时进行优化,结构优化完成的标志是这些参数均达到收敛标准,计算结果令人满意。
。对这3个参数同时进行优化,结构优化完成的标志是这些参数均达到收敛标准,计算结果令人满意。
选取了方铅矿(100)面,黄铁矿(100)面和闪锌矿(110)面作为研究对象,这3种表面均为稳定解理面[44]。经原子层数和真空层厚度测试后,对于方铅矿(100)面采取 8 层原子层,黄铁矿(100)面采取15层原子层,闪锌矿(110)面采取10层原子层,真空层厚度均为 15 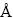 。3种硫化矿物表面模型如图1所示。
。3种硫化矿物表面模型如图1所示。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 表面能带结构
由于矿物表面从三维周期性结构变成二维结构,表面相邻两个原子的波函数会发生交叠,从而导致表面态波函数之间存在相互作用,使表面能级展宽为表面能带。不同的矿物表面结构会影响原子间的波函数作用,从而形成不同于体相的能带结构。下面以具有层状结构的方铅矿和具有立体空间结构的黄铁矿为代表来讨论空间结构对表面能带结构的影响。
方铅矿体相和(100)表面能带结构如图2所示。由图2可见,方铅矿表面能带比体相更密,这是由于采用的表面模型原子数比体相多的缘故。比较方铅矿体相和表面的能带结构,方铅矿表面的禁带宽度从体相0.5 eV增大到0.7 eV,说明方铅矿表面电子结构发生了显著变化,电子从价带跃迁到导带需要更大的能量。另外方铅矿表面能带结构也发生了明显变化:1) 方铅矿表面导带的能带分离成两组,而体相则相互交叉成一组能带,说明表面的出现导致导带能级发生分裂,靠近费米能级的这一组能带更容易获得电子;2) 方铅矿表面价带顶明显比体相方铅矿更靠近费米能级,按照分子轨道理论,价带顶附近是电子最容易给出电子的能级,因此方铅矿表面的电子比体相更容易失去电子。
图3所示为黄铁矿体相和(100)表面能带结构。对于黄铁矿表面,其能带结构和体相有明显的区别,首先黄铁矿表面禁带宽度变窄,只有0.45 eV,而体相禁带为0.62 eV,这一现象和方铅矿表面是相反的,方铅矿表面的禁带宽度比体相的大,说明黄铁矿和方铅矿在半导体性质上具有明显的不同。其次,黄铁矿表面价带下移,说明黄铁矿得电子能力增强,导带底处的能带线比体相平缓,说明黄铁矿表面导带底电子有效质量增大,电子的局域性变强。
由以上讨论可知,方铅矿体相到表面是一个禁带宽度变大的过程,而黄铁矿体相到表面是一个禁带宽度变小的过程。图4所示为方铅矿和黄铁矿两种矿物在表面能带的变化模型。
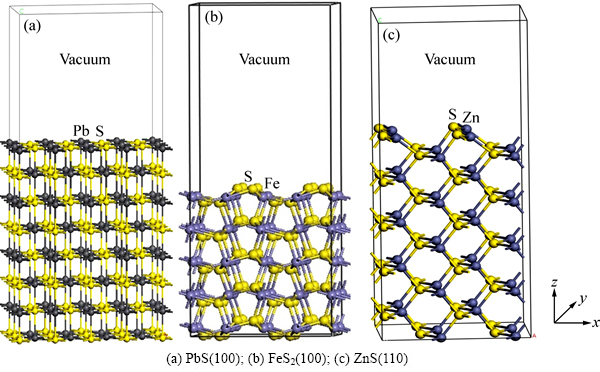
图1 硫化矿物表面层晶模型
Fig. 1 Slab models of sulfide mineral surface
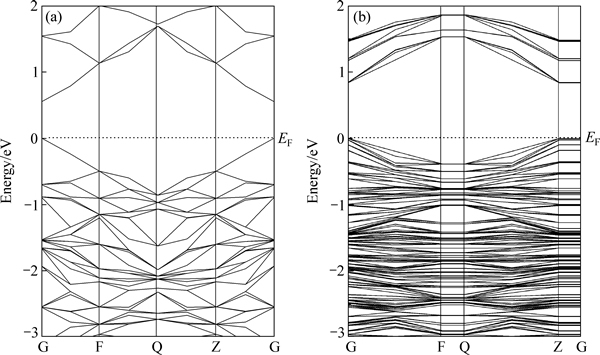
图2 方铅矿体相和(100)表面能带结构
Fig. 2 Band structure of bulk galena (a) and (100) surface (b)
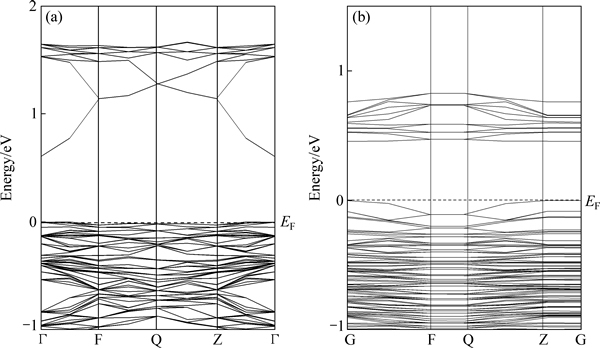
图3 黄铁矿体相和(100)表面能带结构
Fig. 3 Band structure of bulk pyrite (a) and (100) surface (b)
禁带宽度是半导体的一个重要特征参量,其大小与晶体结构和原子的结合性质等有关。禁带宽度的大小实际上是反映了价电子被束缚强弱程度的一个物理量,也就是产生本征激发所需要的最小能量。根据前面对方铅矿和黄铁矿表面结构的弛豫研究[45-46]发现,方铅矿表面具有较大的弛豫,而黄铁矿表面则弛豫很小。因此,可以推测黄铁矿和方铅矿两种硫化矿物表面禁带宽度的变化是由不同的原因造成的。黄铁矿表面禁带宽度的减小不是由表面弛豫造成的,而是由于表面原子配位数减小,对价电子束缚能力减弱,从而减小了价电子跃迁到导带的能量。而方铅矿表面原子的配位数虽然和体相相比也是减小的,但是由于铅原子的原子序数较大,对价电子束缚作用较强,从而弱化了配位数变化的影响,方铅矿表面结构较大弛豫对价电子的束缚产生了显著的影响,导致电子跃迁能量增大。
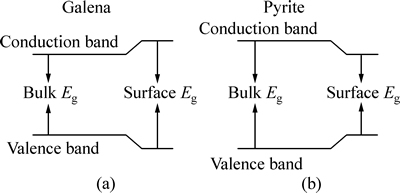
图4 方铅矿和黄铁矿表面能带模型
Fig. 4 Surface band structure model for galena (100) (a) and pyrite (100) (b)
从表面禁带宽度变化方面来看,由于方铅矿表面对价电子的束缚程度要比黄铁矿表面的强,因此,可以认为方铅矿表面的电子活性要比黄铁矿表面弱。研究结果证实:巯基类捕收剂在方铅矿表面都是形成金属盐,没有电化学吸附的捕收剂产物,而黄药、黑药和乙硫氮等捕收剂在黄铁矿表面都可以发生电化学吸附,并形成捕收剂二聚物。
2.2 表面Mulliken电荷分布
表面结构在重新平衡的过程中,不仅几何结构会发生重构,表面原子上的电荷也会发生重新分布。表1~3所列为闪锌矿(110)面、黄铁矿(100)面和方铅矿(100)面表面原子电荷分布情况。
闪锌矿(110)表面原子结构和编号如图5所示。从表1可见,在闪锌矿表面几何重构过程中,外表面层的原子电荷发生重新分布,锌原子电荷分布变化较大,硫原子变化较小。闪锌矿晶体结构中1个锌原子和4个硫原子配位,1个硫原子和4个锌原子配位,锌和硫原子为四配位结构。由于表面原子键的断裂,外表面层原子有两种结构:即三配位的Zn1和S1、四配位的Zn2和S2、不同配位数的原子和不同位置的原子的电子转移和分布不同。
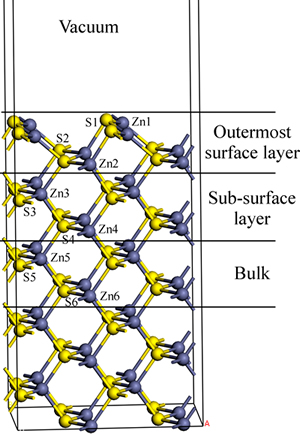
图5 闪锌矿(110)表面结构及原子位置示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of sphalerite (110) surface structure
硫原子价电子构型为3s23p4,锌原子价电子构型为3d104s24p0,闪锌矿体相层硫原子3s轨道失去电子,3p轨道得到电子,锌原子4s和4p轨道发生杂化作用,同时表现为失去电子,3d轨道由于处于较深能级,同时为填满的稳定结构,基本不参与作用,因此,体相层硫原子和锌原子电子转移主要发生s轨道和p轨道。对于次表面层的原子,虽然和体相一样,都是四配位结构,但是由于连接到外表面层,在z方向有不对称结构。不同位置硫原子电荷变化不大,但不同位置的锌原子却有较大的差异,Zn3和Zn4原子的3d和4p轨道电子没有发生变化,3s轨道却有较大差异。相比体相层锌原子,次表面层Zn4原子4s失去电子,Zn3原子4s却得到电子,表现出空间结构对锌原子得电子能力的影响(锌4s轨道为活跃的外层轨道)。最外层结构的锌原子和硫原子,高位的Zn1、S1由于键的断裂,只有三配位,低位的Zn2、S2仍然是四配位,很明显高位硫原子和锌原子由于配位数的减少会引起电子分布的较大改变。高位硫原子(S1)3s轨道获得了较多的电子,S1原子的电荷也比体相层要负;低位硫原子(S2)由于配位数没有发生变化,只是空间结构的对称性发生变化,因此在电荷上只有较小变化,基本接近体相电荷。对于锌原子,高位锌原子和低位锌原子的电荷都发生了较大变化,和体相锌原子相比,锌原子的4s轨道电子数都增加,4p轨道则不同,只有高位锌原子(Zn1)4p轨道失去电子,低位锌原子(Zn2)没有生变化,说明高位三配位的锌原子电子分布受影响最大。
表1 闪锌矿(110)表面弛豫后原子的Mulliken电荷分布
Table 1 Mulliken charge of sphalerite (110) surface after relaxation
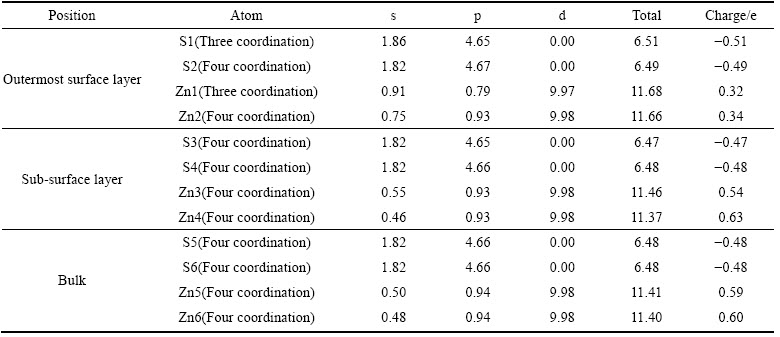
从以上分析可以看出,闪锌矿外表面层原子都比体相层获得了较多的电子,说明闪锌矿表面发生了电子富集,其中三配位锌原子4s轨道电子数明显增加,降低了三配位锌原子的亲电性,不利于巯基类浮选捕收剂分子的作用。
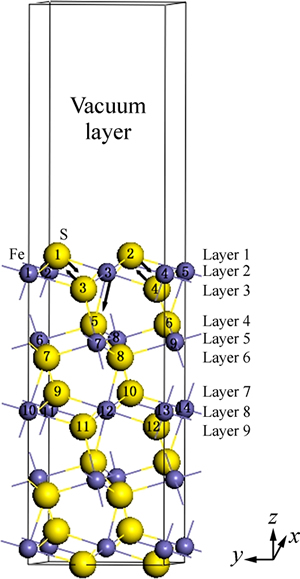
图6 黄铁矿表面不同层原子编号
Fig. 6 Schematic plots of Mulliken charge of pyrite (100) surface
表2 黄铁矿表面弛豫后原子的Mulliken电荷分布
Table 2 Mulliken charge of pyrite (100) surface after relaxation
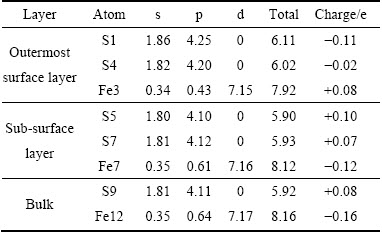
黄铁矿(100)表面原子位置如图6所示。由表2可见,从体相到表面层,黄铁矿硫原子和铁原子电荷有一个非常明显的变化,那就是硫原子从体相的正电荷变到表面的负电荷,铁原子从体相负电荷变到表面的正电荷。从体相层到外表面层,硫原子的3s和3p轨道电子数增加,其中3p轨道上的电子显著增加,说明表面层硫原子在电荷重新平衡过程中获得了铁原子的电子。对于铁原子,从体相层到外表面层,铁的4s和3d轨道上电子数基本不变,4p轨道上电子数则明显减少,从体相0.64减少到0.43,说明表面层铁原子的4p轨道失去了电子,这与外表面硫原子3p轨道得电子相对应,说明在表面原子重构和电荷重新平衡过程中,电荷从铁原子上转移到了硫原子上,并且铁硫原子和原子的电子转移发生在能量相近的p轨道,这一现象可能与黄铁矿表面弛豫较小有关。XPS[30]测试结果也表明,黄铁矿表面电荷由铁原子向硫原子迁移。
一般来说,金属的费米能级高于半导体矿物,对黄铁矿表面态密度的研究结果[46]表明黄铁矿(100)表面具有一些似金属特征而体相为半导体,因此,电子有从表面流向体相的趋势,即黄铁矿表面具有吸电子能力,对其表面原子电荷的分析证实了这一结果。如图7所示,每6个原子层的硫和铁原子数都一样,因此,6个原子层代表1个周期,其中从表面开始第一个六原子层为表面层,第二个六原子层可以看作体相层,图7中的数字为这两种原子层原子的总电荷。结果表明,表面层所带的电荷为-0.33 e,体相层所带电荷为-0.97 e,这说明体相层处于电子富集状态而表面层处于电子缺失状态,因此,黄铁矿(100)表面层具有吸收电子的能力。在浮选实践中,由于黄铁矿表面具有吸电子性,黄药上的电子容易向黄铁矿表面转移,从而发生氧化反应,形成双黄药。
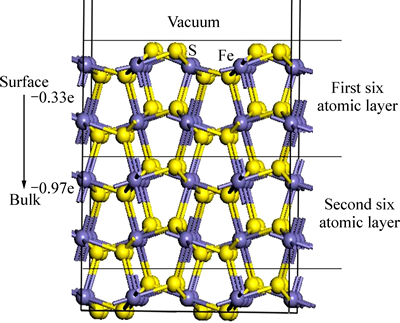
图7 黄铁矿(100)表面层电荷变化示意图
Fig. 7 Schematic plots of Mulliken charge of pyrite (100) surface
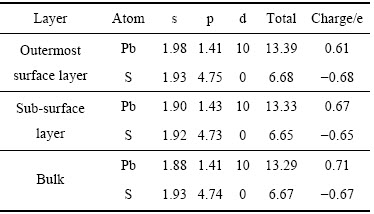
方铅矿表面具有层状结构,每一层的铅原子和硫原子的位置都具有相同z坐标,表面结构相对简单。表面弛豫后的方铅矿表面3层的Mulliken电荷如表3所列。由表3可见,硫原子电荷从体相层到外表面层从-0.67 e变到-0.68 e,变化不大,但是铅原子电荷却有显著的变化,从体相层的0.71 e减少到次表面层的0.67 e,再减少到外表面层0.61 e,方铅矿表面铅原子电荷有从体相到表面递减的趋势。从电子的轨道分布来看,铅原子价电子层为 5d106s26p2,硫原子价电子层为3s23p4,方铅矿晶体中主要是硫3p轨道和铅6p轨道发生作用,铅6p轨道上的电子转移到硫3p轨道上。在方铅矿表面结构弛豫过程中,硫3p轨道和铅6p轨道上的电子基本没有发生变化,说明方铅矿表面结构弛豫基本上不改变硫3p轨道和铅6p轨道的作用,但是外表面层铅原子6s轨道上的电子却明显增多,从体相层的6s1.88变成外表面层的6s1.98。从方铅矿表面电子分布和电荷变化来看,方铅矿外表面总电子数比体相层要大,净电荷的变化则是从体相层0.04 e变化到外表面层的-0.07 e,说明方铅矿表面具有富集电子的性质。方铅矿表面这一性质不利于黄药分子氧化形成双黄药,研究结果表明,方铅矿表面目前只检测到黄原酸铅,没有发现双黄药。
表3 方铅矿(100)表面弛豫后原子的Mulliken电荷分布
Table 3 Mulliken charge of galena (100) surface after relaxation
2.3 表面电子态密度
从理论上讲,原子配位数越少,对价电子束缚越小,电子的局域性减弱,离域性增强,原子反应活性越强。 由于表面结构的不对称性,随着表面结构的弛豫,表面电子也会发生重新分布,形成表面电子态。TAMM[1]早在1932年就提出电子在晶体表面会产生出现在能隙中表面态能级,对于具有d电子的表面来说(大部分硫化矿物都具有d电子),表面最外层原子的配位数要比体相内原子的配位数少,从而导致d电子的势能上升,使原本比较局域的d态产生了高出3d体能带的d电子表面能级,即表面Tamm态。
图8所示为黄铁矿体相和表面具有不同配位数的铁原子电子态密度,其中自由铁原子可以看作配位数为0的特殊情况。由图8可见,对于配位数为0的自由铁原子,其费米能级处的电子态密度主要有由3d和4s构成,当铁原子配位数从3增加到6的时候,费米能级附近p轨道和s轨道电子态消失,只剩下3d态。说明由于硫原子的配位作用,增强了对铁原子电子的束缚程度。另外就铁原子3d电子态的变化情况而言,不同结构下的铁原子3d态具有很大的不同,其中(110)面三配位铁原子的3d电子态离域性最强,轨道没有发生分裂,而其它配位数的铁原子,不管是(210)表面的四配位铁,还是(100)表面的五配位铁和(110)表面的六配位铁,其3d轨道都明显分裂为3部分,其中费米能级处为t2g非键轨道,其他两部分是eg成键轨道和eg*反键轨道。从铁原子表面电子态来看,表面铁原子的电子态密度随着配位数的减少,其3d态越来越向正能级方向移动,即配位数的减少,导致3d电子能级升高,形成表面态能级。
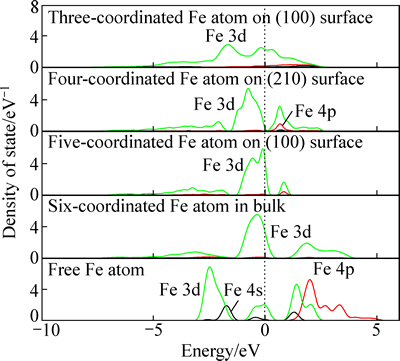
图8 黄铁矿不同配位数的铁原子的电子态密度
Fig. 8 DOS of pyrite Fe atom with different coordination number
3 结论
1) 表面结构弛豫会导致矿物表面能带结构发生变化,方铅矿(100)表面禁带宽度变大;而黄铁矿(100)表面禁带宽度则变窄,表面具有一定的金属性,不利于表面硫原子的氧化,具有较差的无捕收剂浮选行为。
2) 表面化学键的断裂对表面原子电荷分布产生影响。闪锌矿(110)表面发生了电子富集,其中三配位锌原子4s轨道电子数明显增加,降低了三配位锌原子的亲电性,不利于黄药类捕收剂的作用。黄铁矿(100)表面具有吸电子能力,电子从表面向体相转移,同时,黄铁矿表面部分电荷从铁原子转移到硫原子上,有利于黄药氧化为双黄药反应的进行。对于方铅矿,其(100)表面总电荷比体相多,表面电子富集,不利于黄药的电化学氧化作用,在方铅矿表面倾向于捕收剂分子发生化学吸附作用。
3) 表面原子配位数的改变会导致矿物表面电子态的形成。黄铁矿体相和(100)、(210)和(110)表面铁原子的态密度结果表明,随着铁原子配位数减少,导致Fe 3d电子能级升高,表面态能级变大,黄铁矿表面低配位的铁原子是浮选过程中发生作用的表面吸附活性位。
REFERENCES
[1] Tamm I E. On the possible bound states of electrons on a crystal surface[J]. Physcs Z Soviet, 1932, 1: 733-746.
[2] Shockley W. On the surface states associated with a periodic potential[J]. Physical Review, 1939, 56: 317-323.
[3] Becker U, Rosso k M, Hochella M F J R. The proximity effect on semiconducting mineral surfaces: A new aspect of mineral surface reactivity and surface complexation theory[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(16): 2641-2649.
[4] RAI B. Molecular modeling and rational design of flotation reagents[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2003, 72(1/4): 95-110.
[5] 马 鑫, 钟 宏, 王 帅, 胡 元. 硫化矿捕收剂的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2012, 41(10): 1791-1795.
MA Xin, ZHONG Hong, WANG Shuai, HU Yuan. Research on the sulfide ore collectors[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2012, 41(10): 1791-1795.
[6] Heide H V, Hemmel R, Bruggen C F V, Haas C. X-ray photoelectron spectra of 3d transition metal pyrites[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1980, 33(1): 17-25.
[7] Chernyshova I V, Andreev S I. Spectroscopic study of galena surface oxidation in aqueous solutions I. Identification of surface species by XPS and ATR/FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1997, 108: 235-236.
[8] Leiro J A, Mattila S S, Laajalehto K. XPS study of the sulphur 2p spectra of pyrite [J]. Surface Science, 2003, 547: 157-161.
[9] Cai Yuan-feng, Pan Yu-guan, Xue Ji-yue, Sun Qing-feng, Su Gui-zhen, Li Xiang. Comparative XPS study between experimentally and naturally weathered pyrites[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255: 8750-8760.
[10] Laajalehto K, Kartio I, Suoninen E. XPS and SR-XPS techniques applied to sulphide mineral surfaces[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1997, 51:163-170.
[11] Mycroft J R, Bancroft G M, McIntyre N S, Lorimer J W, Hill I R. Detection of sulphur and polysulphides on electrochemically oxidized pyrite surfaces by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry Electrochem, 1990, 292: 139-152.
[12] Nowak P, Laajalehto K. Oxidation of galena surface-An XPS study of the formation of sulfoxy species[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2000, 157: 101-111.
[13] Harmer S L, Goncharova L V, Kolarova R, Lennard W N,  M A, MITCHELL I V, Nesbitt H W. Surface structure of sphalerite studied by medium energy ion scattering and XPS[J]. Surface Science, 2007, 601: 352-361.
M A, MITCHELL I V, Nesbitt H W. Surface structure of sphalerite studied by medium energy ion scattering and XPS[J]. Surface Science, 2007, 601: 352-361.
[14] Becker U, Michael F, Hckhella J R. The calculation of STM images, STS spectra, and XPS peak shifts for galena: New tools for understanding mineral surface chemistry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60: 2413-2426.
[15] Laajalehto K, Smart R St C, Ralston J, Suoninen E. STM and XPS investigation of reaction of galena in air[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1993, 64: 29-39.
[16] Eggleston C M, Hochella M F. Scanning tunneling microscopy of pyrite {100} surface structure and step reconstruction[J]. American Mineralogist, 1992, 77: 221-224.
[17] Mikhlin Y L, Romanchenko A S. Gold deposition on pyrite and the common sulfide minerals: An STM/STS and SR-XPS study of surface reactions and Au nanoparticles[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(24): 5985-6001.
[18] Sugaa S, Tabiguchia M, Shina S, Sekia M, Shibuya S, Sato K, Yamaguchi T. Reflectance and UPS studies of band structures and final state interactions of low-spin pyrites[J]. Physica B+C, 1983, 117/118: 353-355.
[19] Ballester A, Blázquez M L, González F, Román E, Bustillo F J. Studies of zinc sulphide, treated with different solutions of catalyst ions[J]. Vacuum, 39(7/8): 663-664.
[20] Muscata J, Klauber C A. Combined ab initio and photoelectron study of galena (PbS)[J]. Surface Science, 2001, 491: 226-238.
[21] Chaturvedi S, Katz R, Guevremont J, Schoonen M A A, Strongin D R. XPS and LEED study of a single-crystal surface of pyrite[J]. American Mineralogist, 1996, 81: 261-264.
[22] Rosso K M, Becker U, Hochella J R M F. Atomically resolved electronic structure of pyrite {100} surfaces: An experimental and theoretical investigation with implications for reactivity[J]. American Mineralogist, 1999, 84: 1535-1548.
[23] Duke C B, Wang Y R. Surface structure and bonding of the cleavage faces of tetrahedrally coordinated II–VI compounds[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science Technology B, 1988, 6: 1440-1443.
[24] Guevremont J M, Strongin D R, Schoonen M A A. Effects of surface imperfections on the binding of CH3OH and H2O on FeS2(100): Using adsorbed Xe as a probe of mineral surface structure[J]. Surface Science, 1997, 391: 109-124.
[25] Guevremont J M, Strongin DR, Schoonen M A A. Thermal chemistry of H2S and H2O on the (100) plane of pyrite: Unique reactivity of defect sites[J]. American Mineralogist, 1998, 83: 1246-1255.
[26] Becker U, Greatbanks S P, Rosso K M, Hillier I H, Vaughan D J. An embedding approach for the calculation of stm images: Method development and application to galena (PbS)[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1997, 107: 7537-7542.
[27] Mian M, Harrison N M, Saunders V R, Flavell W R. An ab initio Hartree-Fock investigation of galena (PbS)[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1996, 257: 627-632.
[28] Wilson N, Muscat J. The calculation of structural, elastic and phase stability properties of minerals using first principles techniques: A comparison of HF, DFT and hybrid functional treatments of exchange and correlation[J]. Molecular Simulation, 2002, 28: 903-915.
[29] Steele H M, Wright K, Hillier I H. A quantum-mechanical study of the (110) surface of sphalerite (ZnS) and its interaction with Pb2+ species[J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 2003, 30(2): 69-75.
[30] von Oertzen G U, Skinner W M, Nesbitt H W. Ab Initio and XPS studies of pyrite (100) surface states[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2006, 75(11): 1855-1860.
[31] CHEN Jian-hua, Lan Li-hong, CHEN Ye. Computational simulation of adsorption and thermodynamic study of xanthate, dithiophosphate and dithiocarbamate on galena and pyrite surfaces[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2013, 46/47: 136-143.
[32] Stirling A, Bernasconi M, Parrinello M. Defective pyrite (100) surface: An ab initio study[J]. Physical Review B, 2007, 75: 165406 1-8.
[33] CHEN Jian-hua, CHEN Ye, LI Yu-qiong. Effect of vacancy defects on electronic properties and activation of sphalerite (110) surface by first-principles[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(3): 502-506.
[34] Hung A, Muscat J, Yarovsky I, Russo S P. Density-functional theory studies of pyrite FeS2 (100) and (110) surfaces[J]. Surface Science, 2002, 513: 511-524.
[35] CHEN Jian-hua, WANG Lei, CHEN Ye, GUO Jin. A DFT study of the effect of natural impurities on the electronic structure of galena[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2011, 98: 132-136.
[36] Muscat J, Gale J D. First principles studies of the surface of galena PbS[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67: 799-805.
[37] Hung A, Muscat J, Yarovsky I, Russo S P. Density-functional theory studies of pyrite FeS2 (111) and (210) surfaces[J]. Surface Science, 2002, 520: 111-119.
[38] 陈建华, 曾小钦, 陈 晔, 张辉鹏. 含空位和杂质缺陷的闪锌矿电子结构的第一性原理计算[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(4): 765-771.
CHEN Jian-hua, ZENG Xiao-qin, CHEN Ye, ZHANG Hui-peng. First-principle theory calculations of electronic structure of sphalerite with vacancy and impurity[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(4): 765-771.
[39] Payne M C, Teter M P, Allan D C, Arias T A, Joannopoulos J D. Iterative minimization techniques for ab initio total energy calculation: Molecular dynamics and conjugate gradients[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1992, 64: 1045-1097.
[40] PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNEZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple[J]. Physical Review Letter, 1996, 77: 3865-3868.
[41] Perdew J P, Wang Y. Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy[J]. Physical Review B, 1992, 45: 13244-13249.
[42] Vanderbilt D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism[J]. Physical Review B, 1990, 41: 7892-7895.
[43] Monkhorst H J, PACK J D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations[J]. Physical Review B, 1976, 13: 5188-5192.
[44] Vaughan D J, Becker U, Wright K. Sulphide mineral surfaces: Theory and experiment[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1997, 51(1/4): 1-14.
[45] 李玉琼, 陈建华, 蓝丽红, 郭 进. 氧分子在黄铁矿和方铅矿表面的吸附[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(4): 1184-1194.
LI Yu-qiong, CHEN Jian-hua, LAN Li-hong, GUO Jin. Adsorption of O2 on pyrite and galena surfaces[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(4): 1184-1194.
[46] 李玉琼, 陈建华, 陈 晔, 郭 进. 黄铁矿(100)表面性质的密度泛函理论计算及其对浮选的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(4): 919-926.
LI Yu-qiong, CHEN Jian-hua, CHEN Ye, GUO Jin. Density functional theory calculation of surface properties of pyrite (100) with implications for flotation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(4): 919-926.
Effect of spatial structure on band structure and electronic properties of sulphide minerals
CHEN Ye1, 2, CHEN Jian-hua1, 2, LI Yu-qiong1, 2, ZHAO Cui-hua3
(1. College of Resources and Metallurgy, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China;
2. Guangxi Colleges and Universities Key Laboratory of Minerals Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China)
Abstract: The bulk and surface electronic properties of galena, pyrite and sphalerite were calculated by adopting density functional theory, and the effects of spatial structure on the band structure and electronic properties of these three typical sulphide minerals were studied. The results show that surface relaxation leads a greater band gap of PbS (100) surface compared with the bulk PbS, and the surface electrons are more reactive than the bulk electrons, while for the FeS2 (100) surface, the band gap decreases and shows a metallic characteristics. The analysis of surface Mulliken charge of these three sulphide minerals suggests that, for the PbS (100) and ZnS (110), the electrons transfer from the bulk to the surface, however, the electrons of FeS2 (100) transfer from the surface to the bulk. The DOS of bulk pyrite and surface pyrite Fe atom with different coordination number indicate that the decrease of coordination number leads to the increase of Fe 3d energy level and Tamm surface energy level.
Key words: sulfide mineral; spatial structure; density functional theory; electronic property; band structure
Foundation item: Projects(51574092, 51364002, 51304054) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2014GXNSFAA118316) supported by Gangxi Natural Science Foundation, China
Received date: 2015-10-19; Accepted date: 2016-03-18
Corresponding author: CHEN Jian-hua; Tel: +86-771-3232200; E-mail: jhchen@gxu.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51574092,51364002,51304054);广西自然科学基金资助项目(2014GXNSFAA118316)
收稿日期:2015-10-19;修订日期:2016-03-18
通信作者:陈建华,教授,博士;电话:0771-3232200;E-mail:jhchen@gxu.edu.cn