DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.06.12
人造海水温度对Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P合金镀层电化学行为的影响
方信贤1, 2,杜小娟1,高生辉1,张帅1
(1. 南京工程学院 材料工程学院,南京 211167;
2. 南京工程学院 江苏省先进结构材料与应用技术重点实验室,南京 211167)
摘 要:采用化学镀技术在碳钢表面制备Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层,通过电化学方法评定Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的耐蚀性。结果表明:非晶Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P、纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度均随着人造海水温度升高而增大,而阻抗值则减小;共沉积Cu有利于改善非晶Ni-P镀层的耐蚀性,但改善效果随着人造海水温度的升高而减小;400 ℃热处理可显著改善Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的耐蚀性,在80 ℃的人造海水中,热处理Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度较镀态Ni-Cu-P镀层的低一个数量级。
关键词:Ni-P镀层;Ni-Cu-P镀层;人造海水;腐蚀电流密度;阻抗值
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-06-1176-06 中图分类号:TG174.4 文献标志码:A
在石油钻井平台、海水淡化装置、沿海码头机械设备、远洋船舶等中的金属构件,均服役于较复杂的海洋环境之中,由于面临严峻的海水腐蚀或腐蚀磨损等,这类金属构件常因耐蚀性不足导致其服役寿命过短。碳钢[1-3]、不锈钢[4-6]、铜合金[7]和钛合金[8]等是制造这些金属构件常用金属材料,其中碳钢构件的耐蚀性尤其薄弱,表面改性是提高其耐蚀性常采用的技术手段。
据报道,碳钢构件表面涂覆铝合金涂层[9-10]、化学镀层[11-12]和超疏水性膜[13]等均可改善其在海水中的耐蚀性。对于化学镀层, 等[11]研究表明,化学镀Ni-P和Ni-P-Al2O3镀层可显著降低碳钢在pH值为5.0和8.1的人造海水中的腐蚀电流密度,增大其阻抗值;赵丹等[12]研究发现,Ni-P镀层中共沉积Zn可降低镀层在人造海水中的腐蚀速率;TIAN等[14]对在杀菌和未杀菌天然海水中浸泡不同时间的Ni-P和Ni-P-PTFE镀层的电化学行为研究表明,浸泡7 d以内,镀层能对基体形成有效的保护。目前,有关海水温度对化学镀层腐蚀行为影响鲜见报道,而由于夏日受海水飞溅的金属构件及海水淡化装置等中的一些金属构件常服役于较高温度的海水环境;此外,在Ni-P中共沉积Cu有益于改善其在碱性[15]和酸性[16-17]环境中镀层的耐蚀性,但在海水中共沉积Cu是否同样可改善Ni-P镀层的耐蚀性尚缺乏有效的研究。针对上述情况,本文作者以非晶Ni-P镀层作为对比镀层,采用电化学测试方法,系统研究了海水温度对非晶和纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层及其对比非晶Ni-P镀层在人造海水环境中耐蚀性的影响。
等[11]研究表明,化学镀Ni-P和Ni-P-Al2O3镀层可显著降低碳钢在pH值为5.0和8.1的人造海水中的腐蚀电流密度,增大其阻抗值;赵丹等[12]研究发现,Ni-P镀层中共沉积Zn可降低镀层在人造海水中的腐蚀速率;TIAN等[14]对在杀菌和未杀菌天然海水中浸泡不同时间的Ni-P和Ni-P-PTFE镀层的电化学行为研究表明,浸泡7 d以内,镀层能对基体形成有效的保护。目前,有关海水温度对化学镀层腐蚀行为影响鲜见报道,而由于夏日受海水飞溅的金属构件及海水淡化装置等中的一些金属构件常服役于较高温度的海水环境;此外,在Ni-P中共沉积Cu有益于改善其在碱性[15]和酸性[16-17]环境中镀层的耐蚀性,但在海水中共沉积Cu是否同样可改善Ni-P镀层的耐蚀性尚缺乏有效的研究。针对上述情况,本文作者以非晶Ni-P镀层作为对比镀层,采用电化学测试方法,系统研究了海水温度对非晶和纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层及其对比非晶Ni-P镀层在人造海水环境中耐蚀性的影响。
1 实验
1.1 非晶和纳米晶镀层制备
基体试样是直径25.4 mm、厚度2.0 mm的65Mn冷轧钢板圆片试样,采用自行研制的高温酸性化学镀Ni-P镀液和高温碱性化学镀Ni-Cu-P镀液制备非晶Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层,采用HHS-1恒温水浴锅控制Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀液的温度在(82±1) ℃,化学镀时间均为2 h。将镀覆非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的试样放入已升温至400 ℃的箱式电阻炉内保温2 h,获得纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层试样。
1.2 耐蚀性实验
采用电化学方法评定Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层在不同温度人造海水中耐蚀性,用PARSTAT2273电化学工作站测试镀覆Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层试样的极化曲线和交流阻抗谱(EIS),测试介质为人造海水,其成分如表1所列,人造海水温度用HHS-1恒温水浴锅控制。电化学测试采用标准三电极系统,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE),辅助电极为Pt电极,工作电极为待测试样;用待测试样做工作电极时,其裸露的工作面尺寸为10 mm×10 mm,其它表面用环氧树脂封固;极化曲线测试动电位扫描速率为2 mV/s,根据强极化区外加电流与电极极化的关系,用Tafel直线外推法得到腐蚀电流密度Jcorr;EIS测试采用开路电位法,频率范围为100 mHz~100 kHz,以Bode图中低频阻抗模值评定镀层耐蚀性。
表1 人造海水的成分
Table 1 Composition of artificial seawater (g/L)

1.3 组织及结构分析
用JSM6360LVX型扫描电镜(SEM)观察镀层表面形貌,用GENESIS2000XMS60型能谱仪(EDS)分析镀层成分,用UltmaⅣ型X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层结构。
2 结果和讨论
2.1 Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层组织结构
化学镀Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层表面形貌如图1所示,这两种镀层均具有典型的胞状结构特征,EDS分析表明,Ni-P镀层中Ni和P含量分别为87.80%和12.20% (质量分数),Ni-Cu-P镀层中Ni、Cu和P含量分别为70.89%、17.21%和11.90%(质量分数)。XRD分析表明:镀态Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P合金均为非晶合金,400℃热处理的Ni-Cu-P合金为纳米晶合金,且热处理后Ni-Cu-P镀层表面形成了NiO膜(如图2所示)。
2.2 非晶Ni-P镀层在人造海水中的电化学行为
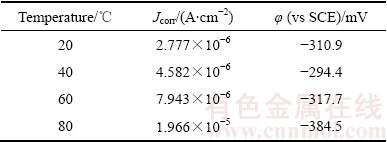
图3所示为在不同温度人造海水中测试的非晶Ni-P镀层的极化曲线和阻抗谱,表2所列为根据极化曲线拟合和Tafel外推法得到的非晶Ni-P镀层的腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流密度。由图3(a)可见,在不同温度的人造海水中,非晶Ni-P的极化曲线相似,在阳极区均没有出现钝化现象,这与常温下 等[11]的电化学测试结果一致。由表2可见,非晶Ni-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度随人造海水温度升高单调增大,与20 ℃时镀层的腐蚀电流密度相比,80 ℃时的腐蚀电流密度提高了一个数量级;非晶Ni-P镀层在20~60 ℃的人造海水中的腐蚀电位差异较小,但在80 ℃的人造海水中,其腐蚀电位发生了显著负移(比20 ℃镀层的腐蚀电位负移了73.6 mV),上述结果表明,随着人造海水温度的升高,非晶Ni-P镀层的耐蚀性下降。
等[11]的电化学测试结果一致。由表2可见,非晶Ni-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度随人造海水温度升高单调增大,与20 ℃时镀层的腐蚀电流密度相比,80 ℃时的腐蚀电流密度提高了一个数量级;非晶Ni-P镀层在20~60 ℃的人造海水中的腐蚀电位差异较小,但在80 ℃的人造海水中,其腐蚀电位发生了显著负移(比20 ℃镀层的腐蚀电位负移了73.6 mV),上述结果表明,随着人造海水温度的升高,非晶Ni-P镀层的耐蚀性下降。
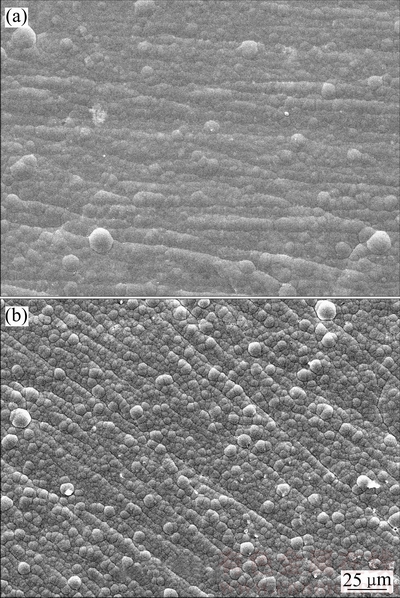
图1 Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层的表面形貌
Fig. 1 Surface morphologies of Ni-P(a) and Ni-Cu-P(b) coatings

图2 Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层的XRD谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of Ni-P and Ni-Cu-P coatings
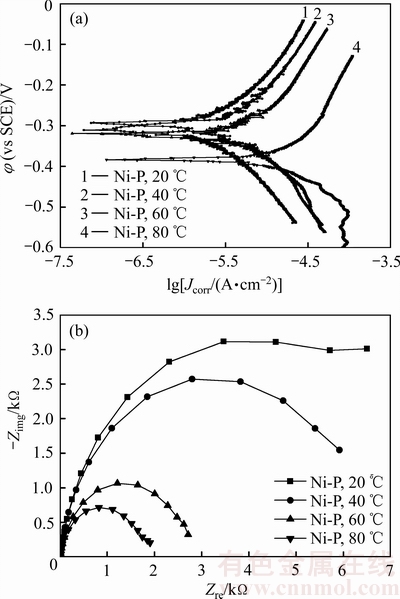
图3 非晶Ni-P镀层的极化曲线和阻抗谱
Fig. 3 Polarization curves(a) and impedance spectra(b) of amorphous Ni-P coatings
表2 非晶Ni-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度和腐蚀电位
Table 2 Jcorr and φcorr of amorphous Ni-P coatings
由图3(b)可见,非晶Ni-P镀层在不同温度的人造海水中的阻抗谱曲线均为半圆形容抗弧,其容抗弧半径和阻抗值均随着人造海水温度提高单调减小,与20 ℃时镀层阻抗值7165.7 Ω·cm2相比,80 ℃时仅为1917.6 Ω,这些结果也表明,提高人造海水温度将导致非晶Ni-P镀层的耐蚀性下降。
2.3 非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的电化学行为
图4所示为非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在不同温度人造海水中测量的极化曲线和阻抗谱曲线,表3所列为不同温度人造海水中非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流密度。由图4(a)可见,不同温度人造海水中非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的极化曲线类似,但在阳极区,与Ni-P镀层的极化曲线不同,非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在阳极区存在钝化现象,随着人造海水温度的升高,不仅阳极钝化变得明显,而且阳极钝化的电位区间存在负移现象(如图4(a)箭头所示)。
由表3可见,非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的腐蚀电位随着海水温度的提高单调负移,80 ℃时镀层的腐蚀电位较20 ℃时的负移了93.1 mV,镀层的腐蚀电流密度随着人造海水的温度提高单调增大,80 ℃时镀层的腐蚀电流密度较20 ℃时的提高了1个数量级,上述结果表明,非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的耐蚀性随着人造海水温度的升高而下降。
对比表2和表3的数据可见,在20、40、60和80 ℃时,非晶Ni-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度依次为非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的2.75、1.35、1.16和1.01倍,人造海水温度越高,非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度与非晶Ni-P镀层的越接近,上述结果表明:在Ni-P镀层中共沉积Cu可改善其在人造海水中的抗腐蚀性能,人造海水温度越低,改善耐蚀性效果越显著。
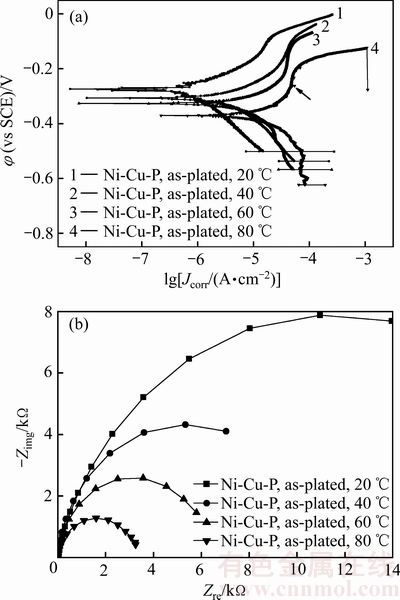
图4 非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的极化曲线和阻抗谱
Fig. 4 Polarization curves(a) and impedance spectra(b) of amorphous Ni-Cu-P coatings
表3 非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度和腐蚀电位
Table 3 Jcorr and φcorr of amorphous Ni-Cu-P coatings
由图4(b)阻抗谱可见,非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在20~80 ℃的人造海水中的阻抗谱均为半圆形的容抗弧,其容抗弧半径和阻抗值随人造海水温度升高单调减小,表明人造海水温度升高将降低该镀层的耐蚀性,这与极化曲线的分析结果一致。
与非晶Ni-P镀层相比,在介质及其温度相同时,非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的阻抗值明显高于非晶Ni-P镀层的,20 ℃时镀层的阻抗值为15932.6 Ω,约为Ni-P镀层的2.2倍,80 ℃时的阻抗值为3280.4 Ω,约为Ni-P镀层的1.7倍,表明在所测试的人造海水温度范围内,非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的耐蚀性优于非晶Ni-P镀层的。
在人造海水中,Ni-Cu-P镀层具有较Ni-P镀层更优异的耐蚀性,主要与Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中存在钝化现象有关。 等[11]研究表明,Ni-P镀层在海水中没有钝化现象,这与本实验结果一致(如图3所示),而由图4可见,Ni-Cu-P镀层在阳极区存在钝化现象,由于本研究中测试的Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层中P含量(分别为12.20%和11.90%,质量分数)接近,表明Ni-Cu-P镀层阳极反应过程中的钝化行为是由镀层中Cu引起的,因此,Ni-P镀层中共沉积Cu有利于改善其在人造海水中的耐蚀性。此外,Ni-Cu-P镀层的胞状组织比Ni-P镀层更细小致密(如图1所示),这种细小的胞状组织具有较Ni-P镀层更低的孔隙率;这也是造成Ni-Cu-P镀层的耐蚀性优于Ni-P镀层的原因之一。
等[11]研究表明,Ni-P镀层在海水中没有钝化现象,这与本实验结果一致(如图3所示),而由图4可见,Ni-Cu-P镀层在阳极区存在钝化现象,由于本研究中测试的Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层中P含量(分别为12.20%和11.90%,质量分数)接近,表明Ni-Cu-P镀层阳极反应过程中的钝化行为是由镀层中Cu引起的,因此,Ni-P镀层中共沉积Cu有利于改善其在人造海水中的耐蚀性。此外,Ni-Cu-P镀层的胞状组织比Ni-P镀层更细小致密(如图1所示),这种细小的胞状组织具有较Ni-P镀层更低的孔隙率;这也是造成Ni-Cu-P镀层的耐蚀性优于Ni-P镀层的原因之一。
2.4 纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的电化学行为
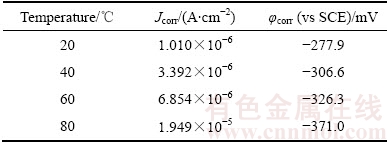
图5所示为纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在不同温度人造海水中测量的极化曲线和阻抗谱,表4所列为不同温度人造海水中纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流密度。由图5(a)可见,纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的极化曲线在阳极区存在类钝化现象,人造海水温度越低,类钝化现象越明显,出现类钝化的电位与人造海水温度无关(如图5(a)中箭头所示)。
纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电位随海水温度提高单调负移,其中80 ℃时镀层的腐蚀电位较20 ℃时的负移了80.4 mV,镀层的腐蚀电流密度随人造海水温度升高单调增大,表明随着人造海水温度的提高,纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的耐蚀性下降。
与非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层相比,纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电位明显正移,而腐蚀电流密度则明显低于非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的,尤其是在80 ℃的高温人造海水 中,纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电位较非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的正移了184.0 mV,其腐蚀电流密度仅约为非晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的0.3倍,表明400 ℃热处理可明显改善Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的抗腐蚀性能,尤其是在高温海水中的耐蚀性。
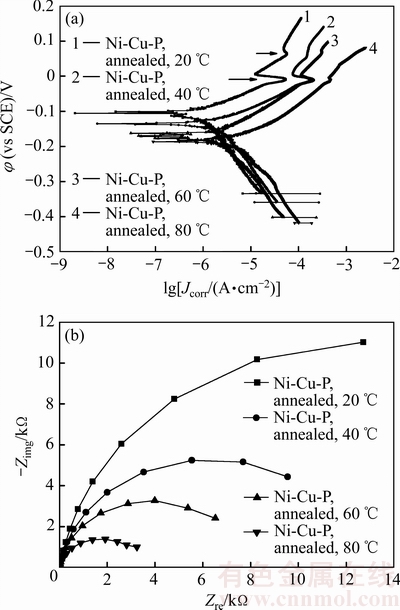
图5 纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的极化曲线和阻抗谱
Fig. 5 Polarization curves(a) and impedance spectra(b) of nanocrystalline Ni-Cu-P coatings
表4 纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电流密度和腐蚀电位
Table 4 Jcorr and φcorr of nanocrystalline Ni-Cu-P coatings

由图5(b)可见,纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在20 ℃至80 ℃的人造海水中的阻抗谱曲线均为半圆形容抗弧,其容抗弧半径和阻抗值随人造海水温度升高单调减小。与20 ℃时镀层的阻抗值16830.1 Ω相比,80 ℃时镀层的阻抗值仅为3390 Ω,表明纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的抗腐蚀性能随人造海水温度的提高而下降。
经400 ℃热处理得到的纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层表面存在氧化膜(如图2所示),该氧化膜具有阻碍Ni的溶解及Ni2+的扩散作用[18],因而400 ℃热处理有利于提高Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的耐蚀性。此外,400 ℃热处理使Ni-P镀层中的孔洞减少[11],因此,400 ℃热处理有利于降低Ni-Cu-P镀层中的孔隙率,进而改善纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在人造海水中的耐蚀性。
3 结论
1) 随着人造海水温度提高,非晶和纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层的腐蚀电位负移、腐蚀电流密度增大,阻抗值减小。
2) 共沉积Cu可改善非晶Ni-P镀层在人造海水中的耐蚀性,但改善效果随人造海水温度的升高而减小。
3) 400 ℃热处理制备的纳米晶Ni-Cu-P镀层在20~80 ℃的人造海水中的耐蚀性均明显优于非晶Ni-P和Ni-Cu-P镀层的。
REFERENCES
[1] 刘智勇, 贾静焕, 杜翠薇, 李晓刚, 王丽颖. X80和X52钢在模拟海水环境中的腐蚀行为与规律[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2014, 34(4): 327-332.
LIU Zhi-yong, JIA Jing-huan, DU Cui-wei, LI Xiao-gang, WANG Li-ying. Corrosion behavior of X80 and X52 steels in simulated seawater environments[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2014, 34(4): 327-332.
[2] 穆 鑫, 魏 洁, 董俊华, 柯 伟. 低碳钢在模拟海洋潮差区的腐蚀行为的电化学研究[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(4): 420-426.
MU Xin, WEI Jie, DONG Jun-hua, KE Wei. Electrochemical study on corrosion behaviors of mild steel in a simulated tidal zone[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(4): 420-426.
[3]  M, TURCU F, ESNAULT L, SCHWEITZER E W, KILIAN R, BASSEGUY R. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel in presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria in seawater environment[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 113(12): 390-406.
M, TURCU F, ESNAULT L, SCHWEITZER E W, KILIAN R, BASSEGUY R. Corrosion behavior of carbon steel in presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria in seawater environment[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 113(12): 390-406.
[4] XIN S S, LI M C. Electrochemical corrosion characteristics of type 316L stainless steel in hot concentratedseawater[J]. Corrosion Science,2014, 81(4): 96-101.
[5] HOSEINIEH S M, HOMBORG A M, SHAHRABI T, MOL J M C, RAMEZANZADEH B. A novel approach for the evaluation of under deposit corrosion in marine environments using combined analysis by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and electrochemical noise[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 217 (10): 226-241.
[6] 辛森森, 李谋成, 沈嘉年. 海水温度和浓缩度对316L不锈钢点蚀性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50(3): 373-378.
XIN Sen-sen, LI Mou-cheng, SHEN Jia-nian. Effect of temperature and concentration ratio on pitting resistance of 316L stainless steel in seawater[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50(3): 373-378.
[7] 赵月红, 林乐耘, 崔大为. 铜镍合金在我国实海海域的局部腐蚀[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(11): 1786-1794.
ZHAO Yue-hong, LIN Le-yun, CAI Da-wei. Localized corrosion of Cu-Ni alloy in China marine[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(11): 1786-1794.
[8] CHEN Jun, ZHANG Qing. Effect of electrochemical state on corrosion-wear behaviors of TC4 alloy in artificial seawater[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2016, 26(4): 1011-1018.
[9] 李 焰, 邢少华, 李 鑫, 魏绪钧. 热浸镀层在青岛站的海水腐蚀行为对比(Ⅰ)——全浸区[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(12): 2083-2091.
LI Yan, XING Shao-hua, LI Xin, WEI Xu-jun. Seawater corrosion behavior of hot dip coatings at Qingdao test station(Ⅰ)—Immersion zone[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(12): 2083-2091.
[10] PARK I C, KIM S J. Electrochemical characteristics in seawater for cold thermal spray-coated Al-Mg alloy layer[J]. Acta Metall Sin (Engl Lett), 2016, 29(8): 727-734.
[11]  C,
C,  E,
E,  J,
J,  J. Annealing temperature effect on the corrosion parameters of autocatalytically produced Ni-P and Ni-P-Al2O3 coatings in artificial seawater[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2010, 205(7): 2425-2431.
J. Annealing temperature effect on the corrosion parameters of autocatalytically produced Ni-P and Ni-P-Al2O3 coatings in artificial seawater[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2010, 205(7): 2425-2431.
[12] 赵 丹, 徐旭仲, 徐 博. Ni-Zn-P合金镀层在人工模拟海水中腐蚀性为的研究[J]. 表面技术, 2016, 45(4): 169-174.
ZHAO Dan, XU Xu-zhong, XU Bo. Corrosion Behavior of Ni-Zn-P alloy coating in artificial seawater[J]. Surface Technology, 2016, 45(4): 169-174.
[13] YU Dong-yun, TIAN Jin-tao, DAI Jin-hui, WANG Xin. Corrosion resistance of three-layer superhydrophobic composite coating on carbon steel in seawater[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 97(5): 409-419.
[14] TIAN Jin-tao, LIU Xue-zhong, WANG Jian-fei, WANG Xin, YIN Yan-sheng. Electrochemical anticorrosion behaviors of the electroless deposited Ni-P and Ni-P-PTFE coatings in sterilized and unsterilized seawater[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 124(1): 751-759.
[15] ABDEL H R M, FEKRY A M. Electrochemical impedance studies of modified Ni-P and Ni-Cu-P deposits in alkaline medium[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(20): 5922-5929.
[16] FANG Xin-xian, ZHOU Heng-zhi, XUE Ya-jun. Corrosion properties of stainless steel 316L/Ni-Cu-P coatings in warm acidic solution[J]. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(8): 2594-2600.
[17] 方信贤, 薛亚军, 戴玉明, 王章忠. Ni-W-Cu-P沉积机制及在酸性溶液中的腐蚀行为[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(11): 1432-1440.
FANG Xin-xian, XUE Ya-jun, DAI Yu-ming, WANG Zhang-zhong. Deposition mechanism of Ni-W-Cu-P coating and its corrosion behavior in acid solution[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(11): 1432-1440.
[18] LIU Gui-chang, HUANG Zong-xiang, WANG Li-da, SUN Wen, WANG Sui-lin, DENG Xin-lü. Effects of Ce4+ on the structure and corrosion resistance of electroless deposited Ni-Cu-P coating[J]. Surface & Coating Technology, 2013, 222(3): 25-30.
Effect of artificial seawater temperature on electrochemical behavior of Ni-P and Ni-Cu-P alloy coatings
FANG Xin-xian1, 2, DU Xiao-juan1, GAO Sheng-hui1, ZHANG Shuai1
(1. School of Material Engineering, Nanjing Institute of Technology, Nanjing 211167, China;
2. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials and Application Technology, Nanjing Institute of Technology, Nanjing 211167, China)
Abstract: The Ni-P and Ni-Cu-P coatings were deposited on carbon steel surface by electroless plating technique. Their corrosion resistances in artificial seawater were evaluated by electrochemical test. The results show that the corrosion current densities of amorphous Ni-P and Ni-Cu-P coatings and nanometer crystalline Ni-Cu-P coatings increase with the increase of artificial seawater temperature. However, their impedance values decease. The corrosion resistance of amorphous Ni-P coating in artificial seawater can be improved by co-depositing Cu element. However, the difference of the corrosion resistance between the Ni-Cu-P and Ni-P coatings gradually decreases with the increase of the artificial seawater temperature. The corrosion resistance of Ni-Cu-P coating in warm artificial water can be greatly improved by annealing at 400 ℃. The corrosion current density of Ni-Cu-P coating annealed at 400 ℃ is an order magnitude lower than that of as-plated Ni-Cu-P coating in 80 ℃ artificial seawater.
Key words: Ni-P coating; Ni-Cu-P coating; artificial seawater; corrosive current density; impedance value
Foundation item: Project(51301088) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (TB201702007) supported by the Innovation Foundation for Students of Nanjing Institute of Technology, China; Project supported by the Outstanding Scientific and Technology Innovation Team in College and Universities of Jiangsu Province, China
Received date: 2017-03-28; Accepted date: 2017-05-12
Corresponding author: FANG Xin-xian; Tel: +86-25-86118276; E-mail: fangxinxian@njit.edu.cn
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51301088);南京工程学院大学生科技创新项目(TB201702007);江苏高校优秀科技创新团队项目
收稿日期:2017-03-28;修订日期:2017-05-12
通信作者:方信贤,教授,博士;电话:025-86118276;E-mail: fangxinxian@njit.edu.cn