文章编号:1004-0609(2010)01-0010-07
第二相在Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金挤压棒超塑性变形中的作用
李 理1, 2,张新明1,邓运来1,周 楠1,唐昌平1
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 湖南工学院 机械工程系,衡阳 421008)
摘 要:采用电子显微镜和XRD研究分析Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金挤压棒材超塑性拉伸前后的微观组织及其超塑性机制。结果表明:在温度为450 ℃、应变速率为2×10?4 s?1的变形条件下获得的挤压棒的最大伸长率为410%,应变速率敏感系数为0.54;合金表观变形激活能远高于镁的晶界扩散激活能或晶格扩散激活能,超塑性变形机制为晶格扩散控制的位错协调晶界滑动机制;微孔洞在基体/方形富稀土相界面处萌生,较软的不规则块状β相承受部分塑性变形,松弛了相界处应力集中。
关键词:Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金;第二相;挤压;超塑性变形
中图分类号:TG 146.2 文献标识码:A
Effect of second phase on superplastic deformation of extruded rod of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy
LI Li1, 2, ZHANG Xin-ming1, DENG Yun-lai1, ZHOU Nan1, TANG Chang-ping1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hunan Institute of Technology, Hengyang 421008, China)
Abstract: The microstructures and superplastic behavior of the extruded rod of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy before and after tensile were investigated and analyzed by microscopy and XRD. And tensile tests at various temperatures and strain rates were performed. The results show that the extruded rod exhibits the maximum elongation of 410% at 450 ℃ and 2×10?4 s?1 and the corresponding strain rate sensitivity of 0.54. The apparent activation energy for the superplastic flow is much higher than the activation energy of grain boundary diffusion or lattice diffusion of magnesium. The high ductility is attributable to grain boundary sliding accommodated by dislocation motion assisted by lattice diffusion. The microstructural results show that the cavities nucleate at the interface between the matrix and the cuboidal Re-rich phase, and that the deformable β phase relaxes the stress concentration at the interface by bearing the partial plastic strain.
Key words: Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy; second phases; extrusion; superplastic deformation
镁合金结构材料的应用在交通运输工具轻量化等方面具有很大的潜力[1]。相对于铝合金材料,镁合金的耐热性能较差,因此,目前镁合金仅仅应用在汽车的仪表板、方向盘、阀门罩等零件上[2]。进一步应用在动力传动系统中的零件,则需要较高的耐热性能(在200~300 ℃)[1]。已有研究表明,在镁中添加Gd以及其它稀土元素(RE),通过固溶强化与析出强化可使镁合金的耐热性能显著提高,Mg-Gd系合金从过饱和状态到平衡态,可析出大量的沉淀相,其析出序列如下:S.S.S.S→β″(DO19)→β′(Cbco)→β(Cubic)。β″和β′为亚稳相,β为平衡相[3?6]。
近年来,超塑性成形(SPF)技术已应用于成形复杂形状的镁合金零件,其力学性能及可靠性明显优于一般铸造件[7?9]。稀土镁合金中的稀土元素大部分存在于第二相中,稀土对超塑性的影响是双方面的[10]。分布于晶界的第二相具有稳定细晶组织的作用,对超塑性变形有利。同时,稀土第二相也阻碍超塑性变形时晶界的滑动,并产生应力集中对进一步的超塑性变形不利。目前,大量SPF研究工作集中于AZ系列[11?12]及ZK[13]系列镁合金,而Mg-Gd系镁合金的超塑性变形研究尚不系统。
本文作者在探明Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金挤压棒的超塑性变形机制基础上,分析Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金中的第二相对超塑性变形的影响。
1 实验
实验合金为Mg-9.0Gd-4.0Y-0.4Zr合金(质量分数,%)。合金铸锭经520 ℃、4 h均匀化后,在375 ℃时挤压成外径为10 mm的棒材,挤压比为14?1,压头速率为2 mm/min。挤压棒被加工成圆柱体拉伸试样,标距长25 mm、直径5 mm。高温拉伸实验在配备有电阻炉的MTS万能试验机上进行,夹头两端及试样标距内安置灵敏的钯铑合金热电偶,数字温孔仪保证3处的温度差不超过2 ℃。拉伸方向平行于挤压方向。
为研究实验合金的超塑性变形机制,恒应变速率拉伸实验用来测定应变速率敏感系数(m值)。应变速率范围为7×10?5~4×10?3 s?1,温度范围400~485 ℃。样品在实验温度下经1 800 s保温后开始拉伸。样品拉断,空冷后进行微观组织观察。
用KYKY2800扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对晶粒结构、孔洞及第二相形貌进行观察。D/Max2500型X射线衍射仪(XRD)与Genesis 60S能谱仪(EDS)用来确定第二相组成与成分。JEM2100透射电子显微镜(TEM)进行微观组织分析。TEM样品的膜面平行于拉伸方向,用离子减薄法获得薄区。
2 结果与分析
2.1 超塑性行为
未经拉伸变形以及获得最大伸长率试样的照片如图1所示。由图1可看出,挤压棒在温度为450 ℃,应变速率为2×10?4 s?1的条件下,获得410%的最大伸长率,且整个标距内没有发生明显的颈缩现象。

图1 未经拉伸变形以及获得最大伸长率Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金试样的照片
Fig.1 Photo of undeformed specimen and fractured specimen exhibiting maximum elongation
图2(a)所示为在应变水平为0.15条件下,流变应力随应变速率变化的趋势。由图2(a)可以看出,流变应力随应变速率的增加而上升。应变速率敏感系数m定义为


图2 未经拉伸变形以及获得最大伸长率的Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金试样流变应力与伸长率随应变速率的变化
Fig.2 Changes of flow stress(a) and elongation(b) with strain rate of undeformed specimen and fractured specimen exhibiting maximum elongation
在各种实验条件下,m值的范围为0.14~0.54。在图2(b)中,最大伸长率对应于较高的m值(0.54)。
2.2 挤压态的微观组织
图3所示为挤压态棒材的SEM像及相应的EDS谱。从图3可以看出,晶粒形状为等轴状,平均晶粒尺寸为10 μm,测量方法按照d=1.74L(其中d为晶粒直径,L为相邻晶界的直线距离),统计晶粒的数量为1 000个。在晶界与晶内分布两种形貌的第二相粒子,一种为圆形粒子,另一种为方形粒子。能谱分析(EDS)显示,圆形粒子富含Zr元素,由于Zr与Gd和Mg均不反应,因此圆形粒子为Zr核;方形相富含Gd,它的存在将提高合金的耐热性能。这两种第二相均是在熔铸时产生的结晶相[14]。

图3 Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金挤压棒的SEM像以及第二相粒子a和b的EDS谱
Fig.3 SEM image of as-extruded Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy rod and EDS spectra of second phase particles a(b) and b(c)
2.3 试样拉伸后的微观组织
图4所示为试样在450 ℃、2×10?4 s?1拉断后的SEM像及相应的EDS谱。由图4(a)中的低倍SEM像可以观察到,孔洞沿拉伸方向(即挤压方向)分布。在经过450 ℃高温拉伸约3 h后,晶粒依然保持为等轴状,且仅仅长大至19 μm,长大速度远远低于AZ或ZK系列镁合金。图4(b)所示为第二相的形貌,除变形前原有的圆形Zr核(标记为Ⅰ)及富稀土方形相(标记为Ⅱ)处,还出现了大量不规则块状相(标记为Ⅲ)。结合Mg-Gd-Y三元相图[15],可以推断析出的不规则块状相为Mg5(Gd, Y)。图4(c)~(e)中相应EDS谱所示为第二相的EDS谱。运用化学计量方法,分析5处不规则块状相的成分,Mg与(Gd+Y)的平均摩尔分数比为5.06?1,可以基本确定不规则块状相为Mg5(Gd, Y),即β相。
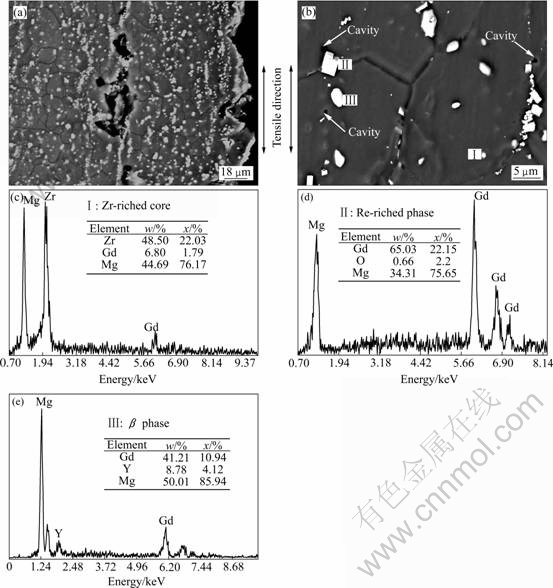
图4 当温度为450 ℃、应变速率为2×10?4 s?1时拉伸后试样的SEM像和第二相的EDS谱
Fig.4 SEM images of specimen tested at 450 ℃ and 2×10?4 s?1 and EDS spectra of second phases: (a) Cavities distributing along tensile direction; (b) Second phases and cavities; (c), (d), (e) EDS spectra
进一步的观察发现,孔洞萌生在基体与方形富稀土相的界面上,而基体与β相的界面未见孔洞。图5所示为挤压棒以及经450 ℃、2×10?4 s?1拉伸后试样的XRD谱。由图5可看出,拉伸前后第二相的组成相同,但是拉伸后的谱线中β的小峰数量明显增加,可知析出更多的β相。
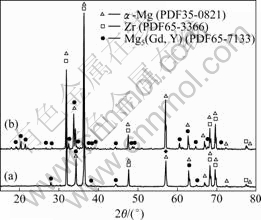
图5挤压棒以及经450 ℃、2×10?4 s?1拉伸后试样的XRD谱
Fig.5 XRD patterns of as-extruded rod(a) and specimen tested at 450 ℃ and 2 ×10?4 s?1(b)
图6所示为试样在450 ℃、2×10?4 s?1拉断后试样的TEM像。图6(a)中观察到方形富稀土相在晶界处钉扎晶界,富稀土相边缘平直;晶内的不规则块状相为β相,边缘出现位错运动留下的台阶。这些迹象表明:在高温条件下,方形富稀土相的强度依然高,未能发生变形,而β相强度较低,并参与变形。
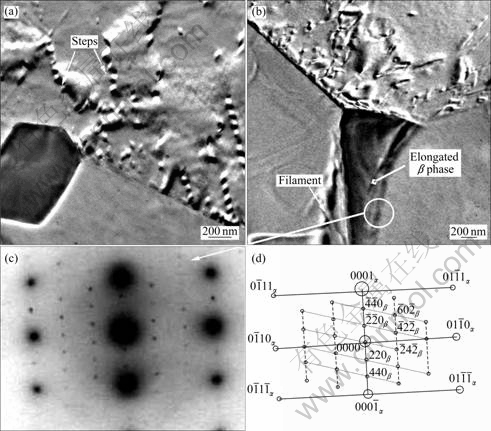
图6 经450 ℃、2×10?4 s?1拉伸断裂后试样的TEM像及SAED谱
Fig.6 TEM images of fractured specimen tested at 450 ℃ and 2×10?4 s?1 and corresponding SAED pattern: (a) Grain boundary pinned by cuboidal Re-riched phase; (b) Dislocation pile-up and elongated β phase at triple junction; (c) SAED pattern for β phase; (d) SAED pattern by zone axis along [ ] of α-Mg matrix
] of α-Mg matrix
图6(b)的TEM照片清晰地显示了三叉晶界处的位错塞积以及被拉长的β相。图中上方晶粒一侧的晶界附近有相当数量的可见位错露头;在基体/β相界面,基体被拉成丝带状,丝带延伸的方向与β相拉长的方向及拉伸方向一致。图6(c)所示为β相与周围基体的选取电子衍射照片。图6(d)中相应的电子衍射斑点分析结果表明,α-Mg基体的晶带轴为[ ],β相的晶带轴为[
],β相的晶带轴为[ ];β相为面心立方结构,晶格常数为a=2.21 nm,其分析结果与其它文献报道的结论基本一致[16?17]。
];β相为面心立方结构,晶格常数为a=2.21 nm,其分析结果与其它文献报道的结论基本一致[16?17]。
3 讨论
晶界滑动(GBS)出现在许多的镁合金超塑性变形中[18]。挤压棒的初始晶粒度为10 μm(见图3),满足晶界滑动对晶粒度的要求[19]。m值约为0.5(见图2(a))及拉断后的等轴晶粒(见图4(a))都证明晶界滑动在变形中起到了决定作用[20?21]。
晶界滑动依靠扩散控制的位错运动来协调[22]。在本研究中可以观察到位错在晶内或晶界协调变形的迹象,如晶内相界上的台阶(见图6(a))及三叉晶界处的位错塞积(见图6(b))。当表观变形激活能Q等于晶格扩散激活能(QL)时,GBS是由晶格扩散控制的;当表观变形激活能Q等于晶界扩散激活能(QGb)时,GBS是由晶界扩散控制的[23]。图7所示为根据式(2)计算的表观变形激活能[24]的曲线。


图7 挤压态Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金超塑性变形的表观变形激活能曲线
Fig.7 Apparent activation energy curves of superplastic deformation of extruded rod of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy
激活能的计算结果为216~460 kJ/mol,远高于镁的QL(134 kJ/mol)与QGb (75 kJ/mol)[25],这与晶界及晶内大量分布的稀土化合物有关。BALL-HUTCHISON提出的位错协调晶界滑动模型认为[9]:GBS会在三叉晶界处或晶界弓出处受阻,而位错的滑移(攀移)及后续位错的塞积可以使GBS克服阻碍继续进行。当晶界及晶内存在第二相时,晶界滑动受阻时,位错易于在相界处塞积,此时会出现两种情况:1) 当温度足够高时,第二相软化并发生变形(见图6(a));2) 当第二相强度较高时,位错依靠扩散在相界处攀移或湮灭于相界的空洞处。这些情况都将消耗更多的能量,致使变形激活能大幅提高。
Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金挤压棒材组织中有3种第二相,即Zr核,方形富稀土相及不规则块状β相,它们都是热稳定相。第二相对晶界或亚晶界有强烈的钉扎作用。因此,第二相抑止晶粒的长大,以至于在历经约3 h的高温拉伸后,晶粒长大并不显著。
β相的熔点为658 ℃,在450 ℃下的高温拉伸过程中,β相已经开始软化,基体/β相界面上未观察到孔洞(见图3(b)),且β相发生明显的变形(见图5(b)),说明相界上的应力集中容易得到松弛,而且变形从基体转移至β相中;方形富稀土相的硬度较高,空洞通常萌生它的相界上。Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金挤压棒材超塑性变形机制如图8所示。

图8 Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金挤压棒材超塑性变形机制示意图
Fig.8 Schematic diagram of superplastic deformation mechanism for extruded rod of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy
4 结论
1) 在温度为450 ℃、应变速率为2×10?4 s?1的 条件下,获得材料的最大伸长率为410%,相应的m值为0.54。
2) Mg-Gd-Y-Zr合金挤压棒材的超塑性表观变形激活能为216~460 kJ/mol,变形主导机制为晶格扩散控制的位错协调晶界滑动。
3) 孔洞在基体/富稀土结晶相界面上形成;拉伸过程中析出大量的块状β相,硬度较低的β相松弛应力集中且变形从基体转移至β相中。
REFERENCES
[1] LUO A A. Recent magnesium alloy development for elevated temperature applications[J]. Inter Mater Rev, 2004, 49(18): 13?30.
[2] MIHRIBAN O P, ARSLAN A K. Creep resistant magnesium alloys for power train applications[J]. Adv Eng Mater, 2003, 5(12): 866?878.
[3] NEUBERT V, STUL?KOV? I, SMOLA B, MORDIKE B L, VLACH M, BAKKAR A, PELCOV? J. Thermal stability and corrosion behaviour of Mg-Y-Nd and Mg-Tb-Nd alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 462(1/2): 329?333.
[4] MORDIKE B L. Creep-resistant magnesium alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 324(1/2): 103?112.
[5] SMOLA B, STUL?OV? I, PELCOV? J, MORDIKE B L. Significance of stable and metastable phases in high temperature creep resistant magnesium-rare earth base alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 378(1/2): 196?201.
[6] 肖 阳, 张新明, 陈健美, 蒋 浩. Mg-9Gd-4Y-0.6Zr合金挤压T5态的高温组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(4): 709?714.
XIAO Yang, ZHANG Xin-ming, CHEN Jian-mei, JIANG Hao. Microstructures and mechanical properties of extruded Mg-9Gd-4Y-0.6Zr-T5 at elevated temperatures[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(4): 709?714.
[7] BLANDIN J J. Superplastic forming of magnesium alloys: Production of microstructures, superplastic properties, cavitation behaviour[J]. Superplasticity in Advanced Materials, 2007, 551/552: 211?217.
[8] DEL VALLE J A, PENLBA F, RUANO O A. Optimization of the microstructure for improving superplastic forming in magnesium alloys[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 467(1/2): 165?171.
[9] 文九巴, 杨蕴林, 杨永顺, 陈拂晓, 张柯柯, 张耀宗. 超塑性应用技术[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2005: 306.
WEN Jiu-ba, YANG Yun-lin, YANG Yong-shun, CHEN Fu-xiao, ZHANG Ke-ke, ZHANG Zhong-Yao. Superplasticity applied technology[M]. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2005: 306.
[10] 马洪涛, 杨蕴林. Mb26合金超塑性的研究[J]. 材料工程, 1998, 9: 11?13.
MA Hong-tao, YANG Yun-lin. Study of MB26 alloy superplasticity[J]. Mater Eng, 1998, 9: 11?13.
[11] WATANABE H. Mechanical properties and texture of a superplastically deformed AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 477(1/2): 153?161.
[12] MUKAI T. Application of superplasticity in commercial magnesium alloy for fabrication of structural components[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 2000, 16(11/12): 1314?1319.
[13] MABUCHI T A M, ASAHINA T, IWASAKI H, HIGASHI K. Experimental investigation of superplastic behavior in magnesium alloys[J]. Mater Sci Technol, 1997, 13: 825?831.
[14] WON S Y, YOU B S, KIM Y S, YANG S H. Prediction of formability for magnesium alloy sheet using finite element polycrystal model[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2006, 20(25/27): 4335?4340.
[15] GUO Yong-chun, LI Jian-ping, LI Jin-shan, YANG Zhong, ZHAO Juan, XIA Feng, LIANG Min-xian. Mg-Gd-Y system phase diagram calculation and experimental clarification[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 450(1/2): 446?451.
[16] NIE J F, MUDDLE B C. Characterisation of strengthening precipitate phases in a Mg-Y-Nd alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2000, 48(8): 1691?1703.
[17] HE S M, ZENG X Q, PENG L M, GAO X, NIE J F, DING W J. Precipitation in a Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.4Zr (wt.%) alloy during isothermal ageing at 250 ℃[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 421(1/2): 309?313.
[18] WATANABE H, TSUTSUI H, MUKAI T, ISHIKAWA K, OKANDA Y, KOHZU M, HIGASHI K. Superplastic behavior in commercial wrought magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2000, 350/351: 171?176.
[19] LANGDON T G. Unified approach to grain boundary sliding in creep and superplasticity[J]. Acta Metall Mater, 1994, 42(7): 2437?2443.
[20] TAN J C, TAN M J. Dynamic continuous recrystallization characteristics in two stage deformation of Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy sheet[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, 339(1/2): 124?132.
[21] TAN J C, TAN M J. Superplasticity in a rolled Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy by two-stage deformation method[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 47(2): 101?106.
[22] SHERBY O D, WADSWORTH J. Superplastic—Recent advances and future direction[J]. Prog Mater Sci, 1989, 33(3): 169?221.
[23] WATANABE H. Superplasticity of a particle-strengthened WE43 magnesium alloy[J]. Mater Trans Jim, 2001, 42(1): 157?162.
[24] WU X, LIU Y. Superplasticity of coarse-grained magnesium alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2002, 46(4): 269?274.
[25] FROST H J, ASHBY M F. Deformation mechanism maps[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1982.
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(5311001E);国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2005AA741062)
收稿日期:2009-02-25;修订日期:2009-05-08
通信作者:张新明,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830265;E-mail: lileewin@163.com
(编辑 李艳红)